Abstract
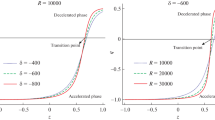
In this paper, we have examined the Sharma–Mittal holographic dark energy model (SMHDE) in the framework of an isotropic and spatially homogeneous flat Friedmann–Robertson–Walker Universe by considering different values of parameter \(\delta \) and R, where the infrared cut-off is taken care by the Hubble horizon. We examined the SMHDE model through the analysis of statefinder hierarchy and the growth rate of perturbation. The evolutionary trajectories of the statefinder hierarchy \(S_3^1\), \(S_3^2\)\(S_4^1\), \(S_4^2\) versus redshift z, show satisfactory behaviour throughout the Universe evaluation. One promising tool for investigating the dark energy models is the CND \(\{ S_3^1 - \epsilon \}\) and \(\{ S_4^1 - \epsilon \}\), where the evolutionary trajectories of the \(S_3^1 - \epsilon \) and \(S_4^1 - \epsilon \) pair present different properties and the departure from \(\Lambda \hbox {CDM}\) could be well evaluated. Additionally, we investigated the dynamical analysis of the model by \(\omega _{D}-\omega '_{D}\) pair analysis.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
A.G. Riess et al., [Supernova Search Team], Observational evidence from supernovae for an accelerating universe and a cosmological constant. Astron. J. 116, 1009 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1086/300499
S. Perlmutter et al., [Supernova Cosmology Project Collaboration], Measurements of \(\Omega \) and \(\Lambda \) from 42 high redshift supernovae. Astrophys. J. 517, 565 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1086/307221. [arxiv:astro-ph/9812133]
N. Aghanim, et al., Planck 2018 results. VI. Cosmological parameters. Preprint (2018). arXiv:1807.06209 [astro-ph.CO]
M. Colless et al., [2DFGRS Collaboration], The 2dF galaxy redshift survey: spectra and redshifts. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 328, 1039 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-8711.2001.04902.x
M. Tegmark et al., [SDSS Collaboration], Cosmological parameters from SDSS and WMAP. Phys. Rev. D 69, 103501 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevD.69.103501
D.N. Spergel et al., [WMAP Collaboration], First year Wilkinson Microwave Anisotropy Probe (WMAP) observations: Determination of cosmological parameters. Astrophys. J. Suppl. 148, 175 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1086/377226
E.J. Copeland, M. Sami, S. Tsujikawa, Dynamics of dark energy. Int. J. Mod. Phys. D 15, 1753 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1142/S021827180600942X. [hep-th/0603057]
K. Bamba, S. Capozziello, S. Nojiri, S.D. Odintsov, Dark energy cosmology: the equivalent description via different theoretical models and cosmography tests. Astrophys. Space Sci. 342, 155 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10509-012-1181-8
W. Yang, S. Pan, E. Di Valentino, R.C. Nunes, S. Vagnozzi, D.F. Mota, Tale of stable interacting dark energy, observational signatures, and the \(H_0\) tension. JCAP 1809, 019 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1088/1475-7516/2018/09/019. [arXiv:1805.08252 [astro-ph.CO]]
L. Amendola, S. Tsujikawa, Dark Energy: Theory and Observations (Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 2010)
V. Sahni, A. Starobinsky, The case for a positive cosmological \(\Lambda \)-term. Int. J. Mod. Phys. D 9(04), 373–443 (2000)
P.J.E. Peebles, B. Ratra, The Cosmological constant and dark energy. Rev. Mod. Phys. 75, 559 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1103/RevModPhys.75.559
T. Padmanabhan, Dark energy and gravity. Gen. Rel. Grav. 40, 529 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10714-007-0555-7
S.M. Carroll, The Cosmological constant. Living Rev. Rel. 4, 1 (2001). https://doi.org/10.12942/lrr-2001-1
S. Weinberg, The cosmological constant problem. Rev. Mod. Phys. 61, 1 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1103/RevModPhys.61.1
