Abstract
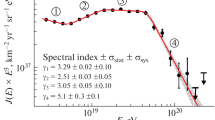
The energy spectrum of ultra-high energy cosmic rays above 1018 eV is measured using the hybrid events collected by the Pierre Auger Observatory between November 2005 and September 2010. The large exposure of the Observatory allows the measurement of the main features of the energy spectrum with high statistics. Full Monte Carlo simulations of the extensive air showers (based on the CORSIKA code) and of the hybrid detector response are adopted here as an independent cross check of the standard analysis (Phys. Lett. B 685, 239 (2010)). The dependence on mass composition and other systematic uncertainties are discussed in detail and, in the full Monte Carlo approach, a region of confidence for flux measurements is defined when all the uncertainties are taken into account. An update is also reported of the energy spectrum obtained by combining the hybrid spectrum and that measured using the surface detector array.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
HiRes Collaboration (R. Abbasi et al.), Phys. Rev. Lett. 100, 101101 (2008).
The Pierre Auger Collaboration, Phys. Lett. B 685, 239 (2010).
The Pierre Auger Collaboration, Phys. Rev. Lett. 101, 061101 (2008).
F. Salamida, for the Pierre Auger Collaboration, Proc. 32th ICRC 2011, Beijing, arXiv:1107.4809.
Telescope Array Collaboration, submitted to Phys. Rev. Lett., arXiv:1205.5067v1.
K. Greisen, Phys. Rev. Lett. 16, 748 (1966).
G.T. Zatsepin, V.A. Kuz'min, Pis'ma Zh. Eksp. Teor. Fiz. 4, 114 (1966).
J. Linsley, Proc. 8th ICRC, Jaipur 4, 77 (1963).
M.A. Lawrence, R.J.O. Reid, A.A. Watson, J. Phys. G 17, 733 (1991).
M. Nagano et al., J. Phys. G 18, 423 (1992).
D.J. Bird et al., Phys. Rev. Lett. 71, 3401 (1993).
A.M. Hillas, Cosmic Rays (Pergamon Press, Oxford, 1972).
T. Wibig, A.W. Wolfendale, J. Phys. G 31, 255 (2005).
A.M. Hillas, J. Phys. G 31, R95 (2005).
A.M. Hillas, Cosmic Rays: Recent Progress and some Current Questions, arXiv:0607109.
B. Peters, Nuovo Cimento 22, 800 (1961).
A.M. Hillas, Phys. Lett. A 24, 677 (1967).
G.R. Blumenthal, Phys. Rev. D 1, 1596 (1970).
V. Berezinsky, A.Z. Gazizov, S.I. Grigorieva, Phys. Rev. D 74, 043005 (2006).
V.S. Berezinsky, S.I. Grigorieva, B.I. Hnatyk, Astropart. Phys. 21, 617625 (2004).
The Pierre Auger Collaboration, Phys. Rev. Lett. 104, 091101 (2010).
P. Facal for the Pierre Auger Collaboration, Proc. 32th ICRC 2011, Beijing, arXiv:1107.4804.
HiRes Collaboration (R. Abbasi et al.), Phys. Rev. Lett. 104, 161101 (2010).
HiRes/MIA Collaboration (T. Abu-Zayyad et al.), Astrophys. J. 557, 686 (2001).
Yakutsk Collaboration (S. Knurenko, A. Sabourov), Proc. XVI ISVHECRI, (2010).
Yakutsk Collaboration (S. Knurenko, A. Sabourov), Nucl. Phys. B 212-213, 241 (2011).
C. Jui for the Telescope Array Collaboration, Proc. APS DPF Meeting, arXiv:1110.0133.
The Pierre Auger Collaboration, Astropart. Phys. 34, 368 (2011).
The Pierre Auger Collaboration, Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. A 523, 50 (2004).
The Pierre Auger Collaboration, Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. A 613, 29 (2010).
The Pierre Auger Collaboration, Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. A 620, 227 (2010).
B.R. Dawson, M. Giller, G. Wieczorek, Proc. 30th ICRC 2007, Merida.
