Abstract
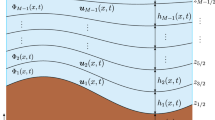
A fast and accurate finite volume method for multilayered shallow water flows with mass exchange over erodible beds is developed. The governing equations consist of the multilayered shallow water equations for the hydraulic variables, a set of transport equations for the suspended sediments in each layer and a class of empirical equations for erosion and deposition effects. Mass exchange terms between layers are accounted for in both water flow and suspended sediments along with terms for sedimentary diffusion. The coupled models for each layer have been reformulated as a coupled system of conservation laws with source terms, and a two-step finite volume method is presented for its numerical solution. The method is simple, fast and second-order accurate. In the first step, the governing equations are rewritten in a non-conservative form and the numerical fluxes are calculated using the method of characteristics. In the second stage, the numerical solutions are updated in a conservative form using the finite volume discretization. Entrainment, deposition and diffusion rates are evaluated in the first stage of a splitting operator. Numerical results are presented for a multilayered dam-break problem over an erodible bed and also for a wind-driven recirculation problem over an erodible non-flat bed. The obtained results for these examples demonstrate the capabilities of the combined multilayered model and the finite volume method to accurately simulate shallow water flows with suspended sediments over erodible beds.Please confirm the corresponding author is correctly identified and amend if necessary.The corresponding author is correctly identified.












Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability Statement
The data underlying the results can be obtained from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
E. Audusse, F. Benkhaldoun, S. Sari, M. Seaid, P. Tassi, A fast finite volume solver for multi-layered shallow water flows with mass exchange. J. Comput. Phys. 272, 23–45 (2014)
E. Audusse, M. Bristeau, M. Pelanti, J. Sainte-Marie, Approximation of the hydrostatic Navier-Stokes system for density stratified flows by a multilayer model: kinetic interpretation and numerical solution. J. Comput. Phys. 230, 3453–3478 (2011)
F. Benkhaldoun, S. Sari, M. Seaid, A flux-limiter method for dam-break flows over erodible sediment beds. Appl. Math. Model. 36, 4847–4861 (2012)
F. Benkhaldoun, M. Seaid, A simple finite volume method for the shallow water equations. J. Comp. Appl. Math. 234, 58–72 (2010)
Z. Cao, P. Carling, Mathematical modelling of alluvial rivers: reality and myth. Part I: general overview. Water Maritime Eng. 154, 207–220 (2002)
Z. Cao, G. Pender, Numerical modelling of alluvial rivers subject to interactive sediment mining and feeding. Adv. Water Resour. 27, 533–546 (2004)
Z. Cao, G. Pender, S. Wallis, P. Carling, Computational dam-break hydraulics over erodible sediment bed. J. Hydraul. Eng. 67, 149–152 (2004)
L. Chumakova, F. Menzaque, P. Milewski, R. Rosales, E. Tabak, C. Turner, Shear instability for stratified hydrostatic flows. Commun. Pure Appl. Math. 62, 183–197 (2009)
P. Dyke, Modeling Costal and Offshore Processes (Imperial College Press, London, 2007)
H.A. Einstein, Formulas for the transportation of bed load. Trans. Am. Soc. Civ. Eng. 107, 561–573 (1949)
E. Fernández-Nieto, E. Koné, T. Morales de Luna, R. Burger, A multilayer shallow water system for polydisperse sedimentation. J. Comput. Phys. 238, 281–314 (2013)
E. Fernández-Nieto, E. Koné, T. Chacón, A multilayer method for the hydrostatic Navier-Stokes equations: a particular weak solution. J. Sci. Comput. 57, 1–30 (2013)
