Abstract
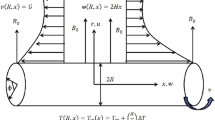
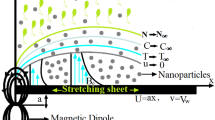
In this article, a mathematical model is envisaged to scrutinize the aspect of swimming motile microorganisms for a steady 3D convectional flow of Carreau nanofluid towards a bidirectional stretching surface. Various researchers in the past years are collaborating in the nanotechnology field due to their improvement in heat capacity, chemotherapy for cancer, microelectronics, cooling of energy storage devices, cooling of nuclear system, air conditioning, and nanochips, etc. The novel concept of activation energy and double stratification effects is considered to analyze the flow problem. Thermal relaxation time and concentration relaxation time properties are both determined by implementing Cattaneo–Christov heat and mass flux in the energy and mass equation. Suitable similarity approximations are utilized to convert governing PDEs into dimensionless ODEs. Numerical solutions are determined to utilize collocation finite difference technique and 3-stages Lobatto-IIIa formula. The obtained ODE’s are resolved numerically by engaged built-in function bvp4c solver in computational software MATLAB. The behavior of various emerging parameters and local skin friction coefficients, local Nusselt numbers, local Sherwood number, motile microorganisms’ number, velocity profiles, temperature profile, concentration profile and microorganism concentration is elaborated with the help of graph and tables. Carreau fluid model is a particular category of established non-Newtonian fluid that exemplifies shear thinning \( n<1 \) , shear thickening \( n>1 \) at high shearing rates. It is examined that the influence of the mixed convection parameter against temperature distribution both the temperature field of the shear-thinning/thickening liquids is reduced.


















Similar content being viewed by others
References
S.U. Choi, J.A. Eastman, Enhancing thermal conductivity of fluids with nanoparticles (No. ANL/MSD/CP-84938; CONF-951135-29). Argonne National Lab., IL, USA (1995)
J. Buongiorno, Convective transport in nanofluids. J. Heat Transf. 128(3), 240–250 (2006)
M. Ahmad, T. Muhammad, I. Ahmad, S. Aly, Time-dependent 3D flow of viscoelastic nanofluid over an unsteady stretching surface. Stat. Mech. Appl. Phys. A. 551, 124004 (2020)
S. Jabeen, T. Hayat, A. Alsaedi, M.S. Alhodaly, Consequences of activation energy and chemical reaction in radiative flow of tangent hyperbolic nanoliquid. Sci. Iran. 26(6), 3928–3937 (2019)
A. Hamid, M. Khan, Thermo-physical characteristics during the flow and heat transfer analysis of GO-nanoparticles adjacent to a continuously moving thin needle. Chin. J. Phys. 64, 227–240 (2020)
J. Ahmed, M. Khan, L. Ahmad, MHD von Karman swirling flow in the Maxwell nanofluid with nonlinear radiative heat flux and chemical reaction. Heat Transf. Res. 51(4), 377–394 (2020)
Y. Menni, A.J. Chamkha, N. Massarotti, H. Ameur, N. Kaid, M. Bensafi, Hydrodynamic and thermal analysis of water, ethylene glycol and water-ethylene glycol as base fluids dispersed by aluminum oxide nano-sized solid particles. Int. J. Numer. Methods Heat Fluid Flow (2020). https://doi.org/10.1108/HFF-10-2019-0739
I. Waini, A. Ishak, I. Pop, Transpiration effects on hybrid nanofluid flow and heat transfer over a stretching/shrinking sheet with uniform shear flow. Alex. Eng. J. 59(1), 91–99 (2020)
S. Nadeem, N. Abbas, M.Y. Malik, Inspection of hybrid based nanofluid flow over a curved surface. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 189, 105193 (2020)
M. Irfan, M. Khan, W.A. Khan, K. Rafiq, Physical aspects of shear thinning/thickening behavior in radiative flow of magnetite Carreau nanofluid with nanoparticle mass flux conditions. Appl. Nanosci. 10, 1–13 (2020)
A. Asadollahi, S. Rashidi, J.A. Esfahani, R. Ellahi, Simulating phase change during the droplet deformation and impact on a wet surface in a square microchannel: an application of oil drops collision. Eur. Phys. J. Plus 133(8), 306 (2018)