P.J.E. Peebles, B. Ratra, Cosmology with a time-variable cosmological’constant. Int. J. Mod. Phys. A 325, L17–L20 (1988)
M.S. Turner, Making sense of the new cosmology. Int. J. Mod. Phys. A 17, 180 (2002)
R.R. Caldwell, M. Kamionkowski et al., Phantom energy and cosmic doomsday. Phys. Rev. Lett. 91, 071301 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.91.071301
T. Chiba, Tracking K-essence. Phys. Rev. D 66, 063514 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevD.66.063514
C. Armendariz-Picon, V.F. Mukhanov, P.J. Steinhardt, Essentials of \(k\) essence. Phys. Rev. D 63, 103510 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevD.63.103510. [arxiv:astro-ph/0006373]
M. Malquarti, E.J. Copeland, A.R. Liddle, M. Trodden, A New view of \(k\)-essence. Phys. Rev. D 67, 123503 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevD.67.123503. [arxiv:astro-ph/0302279]
A. Sen, Universality of the tachyon potential. J. High Energy Phys. 1999(12), 027 (2000)
A.Y. Kamenshchik, U. Moschella et al., An Alternative to quintessence. Phys. Lett. B 511, 265 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0370-2693(01)00571-8
C.H. Brans, R.H. Dicke, Mach’s principle and a relativistic theory of gravitation. Phys. Rev. D 124(3), 925 (1961)
A. De Felice, S. Tsujikawa, \(f(R)\) theories. Living Rev. Rel. 13, 3 (2010). https://doi.org/10.12942/lrr-2010-3
S. Nojiri, S.D. Odintsov, V.K. Oikonomou, Modified gravity theories on a nutshell: inflation, bounce and late-time evolution. Phys. Rep. 692, 1 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physrep.2017.06.001
S. Nojiri, S.D. Odintsov, Unified cosmic history in modified gravity: from \(f(R)\) theory to Lorentz non-invariant models. Phys. Rep. 505, 59 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physrep.2011.04.001
S. Maity, P. Rudra, Gravitational Baryogenesis in \(\text{ Ho }\check{r}\text{ ava }\)-Lifshitz gravity. Mod. Phys. Lett. A 34(25), 1950203 (2019)
T. Harko, F.S.N. Lobo, S. Nojiri, S.D. Odintsov, \(f(R, T)\) gravity. Phys. Rev. D 84, 024020 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevD.84.024020
L. Susskind, The World as a hologram. J. Math. Phys. 36, 6377 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.531249
P. Horava, D. Minic, Probable values of the cosmological constant in a holographic theory. Phys. Rev. Lett. 85, 1610 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.85.1610
S.D. Thomas, Holography stabilizes the vacuum energy. Phys. Rev. Lett. 89, 081301 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.89.081301
S.D.H. Hsu, Entropy bounds and dark energy. Phys. Lett. B 594, 13 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physletb.2004.05.020
M. Li, A Model of holographic dark energy. Phys. Lett. B 603, 1 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physletb.2004.10.014
S. Wang, Y. Wang, M. Li, Holographic dark energy. Phys. Rep. 696, 1 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physrep.2017.06.003
S. Nojiri, S.D. Odintsov, Unifying phantom inflation with late-time acceleration: scalar phantom-non-phantom transition model and generalized holographic dark energy. Gen. Rel. Grav. 38, 1285 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10714-006-0301-6
A. Sheykhi, Holographic scalar fields models of dark energy. Phys. Rev. D 84, 107302 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevD.84.107302
S. Srivastava, U.K. Sharma, A. Pradhan, New holographic dark energy in bianchi- \(III\) Universe with \(k\)-essence. New Astron. 68, 57 (2019)
Y.Z. Ma, Y. Gong, X. Chen, Features of holographic dark energy under the combined cosmological constraints. Eur. Phys. J. C 60, 303 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1140/epjc/s10052-009-0876-7
