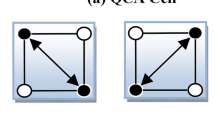
Abstract
The amount of occupied area and energy waste are among the salient indexes that are important in designing and implementing digital circuits. Hence, the inherent properties of the quantum-dot cellular automata (QCA), like ultra-dense structure and ultra-low power consumption, have made this nanotechnology a viable substitute for complementary metal–oxide–semiconductor technology. The arithmetic logic unit (ALU) is each processor's operational and inseparable component. In this paper, a novel reversible ALU is proposed, which comprises a double Feynman gate, two Fredkin gates, and a new coplanar reversible full adder based on the modified TSG in QCA nanotechnology. This structure is implemented by 247 QCA cells in a 0.332 μm2 area, which uses the coplanar clock-zone-based crossover. This layout can perform 20 various arithmetic and logic operations, and its latency is nine clock phases. The proposed QCA layouts are evaluated and simulated by QCADesigner version 2.0.3. The simulation outcomes indicate that the proposed coplanar QCA ALU has a 14.28%, 40%, 48.54%, and 50.3% improvement in quantum cost, latency, cell count, and area occupancy, respectively, compared to the prior best coplanar architecture.





















Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability Statement
No data associated in the manuscript.
References
S.R. Heikalabad, M.N. Asfestani, M. Hosseinzadeh, A full adder structure without cross-wiring in quantum-dot cellular automata with energy dissipation analysis. J. Supercomput. 74(5), 1994–2005 (2018)
W. Yu, B. Zhang, C. Liu, Y. Zhao, W.R. Wu, Z.Y. Xue, M. Chen, D. Buca, J.M. Hartmann, X. Wang, Q.T. Zhao, Impact of Si cap, strain and temperature on the hole mobility of (s) Si/sSiGe/(s) SOI quantum-well p-MOSFETs. Microelectron. Eng. 113, 5–9 (2014)
Y. Adelnia, A. Rezai, A novel adder circuit design in quantum-dot cellular automata technology. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 58(1), 184–200 (2019)
S. Seyedi, N. Jafari Navimipour, Designing a multi-layer full-adder using a new three-input majority gate based on quantum computing. Concurr. Comput. Pract. Exp. 34(4), 6653 (2022)
T. Zhang, V. Pudi, W. Liu, New majority gate-based parallel BCD adder designs for quantum-dot cellular automata. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Express Briefs 66(7), 1232–1236 (2018)
S. Seyedi, N.J. Navimipour, An efficient structure for designing a nano-scale fault-tolerant 2:1 multiplexer based on quantum-dot cellular automata. Optik 251, 168409 (2022)
C.S. Lent, P.D. Tougaw, W. Porod, G.H. Bernstein, Quantum cellular automata. Nanotechnology 4(1), 49–57 (1993)
P.D. Tougaw, C.S. Lent, Logical devices implemented using quantum cellular automata. J. Appl. Phys. 75(3), 1818–1825 (1994)
P.D. Tougaw, C.S. Lent, W. Porod, Bistable saturation in coupled quantum-dot cells. J. Appl. Phys. 74(5), 3558–3566 (1993)
R. Landauer, Irreversibility and heat generation in the computing process. IBM J. Res. Dev. 5(3), 183–191 (1961)
C.H. Bennett, Logical reversibility of computation. IBM J. Res. Dev. 17(6), 525–532 (1973)
E. Knill, R. Laflamme, G.J. Milburn, A scheme for efficient quantum computation with linear optics. Nature 409(6816), 46–52 (2001)
B. Parhami, Fault-tolerant reversible circuits. in 2006 Fortieth Asilomar Conference on Signals, Systems and Computers (IEEE, 2006).
B. Bhuvana, V.K. Bhaaskaran, Quantum cost optimization of reversible adder/subtractor using a novel reversible gate, in Innovations in Electronics and Communication Engineering (Springer, 2018). p. 111–118.