A. Majeed, A. Zeeshan, F.M. Noori, U. Masud, Influence of rotating magnetic field on Maxwell saturated ferrofluid flow over a heated stretching sheet with heat generation/absorption. Mech. Ind. 20(5), 502 (2019)
H. Babazadeh, A. Zeeshan, K. Jacob, A. Hajizadeh, M.M. Bhatti, Numerical modelling for nanoparticle thermal migration with effects of shape of particles and magnetic field inside a porous enclosure. Iran. J. Sci. Technol. Trans. Mech. Eng. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40997-020-00354-9
T. Muhammad, H. Waqas, S.A. Khan, R. Ellahi, S.M. Sait, Significance of nonlinear thermal radiation in 3D Eyring-Powell nanofluid flow with Arrhenius activation energy. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 143, 1–16 (2020)
R. Ellahi, Recent developments of nanofluids. MDPI-Multidisciplinary Digital Publishing Institute (2018)
L. Zhang, M.B. Arain, M.M. Bhatti, A. Zeeshan, H. Hal-Sulami, Effects of magnetic Reynolds number on swimming of gyrotactic microorganisms between rotating circular plates filled with nanofluids. Appl. Math. Mech. 41(4), 637–654 (2020)
P.J. Carreau, Rheological equations from molecular network theories. Trans. Soc. Rheol. 16(1), 99–127 (1972)
M. Khan, M. Irfan, W.A. Khan, A.S. Alshomrani, A new modeling for 3D Carreau fluid flow considering nonlinear thermal radiation. Results Phys. 7, 2692–2704 (2017)
M. Irfan, K. Rafiq, W.A. Khan, M. Khan, Numerical analysis of unsteady Carreau nanofluid flow with variable conductivity. Appl. Nanosci. 10, 1–10 (2020)
M.M. Bhatti, R. Ellahi, A. Zeeshan, M. Marin, N. Ijaz, Numerical study of heat transfer and Hall current impact on peristaltic propulsion of particle-fluid suspension with compliant wall properties. Mod. Phys. Lett. B 33(35), 1950439 (2019)
M.A. Yousif, H.F. Ismael, T. Abbas, R. Ellahi, Numerical study of momentum and heat transfer of MHD Carreau nanofluid over an exponentially stretched plate with internal heat source/sink and radiation. Heat Transf. Res. 50(7), 649–658 (2019)
C.S.K. Raju, M.M. Hoque, N.A. Khan, M. Islam, S. Kumar, Multiple slip effects on magnetic-Carreau fluid in a suspension of gyrotactic microorganisms over a slendering sheet. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part E J. Process Mech. Eng. 233(2), 254–266 (2019)
J.R. Platt, “Bioconvection Patterns” in cultures of free-swimming organisms. Science 133(3466), 1766–1767 (1961)
D. Pal, S.K. Mondal, MHD nanofluid bioconvection over an exponentially stretching sheet in the presence of gyrotactic microorganisms and thermal radiation. BioNanoScience 8(1), 272–287 (2018)
Y. Wang, H. Waqas, M. Tahir, M. Imran, C.Y. Jung, Effective Prandtl aspects on bio-convective thermally developed magnetized tangent hyperbolic nanoliquid with gyrotactic microorganisms and second order velocity slip. IEEE Access 7, 130008–130023 (2019)
S.M.H. Zadeh, S.A.M. Mehryan, M.A. Sheremet, M. Izadi, M. Ghodrat, Numerical study of mixed bio-convection associated with a micropolar fluid. Therm. Sci. Eng. Prog. 18, 100539 (2020)
M.J. Uddin, M.N. Kabir, Y. Alginahi, O.A. Bég, Numerical solution of bio-nano-convection transport from a horizontal plate with blowing and multiple slip effects. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part C J. Mech. Eng. Sci. 233(19–20), 6910–6927 (2019)
A. Imran, R. Akhtar, Z. Zhiyu, M. Shoaib, M.A.Z. Raja, Heat transfer analysis of biological nanofluid flow through ductus efferentes. AIP Adv. 10(3), 035029 (2020)
K. Javid, M. Waqas, Z. Asghar, A. Ghaffari, A theoretical analysis of Biorheological fluid flowing through a complex wavy convergent channel under porosity and electro-magneto-hydrodynamics effects. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 191, 105413 (2020)
S.A. Hussain, G. Ali, S.I.A. Shah, S. Muhammad, M. Ishaq, Bioconvection model for magneto hydrodynamics squeezing nanofluid flow with heat and mass transfer between two parallel plates containing gyrotactic microorganisms under the influence of thermal radiations. J. Math. 51(4), 13–36 (2019). ISSN 1016-2526