R.G. Cai, A dark energy model characterized by the age of the universe. Phys. Lett. B 657, 228 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physletb.2007.09.061
H. Wei, R.G. Cai, A new model of agegraphic dark energy. Phys. Lett. B 660, 113 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physletb.2007.12.030
C. Gao, F. Wu et al., A holographic dark energy model from ricci scalar curvature. Phys. Rev. D 79, 043511 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevD.79.043511
C. Tsallis, L.J.L. Cirto, Black hole thermodynamical entropy. Eur. Phys. J. C 73, 2487 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1140/epjc/s10052-013-2487-6
C. Tsallis, Possible generalization of Boltzmann–Gibbs statistics. J. Stat. Phys. 52, 479 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01016429
A. Rényi, in Proceedings of the 4th Berkely Symposium on Mathematics, Statistics and Probability (University California Press, Berkeley, CA, 1961), pp. 547–561
B.D. Sharma, D.P. Mittal, New non-additive measures of entropy for discrete probability distributions. J. Math. Sci. 10, 28–40 (1975)
B.D. Sharma, D.P. Mittal, J. Comb. Inf. Syst. Sci. 2, 122 (1977)
H. Moradpour, S. Moosavi, I. Lobo, J. Morais Graca, A. Jawad, I. Salako, Thermodynamic approach to holographic dark energy and the \(\text{ R }\acute{e}\text{ nyi }\) entropy. Eur. Phys. J. C 78(10), 829 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1140/epjc/s10052-018-6309-8
M. Tavayef, A. Sheykhi, K. Bamba, H. Moradpour, Tsallis holographic dark energy. Phys. Lett. B 781, 195 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physletb.2018.04.001
M.Abdollahi Zadeh, A. Sheykhi, H. Moradpour, Tsallis agegraphic dark energy model. Mod. Phys. Lett. A 34(11), 1950086 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1142/S021773231950086X
A.Sayahian Jahromi, S.A. Moosavi, H. Moradpour, J.P.Morais Graaa, I.P. Lobo, I.G. Salako, A. Jawad, Generalized entropy formalism and a new holographic dark energy model. Phys. Lett. B 780, 21 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physletb.2018.02.052
S. Nojiri, S .D. Odintsov, E .N. Saridakis, Modified cosmology from extended entropy with varying exponent. Eur. Phys. J. C 79, 242 (2019)
Q. Huang, H. Huang, J. Chen, L. Zhang, F. Tu, Stability analysis of a Tsallis holographic dark energy model. Class. Quant. Grav. 36(17), 175001 (2019)
S. Ghaffari, H. Moradpour, I.P. Lobo, J.P. Morais Graaa, V.B. Bezerra, Tsallis holographic dark energy in the Brans–Dicke cosmology. Eur. Phys. J. C 78(9), 706 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1140/epjc/s10052-018-6198-x
E.N. Saridakis, K. Bamba, R. Myrzakulov, F.K. Anagnostopoulos, Holographic dark energy through Tsallis entropy. JCAP 1812, 012 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1088/1475-7516/2018/12/012
V.C. Dubey, S. Srivastava, U.K. Sharma, A. Pradhan, Tsallis holographic dark energy in Bianchi-I Universe using hybrid expansion law with \(k\)-essence. Pramana 93(5), 78 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12043-019-1843-y
E. Sadri, Observational constraints on interacting Tsallis holographic dark energy model. Eur. Phys. J. C 79(9), 762 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1140/epjc/s10052-019-7263-9
E.M. Barboza, RdC Nunes Jr., E.M.C. Abreu, J. Ananias Neto, Dark energy models through nonextensive Tsallis statistics. Physica A 436, 301 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physa.2015.05.002
T. Golanbari, K. Saaidi, P. Karimi, \(\text{ R }\acute{e}\text{ nyi }\) entropy and the holographic dark energy in flat space time. [arXiv:2002.04097 [astro-ph.CO]]
U. K. Sharma, V. C. Dubey, Interacting \(\text{ R }\acute{e}\text{ nyi }\) holographic dark energy with parametrization on the interaction term. [arXiv:2001.02368 [gr-qc]]
S. Ghaffari, A.H. Ziaie, V.B. Bezerra, H. Moradpour, Inflation in the \(\text{ R }\acute{e}\text{ nyi }\) cosmology. Mod. Phys. Lett. A 35(01), 1950341 (2019)
