Abstract
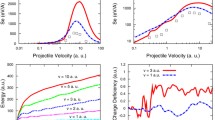
We study the interaction of highly charged ions (Ar\(^{q+}\), Kr\(^{q+}\), and Xe\(^{q+}\), charge \(q\gg 1\)) with metal surfaces for low to moderate ionic velocities. We calculate the neutralization energy and the deposited kinetic energy, both necessary for the nanostructure (hillocks or craters) creation. The cascade neutralization above the surface we analyze within the framework of the time-symmetrized two-state vector model and the micro-staircase model. The energy deposition inside the solid (nuclear stopping power) we consider using the charge dependent ion-target atom interaction potential. We define the critical ionic velocities as a measure of the interplay of the neutralization energy and the deposited kinetic energy in the process of the surface modification. These quantities enable us to distinguish the velocity regions characteristic for the particular nanostructure shapes.
Graphical abstract







Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability Statement
This manuscript has no associated data or the data will not be deposited. [Authors’ comment: All data needed to evaluate the conclusions in this work are present in the paper. Additional raw data are available from the corresponding authors upon reasonable request.]
References
R. Schuch, D. Schneider, D.A. Knapp, D. DeWitt, J. McDonald, M.H. Chen, M.W. Clark, R.E. Marrs, Evidence for internal dielectronic excitation of slow highly charged uranium ions. Phys. Rev. Lett. 70, 1073–1076 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.70.1073
G.A. Machicoane, T. Schenkel, T.R. Niedermayr, M.W. Newmann, A.V. Hamza, A.V. Barnes, J.W. McDonald, J.A. Tanis, D.H. Schneider, Internal dielectronic excitation in highly charged ions colliding with surfaces. Phys. Rev. A 65, 042903 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevA.65.042903
W. Wang, Z.Y. Song, B.Z. Zhang et al., K-x-ray emission of 1.5–20 kev/q Oq+ (q=3, 5, 6) and Nq+ (q=3, 5) ions impinging on nickel surface. Eur. Phys. J. Plus 137, 1015 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/s13360-022-03229-x
F. Aumayr, S. Facsko, A.S. El-Said, C. Trautmann, M. Schleberger, Single ion induced surface nanostructures: a comparison between slow highly charged and swift heavy ions. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 23, 393001 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1088/0953-8984/23/39/393001
R.A. Wilhelm, R. Heller, S. Facsko, Slow highly charged ion induced nanopit formation on the KCl(001) surface. Euro. Phys. Lett. 115, 43001 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1209/0295-5075/115/43001
J.M. Pomeroy, A.C. Perrella, H. Grube, J.D. Gillaspy, Gold nanostructures created by highly charged ions. Phys. Rev. B 75, 241409 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevB.75.241409
I. Stabrawa, D. Banaś, A. Kubala-Kukuś, K. Szary, J.J. Braziewicz, Czub, Ł Jabłoński, P. Jagodziński, D. Sobota, M. Pajek, K. Skrzypiec, E. Mendyk, M. Teodorczyk, Modification of gold and titanium nanolayers using slow highly charged Xe\(^{q+}\) ions. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res.B 408, 235–240 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nimb.2017.05.001
I. Stabrawa, D. Banaś, A. Kubala-Kukuś, Ł Jabłoński, P. Jagodziński, D. Sobota, K. Szary, M. Pajek, E. Mendyk, K. Skrzypiec, M. Borysirwicz, Formation of nanocraters on the surface of gold nanolayer by an impact of highly charged xenon ions. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 1412, 202024 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1088/1742-6596/1412/20/202024
I. Stabrawa, D. Banaś, A. Kubala-Kukuś, Ł. Jabłoński, P. Jagodziński, D. Sobota, K. Szary, M. Pajek, K. Skrzypiec, E. Mendyk, M. Borysirwicz, M.D. Majkić, N.N. Nedeljković, Energy deposition and formation of nanostructures in the interaction of highly charged xenon ions with gold nanolayers (2022 to be published)
K. Nordlund, F. Djurabekova, Multiscale modelling of irradiation in nanostructures. J. Comput. Electron. 13, 122–141 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/962s10825-013-0542-z
E.M. Bringa, K. Nordlund, J. Keinonen, Cratering-energy regimes: from linear collision cascades to heat spikes to macroscopic impacts. Phys. Rev. B 64, 235426 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevB.64.235426
M. Toulemonde, C. Dufour, E. Paumier, Transient thermal process after a high-energy heavy-ion irradiation of amorphous metals and semiconductors. Phys. Rev. B 46, 14362 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevB.46.14362