A. Shahid, H. Huang, M.M. Bhatti, L. Zhang, R. Ellahi, Numerical investigation on the swimming of gyrotactic microorganisms in nanofluids through porous medium over a stretched surface. Mathematics 8(3), 380 (2020)
H. Waqas, S.U. Khan, M. Hassan, M.M. Bhatti, M. Imran, Analysis on the bioconvection flow of modified second-grade nanofluid containing gyrotactic microorganisms and nanoparticles. J. Mol. Liq. 291, 111231 (2019)
T. Muhammad, S.Z. Alamri, H. Waqas, D. Habib, R. Ellahi, Bioconvection flow of magnetized Carreau nanofluid under the influence of slip over a wedge with motile microorganisms. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 143, 1–13 (2021)
A.R. Bestman, Natural convection boundary layer with suction and mass transfer in a porous medium. Int. J. Energy Res. 14(4), 389–96 (1990)
S.U. Khan, H. Waqas, S.A. Shehzad, M. Imran, Theoretical analysis of tangent hyperbolic nanoparticles with combined electrical MHD, activation energy and Wu’s slip features: a mathematical model. Phys. Scr. 94(12), 125211 (2019)
G. Ji, A. Raheem, X. Wang, W. Fu, B. Qu, Y. Gao, Z. Zhang, Kinetic analysis of algae gasification by distributed activation energy model. Processes 8(8), 927 (2020)
D.W. Kang, K.A. Lee, M. Kang, J.M. Kim, M. Moon, J.H. Choe, C.S. Hong, Cost-effective porous-organic-polymer-based electrolyte membranes with superprotonic conductivity and low activation energy. J. Mater. Chem. A 8(3), 1147–1153 (2020)
C. Cattaneo, Sulla conduzioned elcalore. Atti Semin Mat Fis Univ Modena Reggio Emilia. 3, 83–101 (1948)
C.I. Christov, On frame indifferent formulation of the Maxwell-Cattaneo model of finite-speed heat conduction. Mech. Res. Commun. 36, 481–486 (2009)
S.U. Khan, I. Tlili, H. Waqas, M. Imran, Effects of nonlinear thermal radiation and activation energy on modified second-grade nanofluid with Cattaneo-Christov expressions. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 143, 1–12 (2020)
M. Waqas, M.I. Khan, F. Alzahrani, A. Hobiny, Characterization of thermal-dependent conductivity in Cattaneo-Christov (CC)-based buoyancy-driven incompressible flow. Appl. Nanosci. 10, 1–7 (2020)
M. Irfan, M. Khan, W.A. Khan, Interaction between chemical species and generalized Fourier’s law on 3D flow of Carreau fluid with variable thermal conductivity and heat sink/source: a numerical approach. Results Phys. 10, 107–117 (2018)
M. Khan, M. Irfan, W.A. Khan, A.S. Alshomrani, A new modeling for 3D Carreau fluid flow considering nonlinear thermal radiation. Results Phys. 7, 2692–2704 (2017)
M. Irfan, M.S. Anwar, M. Rashid, M. Waqas, W.A. Khan, Arrhenius activation energy aspects in mixed convection Carreau nanofluid with nonlinear thermal radiation. Appl. Nanosci. 10, 1–11 (2020)
C.Y. Wang, The three-dimensional flow due to a stretching flat surface. Phys. Fluids 27(8), 1915–1917 (1984)
I.C. Liu, H.I. Andersson, Heat transfer over a bidirectional stretching sheet with variable thermal conditions. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 51(15–16), 4018–4024 (2008)
A. Munir, A. Shahzad, M. Khan, Convective flow of Sisko fluid over a bidirectional stretching surface. PLoS One 10(6), e0130342 (2015)
M. Irfan, M. Khan, W.A. Khan, On model for three-dimensional Carreau fluid flow with Cattaneo-Christov double diffusion and variable conductivity: a numerical approach. J. Braz. Soc. Mech. Sci. Eng. 40(12), 577 (2018)
W.A. Khan, M. Irfan, M. Khan, An improved heat conduction and mass diffusion models for rotating flow of an Oldroyd-B fluid. Results Phys. 7, 3583–3589 (2017)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Waqas, H., Imran, M. & Bhatti, M.M. Bioconvection aspects in non-Newtonian three-dimensional Carreau nanofluid flow with Cattaneo–Christov model and activation energy. Eur. Phys. J. Spec. Top. 230, 1317–1330 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1140/epjs/s11734-021-00046-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1140/epjs/s11734-021-00046-8