S. Ghaffari, H. Moradpour, V.B. Bezerra, J. Morais Graaa, I. Lobo, Tsallis holographic dark energy in the brane cosmology. Phys. Dark Univ. 23, 100246 (2019)
V.C. Dubey et al., Tsallis holographic dark energy Models in axially symmetric space time. Int. J. Geom. Methods Mod. Phys. 17(1), 2050011 (2020)
Y. Aditya, S. Mandal, P.K. Sahoo, D.R.K. Reddy, Observational constraint on interacting Tsallis holographic dark energy in logarithmic Brans–Dicke theory. Eur. Phys. J. C 7912, 1020 (2019)
R. D’Agostino, Holographic dark energy from nonadditive entropy: cosmological perturbations and observational constraints. Phys. Rev. D 99(10), 103524 (2019)
M. Arabsalmani, V. Sahni, The Statefinder hierarchy: an extended null diagnostic for concordance cosmology. Phys. Rev. D 83, 043501 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevD.83.043501
J.F. Zhang, J.L. Cui et al., Diagnosing holographic dark energy models with statefinder hierarchy. Eur. Phys. J. C 74(10), 3100 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1140/epjc/s10052-014-3100-3
V. Acquaviva, A. Hajian et al., Next generation redshift surveys and the origin of cosmic acceleration. Phys. Rev. D 78, 043514 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevD.78.043514
V. Acquaviva, E. Gawiser, How to falsify the GR+LambdaCDM Model with galaxy redshift surveys. Phys. Rev. D 82, 082001 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevD.82.082001
R. Myrzakulov, M. Shahalam, Statefinder hierarchy of bimetric and galileon models for concordance cosmology. JCAP 1310, 047 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1088/1475-7516/2013/10/047
J. Li, R. Yang et al., Discriminating dark energy models by using the statefinder hierarchy and the growth rate of matter perturbations. JCAP 1412, 043 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1088/1475-7516/2014/12/043
Y. Hu, M. Li et al., Impacts of different SNLS3 light-curve fitters on cosmological consequences of interacting dark energy models. Astron. Astrophys. 592, A101 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1051/0004-6361/201526946
A. Mukherjee, N. Paul, H.K. Jassal, Constraining the dark energy statefinder hierarchy in a kinematic approach. JCAP 1901, 005 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1088/1475-7516/2019/01/005
J. Cui, L. Yin, L. Wang, Y. Li, X. Zhang, A closer look at interacting dark energy with statefinder hierarchy and growth rate of structure. JCAP 09, 024 (2015)
L. Zhou, S. Wang, Diagnosing \(\Lambda \text{ HDE }\) model with statefinder hierarchy and fractional growth parameter. Sci. China Phys. Mech. Astron. 59(7), 670411 (2016)
A. Majumdar, S. Chattopadhyay, A study of modified holographic Ricci dark energy in the framework of \(f\text{(T) }\) modified gravity and its statefinder hierarchy. Can. J. Phys. 97(5), 477 (2019)
Z. Zhao, S. Wang, Diagnosing holographic type dark energy models with the Statefinder hierarchy, composite null diagnostic and \(w-w\) pair. Sci. China Phys. Mech. Astron. 61(3), 039811 (2018)
F. Yu, J.L. Cui, J.F. Zhang, X. Zhang, Statefinder hierarchy exploration of the extended Ricci dark energy. Eur. Phys. J. C 75(6), 274 (2015)
V. Srivastava, U.K. Sharma, Statefinder hierarchy for Tsallis holographic dark energy. New Astron. 78, 101380 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.newast.2020.101380
R.R. Caldwell, E.V. Linder, The Limits of quintessence. Phys. Rev. Lett. 95, 141301 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.95.141301
V. C. Dubey, A. K. Mishra, U. K. Sharma. Diagnosing the \(\text{ R }\acute{e}\text{ nyi }\) Holographic Dark Energy model in a flat Universe. [arXiv:2003.07883 [gr-qc]]
A. Iqbal, A. Jawad, Tsallis, \(\text{ R }\acute{e}\text{ nyi }\) and Sharma-Mittal holographic dark energy models in DGP brane-world. Phys. Dark Univ. 26, 100349 (2019)