A. Grass. Sediment transport by waves and currents. SERC London Cent. Mar. Technol., FL29, (1981)
J. Gula, V. Zeitlin, F. Bouchut, Instabilities of buoyancy-driven coastal currents and their nonlinear evolution in the two-layer rotating shallow water model. Part 2. Active lower layer. J. Fluid Mech. 665, 209–237 (2010)
J. Guo, P.Y. Julien, Turbulent velocity profiles in sediment-laden flows. J. Hydraul. Res. 39(1), 11–23 (2001)
S. Huang, Z. Sun, D. Xu, S. Xia, Vertical distribution of sediment concentration. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. 9(11), 1560–1566 (2008)
E. Kubatko, J. Westerink, Exact discontinuous solutions of Exner bed evolution model: simple theory for sediment bores. J. Hydraul. Eng. 133(3), 305–311 (2007)
W. Liu, B. Yunliang, W. Chao, L. Xin, Assessing the analytical solution of one-dimensional gravity wave model equations using dam-break experimental measurements. Water 10(9), (2018)
X. Liu, New near-wall treatment for suspended sediment transport simulations with high-reynolds number (HRN) turbulence models. J. Hydaul. Eng 140, 333–339 (2014)
X. Liu, A. Mohammadian, J. Sedano, A numerical model for three-dimensional shallow water flows with sharp gradients over mobile topography. Comput. Fluids. 154, 1–11 (2017)
E. Meyer-Peter, R. Müller, Formulas for bed-load transport. Report on 2nd meeting on international association on hydraulic structures research, pages 39–64, (1948)
T. Rowan, M. Seaid, Efficient computational models for shallow water flows over multilayer erodible beds. Eng. Comput. 37, 401–429 (2019)
T. Rowan, M. Seaid, Two-dimensional numerical modelling of shallow water flows over multilayer movable beds. Appl. Math. Model. 88, 474–497 (2020)
W.W. Rubey, Settling velocity of gravel, sand, and silt particles. Am. J. Sci. 148, 325–338 (1933)
C.W. Shu, Total variation diminishing time discretizations. SIAM J. Sci. Stat. Comput. 9, 1073–1084 (1988)
H. Smaoui, F. Boughanim, 1D vertical model for suspended sediment transport in turbulent tidal flow: application to the English channel. Comput. Geosci. 33, 1111–1129 (2007)
K. Terzaghi, R.B. Peck, G. Mersi, Soil Mechanics in Engineering Practice (Wiley, New Jersey, 1996)
L.C. Van Rijn, Unified view of sediment transport by currents and waves. I: initiation of motion, bed roughness, and bed-load transport. J. Hydraul. Eng. 113, 649–667 (2007)
V.A. Vanoni, G.N. Nomicos, Resistance properties of sediment-laden streams. Trans. Am. Soc. Civ. Eng. 125(1), 1140–1167 (1960)
K. Vercruysse, R.C. Grabowski, R.J. Rickson, Multi-scale drivers of temporal variation, Suspended sediment transport dynamics in rivers. Earth Sci. Rev. 166, 38–52 (2017)
Z. B. Wang, R. J. Fokkink, A. Langerak, A dynamic-empirical model for estuarine morphology. In Physics of Estuaries and Coastal Seas, pages 279–286, Balkema, Rotterdam, (1998)
W. Wu, S.S. Wang, Formulas for sediment porosity and settling velocity. J. Hydraul. Eng. 132, 858–862 (2006)
Z. Yang, Z. Zou, W. Xue, D. Sun, Experimental study of near-bed concentration and sediment vertical mixing parameter for vertical concentration distribution in the surf zone. Int. J. Sedim. Res. 35, 27–41 (2020)
S. Zhao, J. Ovadia, X. Liu, Y.T. Zhang, Q. Nie, Operator splitting implicit integration factor methods for stiff reaction-diffusion-advection systems. J. Comput. Phys. 230, 5996–6009 (2011)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Rowan, T., Seaid, M. A multilayered shallow water model for sediment transport in flows over heterogeneous erodible beds. Eur. Phys. J. Plus 137, 974 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/s13360-022-03202-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/s13360-022-03202-8