Abstract.
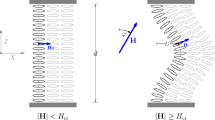
The field-induced realignment of a smectic-A phase is in principle a complicated process involving the director rotation via the interaction with the field and the layer rotation via the molecular interactions. Time-resolved X-ray scattering experiments have revealed major phenomena concerning the maintenance of the integrity of the smectic-A layer structure during the alignment process. In order to obtain a deeper insight into this process, we have carried out a dissipative particle dynamics study of the realignment kinetics of a nanodroplet of a smectic-A liquid crystal suspended in an isotropic fluid following a switch in the direction of an applied magnetic field. The strength of the mesogen-field interaction is small compared to the inter-molecular interactions. The reaction of the smectic configuration to the field switch was found to depend on the balance between the inter-molecular interactions stabilising the formation of the smectic layering and the interaction of the mesogens with the external field. It is found that the rotational behaviour of the smectic layers under the influence of an external magnetic field arises from a combination of stochastic translational displacements and rotational motions of the centres of mass of the mesogens in the nanodroplets. The simulations indicate that X-ray scattering and NMR experiments monitoring the orientational order are sensitive to different aspects of the realignment process.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
W. Bras, J.W. Emsley, Y.K. Levine, G.R. Luckhurst, J.M. Seddon, B.A Timimi, J. Chem. Phys. 121, 4397 (2004).
Y.K. Levine, A. Polimeno, Eur. Phys. J. E 23, 13 (2007).
J.W. Emsley, G.R. Luckhurst, P. Pedrielli, Chem. Phys. Lett. 320, 255 (2000).
C.C. Liew, M. Mikami, Chem. Phys. Lett. 368, 346 (2003).
I. Vattulainen, M. Karttunen, G. Besold, J.M. Polson, J. Chem. Phys. 116, 3967 (2002).
Y.K. Levine, A.E. Gomes, A.F. Martins, A. Polimeno, J. Chem. Phys. 122, 144902 (2005).
D. Frenkel, B. Smit, Understanding Molecular Simulation: From Algorithms to Applications (Academic Press, San Diego, 1996).
G. Ayton, G.A. Voth, Biophys. J. 83, 3357 (2002).
C. Zannoni, in The Molecular Physics of Liquid Crystals, edited by G.R. Luckhurst, G.W. Gray (Academic Press, new York, 1979).
A. Guinier, G. Fournet, Small Angle Scattering of X-rays (Wiley, New York, 1955).
B.K. Vainshtein, Diffraction of X-rays by Chain Molecules (Elsevier, Amsterdam, 1966).
M. van Gurp, H. van Langen, G. van Ginkel, Y.K. Levine, in Polarized Spectroscopy of Ordered Systems, edited by B. Samori, E.W. Thulstrup (Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht, 1988) p. 455.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Levine, Y.K., Bras, W. Field-induced realignment of a smectic nanodroplet in an external magnetic field: A numerical investigation. Eur. Phys. J. E 25, 5–16 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1140/epje/i2007-10255-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1140/epje/i2007-10255-7