Abstract
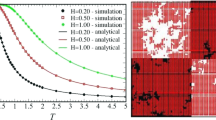
We study how the opinions of a group of individuals determine their spatial distribution and connectivity, through an agent-based model. The interaction between agents is described by a Hamiltonian in which agents are allowed to move freely without an underlying lattice (the average network topology connecting them is determined from the parameters). This kind of model was derived using maximum entropy statistical inference under fixed expectation values of certain probabilities that (we propose) are relevant to social organization. Control parameters emerge as Lagrange multipliers of the maximum entropy problem, and they can be associated with the level of consequence between the personal beliefs and external opinions, and the tendency to socialize with peers of similar or opposing views. These parameters define a phase diagram for the social system, which we studied using Monte Carlo Metropolis simulations. Our model presents both first and second-order phase transitions, depending on the ratio between the internal consequence and the interaction with others. We have found a critical value for the level of internal consequence, below which the personal beliefs of the agents seem to be irrelevant.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
P. Ball, Physica A 314, 1 (2002)
C. Castellano, S. Fortunato, V. Loreto, Rev. Mod. Phys. 81, 591 (2009)
K. Sznajd-Weron, J. Sznajd, Int. J. Mod. Phys. C 11, 1157 (2000)
L. Sabatelli, P. Richmond, Physica A 334, 274 (2004)
R. Wang, L.P. Chi, X. Cai, Chin. Phys. Lett. 25, 1502 (2008)
R. Axelrod, J. Conflict Resol. 41, 203 (1997)
C. Castellano, M. Marsili, A. Vespignani, Phys. Rev. Lett. 85, 3536 (2000)
K. Kacperski, J.A. Holyst, Physica A 269, 511 (1999)
Z. Liu, J. Luo, C. Shao, Phys. Rev. E 64, 046134 (2001)
C. Schulze, Int. J. Mod. Phys. C 16, 351 (2005)
H.-B. Hu, X.-F. Wang, J. Phys. A 42, 225005 (2009)
P. Fronczak, A. Fronczak, J.A. Holyst, Int. J. Mod. Phys. C 17, 1227 (2006)
M. Ausloos, F. Petroni, Europhys. Lett. 77, 38002 (2007)
M. Ausloos, F. Petroni, Physica A 388, 4438 (2009)
K. Klemm, V.M. Eguíluz, R. Toral, M.S. Miguel, Phys. Rev. E 67, 026120 (2003)
K. Klemm, V.M. Eguíluz, R. Toral, M.S. Miguel, Phys. Rev. E 67, 045101 (2003)
P. Fronczak, A. Fronczak, J.A. Holyst, Eur. Phys. J. B 59, 133 (2007)
C. Biely, R. Hanel, S. Thurner, Eur. Phys. J. B 67, 285 (2008)
B. Kozma, A. Barrat, Phys. Rev. E 77, 016102 (2008)
I.J. Benczik, S.Z. Benczik, B. Schmittmann, R.K.P. Zia, Phys. Rev. E 79, 046104 (2009)
E.T. Jaynes, Phys. Rev. 106, 620 (1957)
F.Y. Wu, Rev. Mod. Phys. 54, 235 (1982)
E.T. Jaynes, Probability Theory: The Logic of Science (Cambridge University Press, 2003)
D.P. Landau, K. Binder, A guide to Monte Carlo simulations in statistical physics (Cambridge University Press, 2005)
D.H.E. Gross, E.V. Votyakov, Eur. Phys. J. B 15, 115 (2000)
M.A. Carignano, Chem. Phys. Lett. 361, 291 (2002)
P. Chomaz, F. Gulminelli, Nucl. Phys. A 647, 153 (1999)
P. Chomaz, F. Gulminelli, Eur. Phys. J. A 30, 317 (2006)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Davis, S., Navarrete, Y. & Gutiérrez, G. A maximum entropy model for opinions in social groups. Eur. Phys. J. B 87, 78 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1140/epjb/e2014-40918-6
Received:
Revised:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1140/epjb/e2014-40918-6