Abstract.
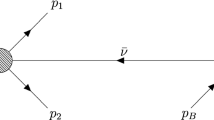
Feynman’s path amplitude formulation of quantum mechanics is used to analyse the production of charged leptons from charged current weak interaction processes. For neutrino induced reactions the interference effects predicted are usually called “neutrino oscillations”. Similar effects in the detection of muons from pion decay are here termed “muon oscillations”. Processes considered include pion decay (at rest and in flight), and muon decay and nuclear \(\beta\)-decay at rest. In all cases studied, a neutrino oscillation phase different from the conventionally used one is found.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
B. Pontecorvo, JETP 33, 599 (1957), [Sov. Phys. JETP 6, 429 (1958)]; JETP 34, 247 (1958) [Sov. Phys. JETP 7, 172 (1958)]
S.M. Bilenky, B. Pontecorvo, Phys. Rep. 41, 225 (1978)
S.M. Bilenky, S.T. Petcov, Rev. Mod. Phys. 59, 671 (1987)
Y. Grossman, H.J. Lipkin, Phys. Rev. D 55, 2760 (1997)
S. De Leo, G. Ducati, P. Rotelli, Mod. Phys. Lett. A 15, 2057 (2000)
R.G. Winter, Lettere al Nuovo Cimento 30, 101 (1981)
R.P. Feynman, Rev. Mod. Phys. 20, 367 (1948)
P.A.M. Dirac, Physikalische Zeitschrift der Sowjetunion Band 3, Heft 1 (1933), reprinted in Selected Papers on Quantum Electrodynamics, edited by J. Schwinger (Dover, New York 1958), p. 312; see also [11], Chapter V, Sect. 32
R.P. Feynman, A.R. Hibbs, Quantum mechanics and path integrals (McGraw Hill, New York 1965); C. Grosche, F. Steiner, Handbook of path integrals, Springer Tracts in Modern Physics (Springer-Verlag, Berlin 1998)
W. Heisenberg, The physical principals of the quantum theory, English translation by C. Eckart, F.C. Hoyt (University of Chicago Press, Chicago 1930), Chapter IV, Sect. 2
P.A.M. Dirac, The principles of quantum mechanics, Fourth edition (O.U.P., London 1958), p. 9
R.P. Feynman, Phys. Rev. 76, 749 (1949)
S. Mohanty, Covariant Treatment of Flavour Oscillations, hep-ph/9702424
C. Athanassopoulos et al. , Phys. Rev. C 58, 2489 (1998); A. Aguilar et al. , hep-ex/0104049
B. Zeitnitz et al. , Progress in Particle and Nuclear Physics, 40, 169 (1998); J. Kleinfeller, Nucl. Phys. B (Proc. Suppl.) 87, 281 (2000)
Z. Maki, M. Nakagawa, S. Sakata, Prog. Theor. Phys. 28, 870 (1962)
L.I. Schiff, Quantum mechanics, 2nd edition (McGraw Hill, New York 1955), Chapter VIII
J.M.Lévy-Leblond, F. Balibar, Quantics, rudiments of quantum physics (North-Holland, Amsterdam 1990), Chapter V
M. Zralek, Acta. Phys. Polon. B 29, 3925 (1998)
C. Giunti, C.W. Kim, Found. Phys. Lett. 14, 213 (2001)
B. Kayser, Neutrino Physics as Explored by Flavour Change, in Phys. Rev. D 66, 010001 (2002) (Review of Particle Properties)
R.E. Shrock, Phys. Lett. B 96, 159 (1980)
R.E. Shrock, Phys. Rev. D 24, 1232 (1981); D 24, 1275 (1981)
J.H. Field, Lepton Flavour Eigenstates do not Exist if Neutrinos are Massive: “Neutrino Oscillations” Reconsidered, hep-ph/0301231
J.H. Field, Eur. Phys. J. C 30, 305 (2003)
C. Giunti, C.W. Kim, U.W. Lee, Phys. Rev. D 45, 2414 (1992)
V. Gribov, B. Pontecorvo, Phys. Lett. B 28, 493 (1969)
S.M. Bilenky, B. Pontecorvo, Phys. Lett. B 61, 248 (1976)
H. Fritsch, P. Minkowski, Phys. Lett. B 62, 72 (1976)
S.M. Bilenky, B. Pontecorvo, Lettere al Nuovo Cimento 17, 569 (1976)
S.M. Bilenky, B. Pontecorvo, Physics Reports 41, 225 (1978)
See [10], Chapter II
B. Kayser, Phys. Rev. D 24, 110 (1981)
Y.N. Srivastava, A. Widom, E. Sassaroli, Charged Lepton Oscillations, hep-ph/9509261
Y.N. Srivastava, A. Widom, E. Sassaroli, Eur. Phys. J C 2, 769 (1998)
A.D. Dolgov et al. , Nucl. Phys. B 502, 3 (1997)
Y.N. Srivastava, A. Widom, Of Course Muons can Oscillate, hep-ph/9707268
B. Kayser, L. Stodolsky, Phys. Lett. B 359, 343 (1995)
Y.N. Srivastava, A. Widom, E. Sassaroli, Phys. Lett. B 344, 436 (1995)
Review of Particle Properties, D.E. Groom et al. , Eur. Phys. J C 15, 1 (2000)
S. DeLeo, P. Rotelli, JETP Lett. 76, 56 (2002)
T. Kajita, Y. Totsuka, Rev. Mod. Phys. 73, 85 (2001)
J.N. Bahcall, M.H. Pinsonneault, S. Basu, Astrophys. J 555, 990 (2001)
H.G. Berry, J.L. Subtil, Phys. Rev. Lett. 27, 1103 (1971)
C. Blondel, C. Delsart, F. Dulieu, Phys. Rev. Lett. 77, 3755 (1996)
C. Bracher et al. , Am. J. Phys. 66, 38 (1998)
C. Blondel, S. Berge, C. Delsart, Am. J. Phys. 69, 810 (2001)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 3 February 2004, Revised: 20 July 2004, Published online: 14 September 2004
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Field, J.H. Spatially dependent quantum interference effects in the detection probability of charged leptons produced in neutrino interactions or weak decay processes. Eur. Phys. J. C 37, 359–377 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1140/epjc/s2004-01988-8
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1140/epjc/s2004-01988-8