N.K. Misra, B. Sen, S. Wairya, B. Bhoi, Testable novel parity-preserving reversible gate and low-cost quantum decoder design in 1D molecular-QCA. J. Circuits Syst. Comput. 26(09), 1750145 (2017)
N.K. Misra, S. Wairya, B. Sen, Design of conservative, reversible sequential logic for cost efficient emerging nano circuits with enhanced testability. Ain Shams Eng. J. 9(4), 2027–2037 (2018)
N.K. Misra, S. Wairya, V.K. Singh, Approach to design a high performance fault-tolerant reversible ALU. Int. J. Circuits Architect. Des. 2(1), 83–103 (2016)
M.M. Mano, Computer System Architecture, vol. 3 (Prentice Hall, Englewood Cliffs, 1993)
A. Gupta, U. Malviya, V. Kapse, Design of speed, energy and power efficient reversible logic based vedic ALU for digital processors. in 2012 Nirma University International Conference on Engineering (NUiCONE) (IEEE, 2012)
S.-S. Ahmadpour, M. Mosleh, S.R. Heikalabad, A revolution in nanostructure designs by proposing a novel QCA full-adder based on optimized 3-input XOR. Phys. B 550, 383–392 (2018)
C.S. Lent, P.D. Tougaw, W. Porod, Bistable saturation in coupled quantum dots for quantum cellular automata. Appl. Phys. Lett. 62(7), 714–716 (1993)
M. Abdullah-Al-Shafi, A.N. Bahar, M.A. Habib, M.M.R. Bhuiyan, F. Ahmad, P.Z. Ahmad, K. Ahmed, Designing single layer counter in quantum-dot cellular automata with energy dissipation analysis. Ain Shams Eng. J. 9(4), 2641–2648 (2018)
A. Roohi, R.F. DeMara, N. Khoshavi, Design and evaluation of an ultra-area-efficient fault-tolerant QCA full adder. Microelectron. J. 46(6), 531–542 (2015)
A. Kamaraj, P. Marichamy, Design of fault-tolerant reversible floating point division. Informacije MIDEM 48(3), 161–172 (2018)
S. Perri, P. Corsonello, G. Cocorullo, Area-delay efficient binary adders in QCA. IEEE Trans. Very Large Scale Integration Syst. 22(5), 1174–1179 (2013)
A. Sadoghifar, S.R. Heikalabad, A Content-Addressable Memory structure using quantum cells in nanotechnology with energy dissipation analysis. Phys. B 537, 202–206 (2018)
T.N. Sasamal, A.K. Singh, U. Ghanekar, Efficient design of coplanar ripple carry adder in QCA. IET Circuits Devices Syst. 12(5), 594–605 (2018)
L. Lu, W. Liu, M. O’Neill, E.E. Swartzlander, QCA systolic array design. IEEE Trans. Comput. 62(3), 548–560 (2011)
G.H. Bernstein, A. Imre, V. Metlushko, A. Orlov, L. Zhou, L. Ji, G. Csaba, W. Porod, Magnetic QCA systems. Microelectron. J. 36(7), 619–624 (2005)
M.S. Daliri, A. Abdoli, K. Navi, N. Bagherzadeh, A 3D universal structure based on molecular-QCA and CNT technologies. J. Mol. Struct. 1119, 86–95 (2016)
G. Snider, A.O. Orlov, I. Amlani, G.H. Bernstein, C.S. Lent, J.L. Merz, W. Porod, Experimental demonstration of quantum-dot cellular automata. Semicond. Sci. Technol. 13(8A), A130 (1998)
G. Toth, C.S. Lent, Quasiadiabatic switching for metal-island quantum-dot cellular automata. J. Appl. Phys. 85(5), 2977–2984 (1999)
M.H. Valavi, G. Jaberipur, K.A.-R. Youssefi, Impact of different types of input wire on defect-tolerance of QCA majority voter. Eur. Phys. J. Plus 137(8), 977 (2022)
M. Momenzadeh, M. Ottavi, F. Lombardi, Modeling QCA defects at molecular-level in combinational circuits, in 20th IEEE International Symposium on Defect and Fault Tolerance in VLSI Systems (DFT'05) (IEEE, 2005)
J. Huang, M. Momenzadeh, M.B. Tahoori, F. Lombardi, Defect characterization for scaling of QCA devices [quantum dot cellular automata], in Proceedings of the 19th IEEE International Symposium on Defect and Fault Tolerance in VLSI Systems, 2004 (DFT 2004) (IEEE, 2004)
X. Yang, L. Cai, S. Wang, Z. Wang, C. Feng, Reliability and performance evaluation of QCA devices with rotation cell defect. IEEE Trans. Nanotechnol. 11(5), 1009–1018 (2012)
M. Crocker, M. Niemier, X.S. Hu, M. Lieberman, Molecular QCA design with chemically reasonable constraints. ACM J. Emerg. Technol. Comput. Syst. 4(2), 1–21 (2008)
