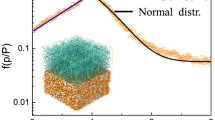
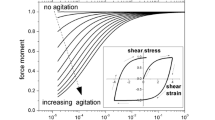
Abstract.
Two approaches exist to account for granular dynamics: The athermal one takes grains as elementary, the thermal one considers the total entropy that includes microscopic degrees of freedom such as phonons and electrons. Discrete element method (DEM), granular kinetic theory and athermal statistical mechanics (ASM) belong to the first, granular solid hydrodynamics (GSH) to the second one. A discussion of the conceptual differences between both is given here, leading, among others, to the following insights: 1) While DEM and granular kinetic theory are well justified to take grains as athermal, any entropic consideration is far less likely to succeed. 2) In addition to modeling grains as a gas of dissipative, rigid mass points, it is very helpful take grains as a thermal solid that has been sliced and diced. 3) General principles that appear invalid in granular media are repaired and restored once the true entropy is included. These abnormalities (such as invalidity of the fluctuation-dissipation theorem, granular temperatures failing to equilibrate, and grains at rest unable to explore the phase space) are consequences of the athermal approximation, not properties of granular media.
Graphical abstract

Similar content being viewed by others
References
P.A. Cundall, O.D.L. Strack, Geotechnique 29, 47 (1979)
H.J. Herrmann, S. Luding, Continuum Mech. Thermodyn. 10, 189 (1998)
J.N. Roux, AIP Conf. Proc. 1542, 46 (2013)
P.K. Haff, J. Fluid Mech. Digital Archive 134, 401 (1983)
J.T. Jenkins, S.B. Savage, J. Fluid Mech. 130, 187 (1983)
S.B. Savage, Adv. Appl. Mech. 24, 289 (1984)
C.S. Campbell, Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 22, 57 (1990)
I. Goldhirsch, Chaos 9, 659 (1999)
I. Goldhirsch, Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 35, 267 (2003)
S.F. Edwards, R.B.S. Oakeshott, Physica A 157, 1080 (1989)
R. Blumenfeld, J.F. Jordan, S.F. Edwards, Phys. Rev. Lett. 109, 238001 (2012)
P. Richard, M. Nicodemi, R. Delannay, P. Ribiere, D. Bideau, Nature 4, 121 (2005)
A. Baldassarri, A. Barrat, G. DAnna, V. Loreto, P. Mayor, A. Puglisi, J. Phys.: Condens. Matter 17, S2405 (2005)
Dapeng Bi, Silke Henkes, Karen E. Daniels, Bulbul Chakraborty, Annu. Review Condens. Matter Phys. 6, 63 (2015) or arXiv:1404.1854, 2014
Y.M. Jiang, M. Liu, Eur. Phys. J. E 22, 255 (2007)
Y.M. Jiang, M. Liu, Granular Matter 11, 139 (2009)
Y.M. Jiang, M. Liu, in Mechanics of Natural Solids, edited by D. Kolymbas, G. Viggiani (Springer, 2009) pp. 27--46
Y.M. Jiang, M. Liu, Acta Mech. 225, 2363 (2014)
G. Gudehus, Y.M. Jiang, M. Liu, Granular Matter 1304, 319 (2011)
Y.M. Jiang, M. Liu, Phys. Rev. Lett. 91, 144301 (2003)
Y.M. Jiang, M. Liu, Phys. Rev. Lett. 93, 148001 (2004)
Y.M. Jiang, M. Liu, Phys. Rev. Lett. 99, 105501 (2007)
D.O. Krimer, M. Pfitzner, K. Bruer, Y. Jiang, M. Liu, Phys. Rev. E 74, 061310 (2006)
K. Bruer, M. Pfitzner, D.O. Krimer, M. Mayer, Y. Jiang, M. Liu, Phys. Rev. E 74, 061311 (2006)
Y.M. Jiang, M. Liu, Phys. Rev. E 77, 021306 (2008)
Y.M. Jiang, M. Liu, AIP Conf. Proc. 1145, 1096 (2009)
M. Mayer, M. Liu, Phys. Rev. E 82, 042301 (2010)
D. Krimer, S. Mahle, M. Liu, Phys. Rev. E 86, 061312 (2012)
Y.M. Jiang, H.P. Zheng, Z. Peng, L.P. Fu, S.X. Song, Q.C. Sun, M. Mayer, M. Liu, Phys. Rev. E 85, 051304 (2012)
Q. Zhang, Y.C. Li, M.Y. Hou, Y.M. Jiang, M. Liu, Phys. Rev. E 85, 031306 (2012)
Y. Jiang, M. Liu, Granul. Matter 15, 237 (2013)
Yimin Jiang, Mario Liu, AIP Conf. Proc. 1542, 52 (2013)
Y.M. Jiang, M. Liu, Eur. Phys. J. E 38, 15 (2015)
D. Kolymbas, Introduction to Hypoplasticity (Balkema, Rotterdam, 2000)
W. Wu, D. Kolymbas, Constitutive Modelling of Granular Materials (Springer, Berlin, 2000)