F. Nerling, J. Bluemer, R. Engel, M. Risse, Astropart. Phys. 24, 421 (2006).
M. Unger, B.R. Dawson, R. Engel, F. Schssler, R. Ulrich, Nucl. Instrum. Methods A 588, 433 (2008).
T. Gaisser, A. Hillas, Proc. 15th ICRC, Plovdiv 8, 353 (1977).
H.M.J. Barbosa, F. Catalani, J.A. Chinellato, C. Dobrigkeit, Astropart. Phys. 22, 159 (2004).
F. Sanchèz, for the Pierre Auger Collaboration, Proceedings of 32th Int. Cosmic Ray Conf. (ICRC 2011) arXiv:1107.4807.
I.C. Maris, for the Pierre Auger Collaboration, Proceedings of 32th Int. Cosmic Ray Conf. (ICRC 2011) arXiv:1107.4809.
H.J. Mathes, for the Pierre Auger Collaboration, Proceedings of 32th Int. Cosmic Ray Conf. (ICRC 2011) arXiv:1107.4807.
J. Rautenberg [Pierre Auger Collaboration], Proceedings of 31th Int. Cosmic Ray Conf. (ICRC 2009) arXiv:0906.2358.
S.Y. BenZvi et al., Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. A 574, 171 (2007).
B. Fick et al., JINST) 1, 11003 (2006).
D. Heck, ``CORSIKA: A Monte Carlo Code to Simulate Extensive Air Showers'', Report FZKA, 6019 (1998).
S. Ostapchenko, Phys. Lett. B 636, 40 (2006).
N.N. Kalmykov, S. Ostapchenko, Sov. J. Nucl. Phys. 50, 315 (1989).
T. Pierog, K. Werner, Phys. Rev. Lett. 101, 171101 (2008).
A. Fassò, CERN-2005-10 (2005) INFN/TC_05/11, SLAC-R-773.
B. Keilhauer et al., Astropart. Phys. 22, 249 (2004).
J. Linsley, private communication by M. Hillas (1988).
S. Argirò et al., Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. A 580, 1485 (2007).
L. Prado et al., Nucl. Instrum. Methods A 545, 632 (2005).
S. Agostinelli et al., Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. A 506, 250 (2003) IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci. 53.
The Pierre Auger Collaboration, Astropart. Phys. 35, 266 (2011).
M. Settimo for the Pierre Auger Collaboration, Proceedings of 32th Int. Cosmic Ray Conf. (ICRC 2011) arXiv:1107.4805.
The Pierre Auger Collaboration, Astropart. Phys. 29, 243 (2008).
T. Bergmann et al., Astropart. Phys. 26, 420 (2007).
K. Werner, F.M. Liu, T. Pierog, Phys. Rev. C 74, 044902 (2006).
K. Kamata, J. Nishimura, Prog. Theoret. Phys. Suppl. 6, 93 (1958).
K. Greisen, Prog. Cosmic Rays Phys. III, 26 (1965).
C. Di Giulio, for the Pierre Auger Collaboration, Proceedings of 31st Int. Cosmic Ray Conf. (ICRC 2009) arXiv:0906.2189.
E.-J. Ahn, R. Engel, T.K. Gaisser, P. Lipari, T. Stanev, Phys. Rev. D 80, 094003 (2009).
M. Nagano, K. Kobayakawa, N. Sakaki, K. Ando, Astropart. Phys. 20, 293 (2003).
A. Castellina, for the Pierre Auger Collaboration, Proceedings of 31th Int. Cosmic Ray Conf. (ICRC 2009) arXiv:0906.2319.
R. Pesce, for the Pierre Auger Collaboration, Proceedings of 32th Int. Cosmic Ray Conf. (ICRC 2011) arXiv:1107.4809.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Consortia
Corresponding author
Additional information
This paper is based on the author’s PhD thesis, that was awarded the INFN Bruno Rossi Prize in 2011.
Lists of authors and their affiliations appear at the end of the paper.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Settimo, M., Pierre Auger Collaboration. Measurement of the cosmic ray energy spectrum using hybrid events of the Pierre Auger Observatory. Eur. Phys. J. Plus 127, 87 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/i2012-12087-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/i2012-12087-9