Abstract
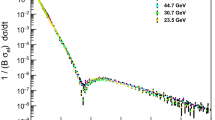
The soft physics, pT<2 GeV/c, observables at both RHIC and the SPS have now been mapped out in quite specific detail. From these results there is mounting evidence that this regime is primarily driven by the multiplicity per unit rapidity, dNch/dη. This suggests that the entropy of the system alone is the underlying driving force for many of the global observables measured in heavy-ion collisions. That this is the case and there is an apparent independence on collision energy is surprising. I present the evidence for this multiplicity scaling and use it to make some extremely naive predictions for the soft sector results at the LHC.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
R. Hagedron, Nuovo Cim. Suppl. 3, 147 (1965)
H. Satz, Nucl. Phys. A 715, 3c (2003)
L.D. Landau, Izv. Akad. Nauk SSSR Ser. Fiz 17, 51 (1953)
E. Fermi, Prog. Theor. Phys. 5, 570 (1950)
P. Seyboth, Proceedings of the 17th Winter Workshop (2001). http://na49info.cern.ch/cgi-bin/wwwd-util/NA49/NOTE?265.
M. Gazdicki, D. Rörich, Z. Phys. C 65, 215 (1995)
M.A. Lisa, S. Pratt, R. Soltz, U. Wiedemann, Ann. Rev. Nucl. Part. Sci. 55, 311 (2005)
M. Lisa, these proceedings.
M. Lisa, nucl-ex/0512008 (2005)
D. Adamova, et al., Phys. Rev. Lett. 90, 022301 (2003)
PHOBOS Collaboration, G. Roland et al., nucl-ex/0510042 (2005)
PHOBOS Collaboration, S. Manly et al., nucl-ex/0510031 (2005)
A. Tounsi, A. Mischke, K. Redlich, Nucl. Phys. A 715, 565 (2003)
H. Caines, nucl-ex/0608008 (2006)
WA97 Collaboration, E. Andersen et al., Phys. Lett. 449, 401 (1999)
WA97/NA57 Collaboration, F. Antinori et al., Nucl. Phys. A 698, 118 (2002)
STAR Collaboration, O. Barannik et al., J. Phys. G 31, S93 (2005)
B.B. Back et al., Nucl. Phys. A 757, 28 (2005)
STAR Collaboration, J. Adams et al., Phys. Rev. Lett. 92, 112301 (2004)
PHENIX Collaboration, S. Adler et al., Phys. Rev. C 69, 034909 (2004)
STAR Collaboration, J. Adams et al., nucl-ex/0604019 (2006)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Caines, H. Is soft physics entropy driven?. Eur. Phys. J. C 49, 297–301 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1140/epjc/s10052-006-0109-2
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1140/epjc/s10052-006-0109-2