Abstract
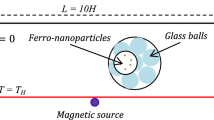
The problem of forced convection ferrofluid flow inside rectangular channel under the influence of a non-uniform magnetic field was numerically studied. The magnetic field was created by placing four magnetic sources in vicinity of four heaters, located at the bottom wall of the channel. The governing equations which are take account of the ferrohydrodynamic effect were solved by the finite volume method with the prediction-projection scheme. The effects of magnetic number, Reynolds number, volume fraction of nanoparticles and magnetic sources locations on the flow and heat transfer behaviors were examined. Results show the formation of vortices near the magnetic sources in the presence of magnetic field. The skin friction coefficient increases by increasing the magnetic field strength; however it decreases by augmenting the Reynolds number and the volume fraction of nanoparticles. The heat transfer rate increases by increasing magnetic number, Reynolds number and volume fraction of nanoparticles. An optimum position of magnetic sources was obtained giving maximum heat transfer rate. In the absence of magnetic field, the effect of nanoparticles gives an enhancement of heat transfer of 23%. It can be enhanced up to 228% under the effect of the magnetic field only. The coupled effects of both nanoparticles and magnetic field enhance the heat transfer up to 300%.











Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- c p :
-
Specific heat (J/Kg K)
- C f :
-
Local skin friction coefficient
- C f m :
-
Average skin friction coefficient
- Ec, :
-
Eckert number, \(\rho_{{{\text{bf}}}} u_{0}^{2} /\left( {\rho C_{{\text{P}}} } \right)_{{{\text{bf}}}} \Delta T\)
- h :
-
Heat transfer coefficient (W/m2K)
- \(\vec{H}\) :
-
Magnetic field vector
- H :
-
Height of channel (m)
- I :
-
Electric current (A)
- k :
-
Thermal conductivity (W/mK)
- L :
-
Length of the channel (m)
- \(l\) :
-
Heater length (m)
- \(M\) :
-
Magnetization
- Mn :
-
Magnetic number, \(\mu_{0} H_{0}^{2} K^{\prime}\Delta T/\rho_{bf} u_{0}^{2}\)
- Nu :
-
Local Nusselt number
- Nu m :
-
Average Nusselt number
- P :
-
Non-dimensional pressure, p/ρbf \(u_{0}^{2}\)
- p :
-
Pressure (Pa)
- Pr :
-
Prandtl number, \(\mu_{bf} c_{p,bf} /k_{bf}\)
- Re :
-
Reynolds number, \(\rho_{bf} u_{0} h/\mu_{bf}\)
- t :
-
Time (s)
- T :
-
Temperature (K)
- u 0 :
-
Inlet velocity (m/s)
- \(\vec{v}\) :
-
Velocity vector
- \(\vec{V}\) :
-
Dimensionless velocity vector, \(\vec{v}/u_{0}\)
- x, y :
-
Coordinates (m)
- X,Y :
-
Dimensionless coordinates, x/H, y/H
- \(x_{S}\) :
-
Abscissa of magnetic sources (m)
- \(X_{S}\) :
-
Dimensionless modified abscissa of magnetic sources, \(X_{S} = (x_{S} - x_{i} )/l\)
- μ :
-
Dynamic viscosity (Kg/ms)
- ρ :
-
Density (Kg/m3)
- θ :
-
Dimensionless temperature, (T-TC)/(TH−TC)
- φ :
-
Volume fraction of nanoparticles
- τ :
-
Dimensionless time, tu0/H
- bf :
-
Base fluid
- C :
-
Cold
- H :
-
Hot
- m :
-
Average
- nf :
-
Nanofluid
- p :
-
Particles
References
R.E. Rosensweig, R. Kaiser, G. Miskolczy, Viscosity of magnetic fluid in a magnetic field. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 29(4), 680–686 (1969)
M.A. Khairul, E. Doroodchi, R. Azizian, B. Moghtaderi, Advanced applications of tunable ferrofluids in energy systems and energy harvesters: a critical review. Energy Convers. Manag. 149, 660–674 (2017)
M. Latikka, M. Backholm, J.V.I. Timonen, R.H.A. Ras, Wetting of ferrofluids: phenomena and control. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 36, 118–129 (2018)
S.O. Aisida, P.A. Akpa, I. Ahmad, T.-K. Zhao, M. Maaza, F.I. Ezema, Bio-inspired encapsulation and functionalization of iron oxide nanoparticles for biomedical applications. Eur. Polymer J. 122, 109371 (2020)
J. Sadhasivam, A. Sugumaran, Magnetic nanocarriers: Emerging tool for the effective targeted treatment of lung cancer. Journal of Drug Delivery Science and Technology 55, 101493 (2020)