C. Dufour, V. Khomrenkov, Y.Y. Wang, Z.G. Wang, F. Aumayr, M. Toulemonde, An attempt to apply the inelastic thermal spike model to surface modifications of CaF2 induced by highly charged ions: comparison to swift heavy ions effect and extension to some others material. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 29, 095001 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1088/1361-648X/855aa547a
M.D. Majkić, N.N. Nedeljković, R.J. Dojčilović, Interaction of slow highly charged ions with a metal surface covered with a thin dielectric film. The role of the neutralization energy in the nanostructures formation. Mater. Res. Express 4, 095027 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1088/2053-1591/aa8bc7
M.D. Majkić, N.N. Nedeljković, M.A. Mirković, Neutralization energy contribution to the nanostructure creation by the impact of highly charged ions at arbitrary angle of incidence upon a metal surface covered with a thin dielectric film. Vacuum 165, 62–67 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vacuum.2019.04.002
M.D. Majkić, N.N. Nedeljković, Velocity effect on the nanostructure creation at a solid surface by the impact of slow highly charged ions. Vacuum (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vacuum.2021.110301
N.N. Nedeljković, Lj. D. Nedeljković, S.B. Vojvodić, M.A. Mirković, Selective Rydberg-level population of multiply charged ions at solid surfaces: A dynamic theory for low-angular-momentum ionic states. Phys. Rev. B. 49, 5621 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevB.49.5621
N.N. Nedeljković, M.D. Majkić, Intermediate stages of the Rydberg-level population of multiply charged ions escaping solid surfaces. Phys. Rev. A 76, 042902 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevA.76.042902
I.P. Prlina, N.N. Nedeljković, Time-symmetrized description of nonunitary time asymmetric quantum evolution. J. Phys. A Math. Theor. 49, 035301 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1088/1751-8113/49/3/03530
N.N. Nedeljković, M.D. Majkić, D.K. Božanić, R.J. Dojčilović, Dynamics of the Rydberg state population of slow highly charged ions impinging a solid surface at arbitrary collision geometry. J. Phys. B At. Mol. Opt. Phys. 49, 125201 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1088/0953-4075/49/12/125201
N.N. Nedeljković, M.D. Majkić, S.M.D. Galijaš, Grazing incidence collisions of multiply charged ions on solid surfaces. Influence of the formation of intermediate Rydberg states. J. Phys. B At. Mol. Opt. Phys. 45, 21502 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1088/0953-4075/45/21/215202
R.E. Lake, N.R. Arista, Kinetic-energy transfer in highly-charged-ion collisions with carbon. Phys. Rev. A 92, 052710 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevA.92.052710
R.A. Wilhelm, A.S. El-Said, F. Krokc, R. Heller, E. Gruber, F. Aumayr, S. Facsko, Highly charged ion induced nanostructures at surfaces by strong electronic excitations. Prog. Surf. 90, 377–395 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.progsurf.2015.06.001
A.V. Krasheninnikov, K. Nordlund, Ion and electron irradiation-induced effects in nanostructured materials. J. Appl. Phys. 107, 071301 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.3318261
R. Lake, J.M. Pomeroy, H. Grube, C.E. Sosolik, Charge state dependent energy deposition by ion impact. Phys. Rev. Lett. 107, 063202 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.107.063202
R.A. Wilhelm, W. Moller, Charge-state-dependent energy loss of slow ions. II. Statistical atom model. Phys. Rev. A 93, 052709 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevA.93.052709
M.D. Majkić, N.N. Nedeljković, M.A. Mirković, Effect of the Ionic Type on the Shape of the Nanostructures Created by an Impact of Slow Highly Charged Ions on Gold Surface. Publ. Astron. Obs. Belgrade 102, 121–124 (2022)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported in part by the Ministry of Education, Science and Technological Development of the Republic of Serbia (Project 171016, 171029).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors were involved in the preparation of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Nedeljković, N.N., Majkić, M.D. Critical velocities for the nanostructure creation on a metal surface by an impact of slow highly charged Ar\(^{q+}\), Kr\(^{q+}\), and Xe\(^{q+}\) ions. Eur. Phys. J. D 77, 3 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1140/epjd/s10053-022-00588-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1140/epjd/s10053-022-00588-z