A. Pulimeno, M. Graziano, A. Sanginario, V. Cauda, D. Demarchi, G. Piccinini, Bis-ferrocene molecular QCA wire: ab initio simulations of fabrication driven fault tolerance. IEEE Trans. Nanotechnol. 12(4), 498–507 (2013)
S.S. Ahmadpour, M. Mosleh, S. Rasouli Heikalabad, Robust QCA full-adders using an efficient fault-tolerant five-input majority gate. Int. J. Circuit Theory Appl. 47(7), 1037–1056 (2019)
Y.Z. Barughi, S.R. Heikalabad, A three-layer full adder/subtractor structure in quantum-dot cellular automata. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 56(9), 2848–2858 (2017)
J. Maharaj, S. Muthurathinam, Effective RCA design using quantum dot cellular automata. Microprocess. Microsyst. 73, 102964 (2020)
N. Safoev, J.-C. Jeon, A novel controllable inverter and adder/subtractor in quantum-dot cellular automata using cell interaction based XOR gate. Microelectron. Eng. 222, 111197 (2020)
H. Hosseinzadeh, S.R. Heikalabad, A novel fault tolerant majority gate in quantum-dot cellular automata to create a revolution in design of fault tolerant nanostructures, with physical verification. Microelectron. Eng. 192, 52–60 (2018)
Y. Zhang, G. Xie, M. Sun, H. Lv, An efficient module for full adders in quantum-dot cellular automata. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 57(10), 3005–3025 (2018)
S. Angizi, E. Alkaldy, N. Bagherzadeh, K. Navi, Novel robust single layer wire crossing approach for exclusive or sum of products logic design with quantum-dot cellular automata. J. Low Power Electron. 10(2), 259–271 (2014)
K. Walus, T.J. Dysart, G.A. Jullien, R.A. Budiman, QCADesigner: a rapid design and simulation tool for quantum-dot cellular automata. IEEE Trans. Nanotechnol. 3(1), 26–31 (2004)
R. Wille, M. Soeken, D.M. Miller, R. Drechsler, Trading off circuit lines and gate costs in the synthesis of reversible logic. Integration 47(2), 284–294 (2014)
D.M. Miller, R. Wille, R. Drechsler. Reducing reversible circuit cost by adding lines, in 2010 40th IEEE International Symposium on Multiple-Valued Logic (IEEE, 2010)
T. Toffoli, Reversible computing, in International Colloquium on Automata, Languages, and Programming (Springer, Berlin, 1980)
E. Fredkin, T. Toffoli, Conservative logic. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 21(3), 219–253 (1982)
R.P. Feynman, Quantum mechanical computers. Found. Phys. 16(6), 507–531 (1986)
A. Peres, Reversible logic and quantum computers. Phys. Rev. A 32(6), 3266 (1985)
H. Thapliyal, M. Srinivas, A novel reversible TSG gate and its application for designing reversible carry look-ahead and other adder architectures, in Asia-Pacific Conference on Advances in Computer Systems Architecture (Springer, 2005)
A.K. Biswas, M.M. Hasan, A.R. Chowdhury, H.M.H. Babu, Efficient approaches for designing reversible binary coded decimal adders. Microelectron. J. 39(12), 1693–1703 (2008)
M. Mohammadi, M. Eshghi, On figures of merit in reversible and quantum logic designs. Quantum Inf. Process. 8(4), 297–318 (2009)
M. Haghparast, K. Navi, A novel reversible BCD adder for nanotechnology based systems. Am. J. Appl. Sci. 5(3), 282–288 (2008)
A. Barenco, C.H. Bennett, R. Cleve, D.P. DiVincenzo, N. Margolus, P. Shor, T. Sleator, J.A. Smolin, H. Weinfurter, Elementary gates for quantum computation. Phys. Rev. A 52(5), 3457 (1995)
E. Taherkhani, M.H. Moaiyeri, S. Angizi, Design of an ultra-efficient reversible full adder-subtractor in quantum-dot cellular automata. Optik 142, 557–563 (2017)
T.N. Sasamal, A.K. Singh, A. Mohan, Design of cost-efficient qca reversible circuits via clock-zone-based crossover. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 57(10), 3127–3140 (2018)
S. Hashemi, M.R. Azghadi, K. Navi, Design and analysis of efficient QCA reversible adders. J. Supercomput. 75(4), 2106–2125 (2019)
