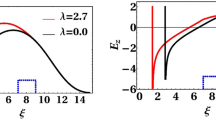
Abstract
Numerical studies are conducted on the electron injection into the first acceleration bucket of a laser wakefield by a weak counter-propagating laser pulse. It is shown that there are two injection mechanisms involved during the colliding laser interaction, the collective injection and stochastic injection. They are caused by the time-averaged ponderomotive force push and stochastic acceleration in the interfering fields, respectively. The threshold amplitude of the injection laser pulse is estimated for the occurrence of electron injection, which is close to that for stochastic acceleration and depends weakly upon the plasma density. The trapping of a large number of injection electrons can result in significant decay of the laser wakefield behind the first wave bucket.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
S.M. Hooker, D.A. Jaroszynski, K. Burnett, Phil. Trans. R. Soc. A 364, 553 (2006) and references therein
E. Esarey, P. Sprangle, J. Krall, A. Ting, IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. PS-24, 252 (1996)
A. Pukhov, J. Meyer-ter-Vehn, Appl. Phys. B 74, 355 (2002)
W. Lu, C. Huang, M. Zhou, W.B. Mori, T. Katsouleas, Phys. Rev. Lett. 96, 165002 (2006)
S.P.D. Mangles, et al., Nature (London) 431, 535 (2004); C.G.R. Geddes, et al., Nature (London) 431, 538 (2004); J. Faure, et al., Nature (London) 431, 541 (2004)
W.P. Leemans, B. Nagler, A.J. Gonsalves, et al., Nat. Phys. 418, 1 (2006)
J.M. Dawson, Phys. Rev. 113, 383 (1959); T.P. Coffey, Phys. Fluids 14, 1402 (1971)
T. Katsouleas, W.B. Mori, Phys. Rev. Lett. 61, 90 (1988)
J.B. Rosenzweig, Phys. Rev. A 38, 3634 (1988)
Z.M. Sheng, J. Meyer-ter-Vehn, Phys. Plasmas 4, 493 (1997)
C.B. Schroeder, E. Esarey, B.A. Shadwick, Phys. Rev. E 72, 055401(R) (2005)
R.M.G.M. Trines, et al., Phys. Rev. E 63, 026406 (2001)
R.M.G.M. Trines, P.A. Norreys, Phys. Plasmas 13, 123102 (2006)
D. Umstadter, J.K. Kim, E. Dodd, Phys. Rev. Lett. 76, 2073 (1996)
E. Esarey, et al., Phys. Rev. Lett. 79, 2682 (1997)
R.G. Hemker, et al., Phys. Rev. E 57, 5920 (1998)
S. Bulanov, N. Naumova, F. Pegoraro, J. Sakai, Phys. Rev. E 58, R5257 (1998)
C.B. Schroeder, et al., Phys. Rev. E 59, 6037 (1999)
Z.-M. Sheng, K. Mima, J. Zhang, J. Meyer-ter-Vehn, D. Umstadter, 31st EPS Conference on Plasma Phys. London, 28 June – 2 July 2004 ECA, vol. 28G, O-1.29 (2004)
P. Zhang, et al., Phys. Plasmas 10, 2093 (2003); Phys. Rev. Lett. 91, 225001 (2003)
Z.-M. Sheng, et al., Phys. Rev. Lett. 88, 055004 (2002); Phys. Rev. E 69, 016407 (2004)
A. Bourdier, D. Patin, Eur. Phys. J. D 32, 361 (2005)
A.L. Pokrovsky, A.E. Kaplan, Phys. Rev. A 72, 043401 (2005)
M. Chen, Z.-M. Sheng, Y.-Y. Ma, J. Zhang, J. Appl. Phys. 99, 056109 (2006)
H. Suk, N. Barov, J.B. Rosenzweig, E. Esarey, Phys. Rev. Lett. 86, 1011 (2001)
H. Kotaki, S. Masuda, M. Kando, J.K. Koga, K. Nakajima, Phys. Plasmas 11, 3296 (2004)
G. Fubiani, E. Esarey, C.B. Schroeder, W.P. Leemans, Phys. Rev. E 70, 016402 (2004)
J. Cary, R.E. Giacone, C. Nieter, D.L. Bruhwiler, Phys. Plasmas 12, 056704 (2004)
J. Faure, C. Rechatin, A. Norlin, A. Liftschitz, Y. Glinec, V. Malka, Nature 444, 737 (2006)
Z.M. Sheng, J. Zhang, D. Umstader, Appl. Phys. B 77, 673 (2003)
The plasma wavebreaking usually appears at a few plasma wave wavelengths (depending upon the plasma wave amplitude) behind the driving pulse due to the relativistic effect. See, for example, H. Xu, Z.-M. Sheng, J. Zhang, Phys. Scr. 74, 673 (2006); E. Infeld, G. Rowlands, Phys. Rev. Lett. 62, 1122 (1989)
W.M. Wang, Z.M. Sheng, Phys. Plasmas 15, 013101 (2008)
E. Esarey, M. Pilloff, Phys. Plasmas 2, 1432 (1995)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sheng, Z., Wang, W., Trines, R. et al. Mechanisms of electron injection into laser wakefields by a weak counter-propagating pulse. Eur. Phys. J. Spec. Top. 175, 49–55 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1140/epjst/e2009-01116-5
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1140/epjst/e2009-01116-5