H. Ali, H. Soleimani, N. Yahya, L. Khodapanah, M. Sabet, B.M.R. Demiral, T. Hussain, L. Lanre Adebayo, Enhanced oil recovery by using electromagnetic-assisted nanofluids: a review. J. Mol. Liq. 309, 113095 (2020)
K. Zhou, X. Zhou, J. Liu, Z. Huang, Application of magnetic nanoparticles in petroleum industry: a review. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 188, 106943 (2020)
P. Thakur, D. Chahar, S. Taneja, N. Bhalla, A. Thakur, A review on MnZn ferrites: synthesis, characterization and applications. Ceram. Int. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2020.03.287,Inpress
M. Amani, M. Ameri, A. Kasaeian, Hydrothermal assessment of ferrofluids in a metal foam tube under low frequency magnetic field. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 127, 242–251 (2018)
A. Salehpour, S. Salehi, S. Salehpour, M. Ashjaee, Thermal and hydrodynamic performances of MHD ferrofluid flow inside a porous channel. Exp. Thermal Fluid Sci. 90, 1–13 (2018)
Mohammad Behshad Shafii, Mohsen Keshavarz, Experimental study of internal forced convection of ferrofluid flow in nonmagnetizable/magnetizable porous media. Exp. Thermal Fluid Sci. 96, 441–450 (2018)
A. Abadeh, M. Sardarabadi, M. Abedi, M. Pourramezan, M. Passandideh-Fard, Mohammad Javad Maghrebi, Experimental characterization of magnetic field effects on heat transfer coefficient and pressure drop for a ferrofluid flow in a circular tube. J. Mol. Liq. 299, 112206 (2020)
M. Mokhtari, S. Hariri, M. Barzegar Gerdroodbary, Y. Rezvan, Effect of non-uniform magnetic field on heat transfer of swirling ferrofluid flow inside tube with twisted tapes. Chem. Eng. Process. Process Intens. 117, 70–79 (2017)
W. Nessab, H. Kahalerras, B. Fersadou, D. Hammoudi, Numerical investigation of ferrofluid jet flow and convective heat transfer under the influence of magnetic sources. Appl. Therm. Eng. 150, 271–284 (2019)
M. Izadi, R. Mohebbi, Amin Amiri Delouei, Hasan Sajjadi, Natural convection of a magnetizable hybrid nanofluid inside a porous enclosure subjected to two variable magnetic fields. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 151, 154–169 (2019)
M.R. Daneshvar Garmroodi, A. Ahmadpour, M.R. Hajmohammadi, S. Gholamrezaie, Natural convection of a non-Newtonian ferrofluid in a porous elliptical enclosure in the presence of a non-uniform magnetic field. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-019-09045-3
S. Morteza Mousavi, M. Biglarian, A. Ali Rabienataj Darzi, M. Farhadi, H. Hassanzadeh Afrouzi, D. Toghraie, Heat transfer enhancement of ferrofluid flow within a wavy channel by applying a non-uniform magnetic field. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 139, 3331–3343 (2020)
A.M. Aly, S.E. Ahmed, ISPH simulations for a variable magneto-convective flow of a ferrofluid in a closed space includes open circular pipes. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transfer 110, 104412 (2020)
Abuzar Abid Siddiqui, Mustafa Turkyilmazoglu, Natural convection in the ferrofluid enclosed in a porous and permeable cavity. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transfer 113, 104499 (2020)
M. Bezaatpour, H. Rostamzadeh, Heat transfer enhancement of a fin-and-tube compact heat exchanger by employing magnetite ferrofluid flow and an external magnetic field. Appl. Therm. Eng. 164, 114462 (2020)
Hamid Kazemi Moghadam, Saeed Samadzadeh Baghbani & Houman Babazadeh, Study of thermal performance of a ferrofluid with multivariable dependence viscosity within a wavy duct with external magnetic force. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-020-09324-4
T.D. Manh, A.M. Abazari, M. Barzegar Gerdroodbary, N.D. Nam, R. Moradi, H. Babazadeh, Computational simulation of variable magnetic force on heat characteristics of backward-facing step flow. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-020-09608-9
