Abstract
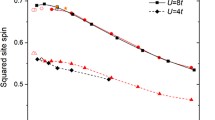
Finite temperature electronic and magnetic properties of small clusters are investigated in the framework of the Hubbard model by using exact diagonalization methods and by sampling the different cluster topologies exhaustively. Results are discussed for the specific heat C(T), magnetic susceptibility χ(T), local magnetic moments μi(T), average magnetic moments \(\overline\mu_N(T)\)and spin-correlation functions γij(T). Representative cluster sizes and band-fillings are considered showing antiferromagnetic-like (AF) and ferromagnetic-like (FM) behaviors. For half-band filling ν= N the susceptibility shows an AF high-temperature behavior of the form χ≈1/(T + TN) from which the cluster `Néel’ temperature TN is derived. In contrast, for ν= N + 1 a FM high-temperature behavior of the form χ≈1/(T - TC) is found, where TC can be interpreted as the cluster `Curie’ temperature. In both cases one also observes peaks in C(T), either at T≃TN or T≃TC, which reflect the development of spin fluctuationsand the breakdown of the low-temperature short-range magnetic order. The dependence of TN and TC on cluster size N and interaction strength U/t is analyzed in terms of effective Heisenberg spin interactions. Finally, the effects of temperature-induced structural fluctuations are discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
See, for instance, J. Bansmann et al., Surf. Sci. Rep. 56, 189 (2005)
I.M.L. Billas, A. Châtelain, W.A. de Heer, Science 265, 1682 (1994)
S.E. Apsel, J.W. Emert, J. Deng, L.A. Bloomfield, Phys. Rev. Lett. 76, 1441 (1996)
M.B. Knickelbein, Phys. Rev. Lett. 86, 5255 (2001)
G. Nicolas, J. Dorantes-Dávila, G.M. Pastor, Phys. Rev. B 74, 014415 (2006) and references therein
G.M. Pastor, J. Dorantes-Dávila, K.H. Bennemann, Phys. Rev. B 70, 064420 (2004)
R. Garibay-Alonso, J. Dorantes-Dávila, G.M. Pastor, Eur. Phys. J. D 52, 167 (2009)
G.M. Pastor, J. Dorantes-Dávila, K.H. Bennemann, Phys. Rev. B 40, 7642 (1989)
L.M. Falicov, R.H. Victora, Phys. Rev. B 30, 1695 (1984); Y. Ishii, S. Sugano, J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 53, 3895 (1984); J. Callaway, D.P. Chen, R. Tang, Z. Phys D 3, 91 (1986); Phys. Rev. B 35, 3705 (1987)
G.M. Pastor, R. Hirsch, B. Mühlschlegel, Phys. Rev. Lett. 72, 3879 (1994); Phys. Rev. B 53, 10382 (1996)
F. López-Urías, G.M. Pastor, Phys. Rev. B 59, 5223 (1999)
F. López-Urías, G.M. Pastor, J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 294, e27 (2005)
J. Hubbard, Proc. R. Soc. London A 276, 238 (1963); J. Hubbard, Proc. R. Soc. London A 281, 401 (1964); J. Kanamori, Progr. Theor. Phys. 30, 275 (1963); M.C. Gutzwiller, Phys. Rev. Lett. 10, 159 (1963)
A comprehensive account of our results and a detailed analysis will be published elsewhere
Notice that in a finite system the position of the peaks in the specific heat and magnetic susceptibility need not to coincide
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
López-Urías, F., Pastor, G. Exact diagonalization of Hubbard clusters at finite temperatures. Eur. Phys. J. D 52, 159–162 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1140/epjd/e2009-00009-9
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1140/epjd/e2009-00009-9