D.L. Henann, K. Kamrin, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 110, 6730 (2012)
K. Kamrin, G. Koval, Phys. Rev. Lett. 108, 178301 (2012)
GDR MiDi, Eur. Phys. J. E 14, 341 (2004)
Yoël Forterre, Olivier Pouliquen, Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 40, 1 (2008)
Y. Forterre, O. Pouliquen, Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 40, 1 (2008)
D.P. Bi, J. Chang, B. Chakraborty, R.P. Behringer, Nature 480, 355 (2011)
Somayeh Farhadi, Robert P. Behringer, Phys. Rev. Lett. 112, 148301 (2014)
N. Kumar, Stefan Luding, Granular Matter 18, 58 (2016)
S. Luding, Nat. Phys. 12, 531 (2016)
Van Bau Nguyen, Thierry Darnige, Ary Bruand, Eric Clement, Phys. Rev. Lett. 107, 138303 (2011)
I.M. Khalatnikov, Introduction to the Theory of Superfluidity (Benjamin, New York, 1965)
L.D. Landau, E.M. Lifshitz, Fluid Mechanics (Butterworth-Heinemann, 1987)
P.G. de Gennes, J. Prost, The Physics of Liquid Crystals (Clarendon Press, Oxford, 1993)
R. Kubo, Rep. Prog. Phys. 29, 255 (1966)
T. Wichtmann, A. Niemunis, T. Triantafyllidis, Int. J. Numer. Anal. Meth. Geomech. 34, 440 (2010)
I.F. Collins, G.T. Houlsby, Proc. R. Soc. London, Ser. A 453, 1975 (1997)
H. Temmen, H. Pleiner, M. Liu, H.R. Brand, Phys. Rev. Lett. 84, 3228 (2000)
H. Temmen, H. Pleiner, M. Liu, H.R. Brand, Phys. Rev. Lett. 86, 745 (2001)
Oliver Müller, Mario Liu, Harald Pleiner, Helmut R. Brand, Phys. Rev. E 93, 023113 (2016)
Oliver Müller, Mario Liu, Harald Pleiner, Helmut R. Brand, Phys. Rev. E 93, 023114 (2016)
B.O. Hardin, F.E. Richart, J. Soil Mech. Found. Div. ASCE 89, SM1:33 (1963)
Stefan Luding, Nonlinearity 22, 101 (2009)
L. Bocquet, W. Losert, D. Schalk, T.C. Lubensky, J.P. Gollub, Phys. Rev. E 65, 011307 (2001)
C. Josserand, A.V. Tkachenko, D.M. Mueth, H.M. Jaeger, Phys. Rev. Lett. 85, 3632 (2000)
J.A. Dijksman, G.H. Wortel, L.T.H. van Dellen, O. Dauchot, M. van Hecke, Phys. Rev. Lett. 107, 108303 (2011)
S. Luding, M. Nicolas, O. Pouliquen, in Compaction of Soils, Granulates and Powders, edited by D. Kolymbas, W. Fellin (Balkema, Rotterdam, 2000)
Andrzej Niemunis, Carlos E. Grandas Tavera, Torsten Wichtmann, in Holistic Simulation of Geotechnical Installation Processes, edited by T. Triantafyllidis, Lect. Notes Appl. Computat. Mech. Vol. 80 (Springer, 2016)
Jiang, Liu, Acta Geotech. 11, 519 (2016)
I.S. Aranson, L.S. Tsimring, Phys. Rev. E 65, 061303 (2002)
I.S. Aranson, L.S. Tsimring, Rev. Mod. Phys. 78, 641 (2006)
Wei Wu, J. Engin. Math. 56, 23 (2006)
J. Tejchman, W. Wu, Granular Matter 12, 399 (2010)
R.A. Bagnold, Proc. R. Soc. London, Ser. A: Math. Phys. Sci. 225, 49 (1954)
P. Wroth, A. Schofield, Critical State Soil Mechanics (McGraw-Hill, London, 1968).
D.M. Wood, Soil Behaviour and Critical State Soil Mechanics (Cambridge University Press, 1990)
S. Roy, S. Luding, T. Weinhart, submitted to New J. Phys. (2016)
C.S. Campbell, J. Fluid Mech. 465, 261 (2002)
A. Singh, K. Saitoh, V. Magnanimo, S. Luding, New J. Phys. 17, 043028 (2015)
T.S. Komatsu, S. Inagaki, N. Nakagawa, S. Nasuno, Phys. Rev. Lett. 86, 1757 (2001)
J. Crassous, J.-F. Metayer, P. Richard, C. Laroche, J. Stat. Mech. 2008, P03009 (2008)
D. Fenistein, J.W. van de Meent, M. van Hecke, Nature 425, 695 (2003)
D. Fenistein, J.W. van de Meent, M. van Hecke, Phys. Rev. Lett. 96, 118001 (2006)
D. Fenistein, J.W. van de Meent, M. van Hecke, Phys. Rev. Lett. 96, 038001 (2006)
Ken Kamrin, Eran Bouchbinder, J. Mech. Phys. Solids 73, 269 (2014)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jiang, Y., Liu, M. Why granular media are thermal, and quite normal, after all. Eur. Phys. J. E 40, 10 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1140/epje/i2017-11497-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1140/epje/i2017-11497-4