M. Younas, A. Jawad, S. Qummer, H. Moradpour, S. Rani, Cosmological implications of the generalized entropy based holographic dark energy models in dynamical Chern–Simons modified gravity. Adv. High Energy Phys. 2019, 1287932 (2019)
S. Rani, A. Jawad, K. Bamba, I.U. Malik, Cosmological consequences of new dark energy models in Einstein–Aether gravity. Symmetry 11(4), 509 (2019)
A. Jawad, K. Bamba, M. Younas, S. Qummer, S. Rani, Tsallis, \(\text{ R }\acute{e}\text{ nyi }\) and Sharma-Mittal holographic dark energy models in loop quantum cosmology. Symmetry 10(11), 635 (2018)
A. Jawad, S. Rani, M.H. Hussain, Cosmological implications and thermodynamics of some reconstructed modified gravity models. Phys. Dark Univ. 27, 100409 (2020)
C. Tsallis, The nonadditive entropy \(S_{q}\) and its applications in physics and elsewhere: some remarks. Entropy 13, 1765 (2011)
R. C. Nunes, E. M. Barboza Jr., E. M. C. Abreu, J. N. Neto, Probing the cosmological viability of non-gaussian statistics, JCAP08 (2016) 051; [arXiv:1509.05059 [gr-qc]]
M. Masi, A step beyond Tsallis and \(\text{ R }\acute{e}\text{ nyi }\) entropies. Phys. Lett. A 338, 217 (2005)
E. M. C. Abreu, J. A. Neto, E. M. Barboza, A. C. R. Mendes, B. B. Soares, On the equipartition theorem and black holes nongaussian entropies. arXiv:2002.02435 [gr-qc]
A.G. Cohen, D.B. Kaplan, A.E. Nelson, Effective field theory, black holes, and the cosmological constant. Phys. Rev. Lett. 82, 4971 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.82.4971
V. Sahni, A. Shafieloo et al., Two new diagnostics of dark energy. Phys. Rev. D 78, 103502 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevD.78.103502
L.M. Wang, P.J. Steinhardt, Cluster abundance constraints on quintessence models. Astrophys. J. 508, 483 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1086/306436
E.V. Linder, Cosmic growth history and expansion history. Phys. Rev. D 72, 043529 (2005)
M. Malekjani, A. Khodam-Mohammadi, Agegraphic dark energy model in non-flat universe: statefinder diagnostic and \(w-w^{\prime }\) analysis. Int. J. Mod. Phys. D 19, 1857 (2010)
A. Khodam-Mohammadi, M. Malekjani, Cosmic Behavior, Statefinder Diagnostic and \(w-w^{\prime }\) Analysis for Interacting NADE model in Non-flat Universe. Astrophys. Space Sci. 331, 265 (2011)
U.K. Sharma, A. Pradhan, Diagnosing Tsallis holographic dark energy models with statefinder and \(\omega \) - \(\omega ^{^{\prime }}\) pair. Mod. Phys. Lett. A 34(13), 1950101 (2019)
G. Varshney, U.K. Sharma, A. Pradhan, Statefinder diagnosis for interacting Tsallis holographic dark energy models with \(\omega - \omega ^{^{\prime }}\) pair. New Astron. 70, 36 (2019)
N. Zhang, Y.B. Wu, J.N. Chi, Z. Yu, D.F. Xu, Diagnosing Tsallis Holographic Dark Energy models with interactions. Mod. Phys. Lett. A 35(08), 2050044 (2019)
V.C. Dubey, U.K. Sharma, A. Beesham, Tsallis holographic model of dark energy: cosmic behavior, statefinder analysis and \(\omega _D-\omega _D^{\prime }\) pair in the nonflat universe. Int. J. Mod. Phys. D 28(15), 1950164 (2019)
S. Srivastava, V.C. Dubey, U.K. Sharma, Statefinder diagnosis for Tsallis agegraphic dark energy model with \(\omega _{D}-\omega _{D}^{^{\prime }}\) pair. Int. J. Mod. Phys. A 35, 2050027 (2020)
Acknowledgements
The authors are thankful for valuable suggestions given by Dr. Prateek Pandey, GLA University, Mathura, India, in this research work. The authors are also thankful to the anonymous referee for his/her constructive comments which helped to improve the quality of paper in the present form.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sharma, U.K., Dubey, V.C. Exploring the Sharma–Mittal HDE models with different diagnostic tools. Eur. Phys. J. Plus 135, 391 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/s13360-020-00411-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/s13360-020-00411-x