P. Kumar, S. Singh, Optimization of the area efficiency and robustness of a QCA-based reversible full adder. J. Comput. Electron. 18(4), 1478–1489 (2019)
B. Sen, M. Dutta, M. Goswami, B.K. Sikdar, Modular design of testable reversible ALU by QCA multiplexer with increase in programmability. Microelectron. J. 45(11), 1522–1532 (2014)
T.N. Sasamal, A.K. Singh, A. Mohan, Efficient design of reversible alu in quantum-dot cellular automata. Optik 127(15), 6172–6182 (2016)
T.N. Sasamal, A. Mohan, A.K. Singh, Efficient design of reversible logic ALU using coplanar quantum-dot cellular automata. J. Circuits Syst. Comput. 27(02), 1850021 (2018)
M. Norouzi, S.R. Heikalabad, F. Salimzadeh, A reversible ALU using HNG and Ferdkin gates in QCA nanotechnology. Int. J. Circuit Theory Appl. 48(8), 1291–1303 (2020)
M. Mosleh, A novel full adder/subtractor in quantum-dot cellular automata. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 58(1), 221–246 (2019)
S.S. Ahmadpour, M. Mosleh, S.R. Heikalabad (2022) Efficient designs of quantum-dot cellular automata multiplexer and RAM with physical proof along with power analysis. J. Supercomput. 78(2), 1672–1695. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11227-021-03913-2
S.R. Heikalabad, F. Salimzadeh, Y.Z. Barughi (2020) A unique three-layer full adder in quantum-dot cellular automata. Comput. Electr. Eng. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compeleceng.2020.106735
F. Salimzadeh, S.R. Heikalabad (2021) A full adder structure with a unique XNOR gate based on Coulomb interaction in QCA nanotechnology. Opt. Quant. Electron. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11082-021-03127-z
A. Norouzi, S.R. Heikalabad (2019) Design of reversible parity generator and checker for the implementation of nano-communication systems in quantum-dot cellular automata. Photon. Netw. Commun. 38(2), 231–243. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11107-019-00850-2
S.R. Heikalabad, H. Kamrani (2019) Design and implementation of circuit-switched network based on nanoscale quantum-dot cellular automata. Photon. Netw. Commun. 38(3), 356–377. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11107-019-00864-w
H. Kamrani, S.R. Heikalabad (2021) Design and implementation of multiplication algorithm in quantum-dot cellular automata with energy dissipation analysis. J. Supercomput. 77(6), 5779–5805. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11227-020-03478-6
S.R. Heikalabad (2021) Non-coplanar counter in quantum-dot cellular automata. Eur. Phys. J. Plus. https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/s13360-021-01198-1
F. Salimzadeh, E. Safarpoor, S. Rasouli Heikalabad (2021) Designing and Implementing a Fault-Tolerant Priority Encoder in QCA Nanotechnology. ECS J. Solid State Sci. Technol. https://doi.org/10.1149/2162-8777/ac0118
S.R. Heikalabad, R. Ahmadi, F. Salimzadeh (2021) Introducing a Full-Adder Structure for Finite Field in QCA. ECS J. Solid State Sci. Technol. https://doi.org/10.1149/2162-8777/ac08d9
S.R. Heikalabad, M.R. Gadim (2018) Design of Improved Arithmetic Logic Unit in Quantum-Dot Cellular Automata. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 57(6), 1733–1747. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10773-018-3699-1
F. Salimzadeh, S.R. Heikalabad (2019) Design of a novel reversible structure for full adder/subtractor in quantum-dot cellular automata. Physica. B Condensed Matter. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physb.2018.12.028
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Aliabadian, R., Golsorkhtabaramiri, M., Heikalabad, S.R. et al. Design of an ultra-high-speed coplanar QCA reversible ALU with a novel coplanar reversible full adder based on MTSG. Eur. Phys. J. Plus 138, 481 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/s13360-023-04007-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/s13360-023-04007-z