Z. Mehrez, A. El Cafsi, Heat exchange enhancement of ferrofluid flow into rectangular channel in the presence of a magnetic field. Appl. Math. Comput. 391, 125634 (2021)
A. Jarray, Z. Mehrez, A. El Cafsi, Effect of magnetic field on the mixed convection Fe3O4/water ferrofluid flow in a horizontal porous channel. Pramana J. Phys. 94, 156 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12043-020-02015-7
M. Turkyilmazoglu, Natural convective flow of nanofluids past a radiative and impulsive vertical plate. J. Aerosp. Eng. 29, 04016049 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)AS.1943-5525.0000643
M. Turkyilmazoglu, Single phase nanofluids in fluid mechanics and their hydrodynamic linear stability analysis. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 187, 105171 (2020)
M. Turkyilmazoglu, Fully developed slip flow in a concentric annuli via single and dual phase nanofluids models. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 179, 104997 (2019)
M. Turkyilmazoglu, Nanoliquid film flow due to a moving substrate and heat transfer. Eur. Phys. J. Plus 135, 781 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/s13360-020-00812-y
M. Sheikholeslami, M.M. Rashidi, Ferrofluid heat transfer treatment in the presence of variable magnetic field. Eur. Phys. J. Plus 130, 115 (2015)
Z. Mehrez, A. El Cafsi, Forced convection magnetohydrodynamic Al2O3–Cu/water hybrid nanofluid flow over a backward-facing step. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 135, 1417 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-018-7541-z
H.C. Brinkman, The viscosity of concentrated suspensions and solutions. J. Chem. Phys. 20, 571–581 (1952)
J.C. Maxwell, A Treatise on Electricity and Magnetism, 2nd edn. (Oxford University Press, Cambridge, 1904), pp. 435–441
A. Jarray, Z. Mehrez, A. El Cafsi, Mixed convection Ag-MgO/water hybrid nanofluid flow in a porous horizontal channel. Eur. Phys. J. Spec. Top. 228, 2677–2693 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1140/epjst/e2019-900068-8
A. Chorin, Numerical simulation of the Navier-Stokes equations. J. Math. Comput. 22, 745–762 (1968)
R. Temam, Une méthode d’approximation de la solution des équations de Navier-Stokes. Bull. Soc. Math. France 98, 115–152 (1968)
F. Zamzari, Z. Mehrez, A. El Cafsi, A. Belghith, Entropy generation and mixed convection in a horizontal channel with an open cavity. Int. J. Exergy 17(2), 219 (2015)
Z. Mehrez, A. El Cafsi, A. Belghith, P. Le Quéré, MHD effects on heat transfer and entropy generation of nanofluid flow in an open cavity. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 374, 214–224 (2015)
Z. Mehrez, M. Bouterra, A. El Cafsi, A. Belghith, P. Le Quere, Simulation of the periodically perturbed separated and reattaching flow over a backward-facing step. J. Appl. Fluid Mech. JAFM 3(2), 1–8 (2010)
G. Evans, S. Paolucci, The thermoconvective in sta bility of plane poiseuille flow heated from below: a bench mark solution for open boundary flow. Int. J. Numer. Method Fluids 11(7), 1001–1013 (1990)
G. Comini, M. Manzan, G. Cortella, Open boundary conditions for the stream function of unsteady laminar convection. Numer. Heat Transfer Part B 31(2), 217–234 (1997)
M. Nourollahi, M. Farhadi, K. Sedighi, Numerical study of mixed convection and entropy generation in the poiseulle-benard channel in different angles. Thermal Sci. 14(2), 329–340 (2010)
M. Nassim, Sahraoui, Samir Houat, and Nawal Saidi, Simulation of mixed convection in a horizontal channel heated from below by the lattice Boltzmann method. Eur. Phys. J. Appl. Phys. 78, 34806 (2017)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mehrez, Z., El Cafsi, A. Forced convection Fe3O4/water nanofluid flow through a horizontal channel under the influence of a non-uniform magnetic field. Eur. Phys. J. Plus 136, 451 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/s13360-021-01410-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/s13360-021-01410-2