Abstract
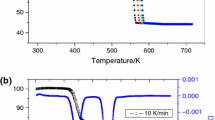
In the processes of preparation and application of nanomaterials, the thermal decomposition of nanoparticles is often involved. An improved general theory of thermal decomposition kinetics of nanoparticles, developed over the past 10 years, was presented in this paper where the relations between reaction kinetic parameters and particle size were derived. Experimentally, the thermal decomposition kinetics of nano-sized calcium oxalate (nano- CaC2O4 with different sizes was studied by means of Thermogravimetry Analysis (TGA) at different heating rates. The values of the apparent activation energy and the logarithm of pre-exponential factor were calculated using the equation of Iterative Kissinger-Akahira-Sunose (IKAS) and its deformations. The influence regularities of particle size on the apparent activation energy and the pre-exponential factor were summarized, which are consistent with the thermal decomposition kinetics theory of nanoparticles. Based on the theory, the method of obtaining the surface thermodynamic properties by the determination of kinetic parameters was presented. Theoretical and experimental results show that the particle size, through the effect on the surface thermodynamic properties, has notable effect on the thermal decomposition kinetics. With the particle size decreasing, the partial molar surface enthalpy and the partial molar surface entropy increases, leading to the decrease of the apparent activation energy and the pre-exponential factor, respectively. Furthermore, the apparent activation energy, the pre-exponential factor, the partial molar surface enthalpy and the partial molar surface entropy are linearly related to the reciprocal of particle diameter, respectively.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
H. Lv, D.D. Sang, H.D. Li, X.B. Du, D.M. Li, G.T. Zou, Nanoscale Res. Lett. 5, 620 (2010).
L. Nicole, C. Laberty, L. Rozes, C. Sanchez, Nanoscale 6, 6267 (2014).
I. Polyakov, E. Epifanovsky, B. Grigorenko, A.I. Krylov, A. Nemukhin, J. Chem. Theory Comp. 5, 1907 (2009).
V. Aishwarya. K.S. Suganthi. K.S. Rajan, J. Nanopart. Res. 15, 1774/1 (2013).
D.X. Li, H.Y. Shi, J. Deng, Y.Z. Xu, J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. 4, 363 (2003).
R. Liu, W.F. Yu, T.L. Zhang, L. Yang, Z.N. Zhou, Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 15, 7889 (2013).
N.N. Nassar, A. Hassan, P. Pereira-Almao, J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 110, 1327 (2012).
M. Fathollahi, B. Mohammadi, J. Mohammadi, Fuel 104, 95 (2013).
Z.Y. Li, K. Yu, J. Liu, Y.W. Tian, Y.C. Zhai, Curr. Nanosci. 8, 97 (2012).
L. Zhou, A. Rai, N. Piekiel, X.F. Ma, J. Phys. Chem. C 112, 16209 (2008).
X.D. Chen, W.A. Luo, Z.F. Liao, Nanosci. 11, 311 (2006).
J.H. Hin, D.H. Bae, Mater. Chem. Phys. 143, 1423 (2014).
Y.P. Lu, Q.F. Liu, Y.D. Zhang, New Chem. Mater. 37, 47 (2009).
Z.X. Cui, Y.Q. Xue, L.B. Xiao, T.T. Wang, J. Comput. Theor. Nanosci. 10, 569 (2013).
Y.Q. Xue, J.P. Du, P.D. Wang, Z.Z. Wang, Acta Phys. Chim. Sin. 21, 758 (2005).
Y.Q. Xue, H. Zhao, J.P. Du, Chinese J. Inorg. Chem. 22, 1952 (2006).
Y.Q. Xue, X.P. Wang, Z.X. Cui, Prog. React. Kinet. Mec. 36, 329 (2011).
Y.Q. Xue, X.Y. Xia, Z.X. Cui, J.Q. Shi, J. Comput. Theor. Nanosci. 11, 1 (2014).
International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry, Physical and chemical symbols, terminology and unit committee. Quantities, Units and Symbols in Physical Chemistry (Science and Technology Documentation Press, 1991) pp. 52, 56--57.
P. Atkins, J. Paula, Atkins’ Physical Chemistry (Higher Education Press, Beijing, 2006) p. 961.
G.C. Fan, L. Sun, Z.Y. Huang, J.Y. Jiang, Y.F. Li, Mater. Lett. 65, 2783 (2011).
Y.Q. Xue, X.C.Yang, Z.X. Cui, W.P. Lai, J. Phys. Chem. B 115, 109 (2011).
W. Abdel Wareth, X. Xu, J. Aerosp. Power 27, 1179 (2012).
W.N. Zhang, Y.H. Yuan, L.Q. Li, D.H. Chen, Acta Phys. Chim. Sin. 20, 33 (2004).
Z. Gao, M. Nakada, I. Amasaki, Thermochim. Acta 369, 137 (2001).
W.J. Tang, D.H. Chen, Acta Phys. Chim. Sin. 23, 605 (2007).
W.J. Tang, D.H. Chen, M. Wu, Zhongnan Minzu Daxue Xuebao, Ziran Kexue Ban 26, 16 (2007).
J.X. Liu, Q.Q. Zheng, X.Y. Gao, Acta Chim. Sinica 41, 169 (1983).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fu, Q., Cui, Z. & Xue, Y. Size dependence of the thermal decomposition kinetics of nano- CaC2O4: A theoretical and experimental study. Eur. Phys. J. Plus 130, 212 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/i2015-15212-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/i2015-15212-4