Abstract
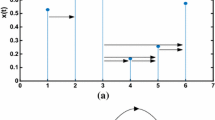
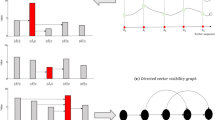
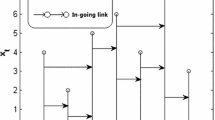
We propose a method to measure real-valued time series irreversibility which combines two different tools: the horizontal visibility algorithm and the Kullback-Leibler divergence. This method maps a time series to a directed network according to a geometric criterion. The degree of irreversibility of the series is then estimated by the Kullback-Leibler divergence (i.e. the distinguishability) between the inand outdegree distributions of the associated graph. The method is computationally efficient and does not require any ad hoc symbolization process. We find that the method correctly distinguishes between reversible and irreversible stationary time series, including analytical and numerical studies of its performance for: (i) reversible stochastic processes (uncorrelated and Gaussian linearly correlated), (ii) irreversible stochastic processes (a discrete flashing ratchet in an asymmetric potential), (iii) reversible (conservative) and irreversible (dissipative) chaotic maps, and (iv) dissipative chaotic maps in the presence of noise. Two alternative graph functionals, the degree and the degree-degree distributions, can be used as the Kullback-Leibler divergence argument. The former is simpler and more intuitive and can be used as a benchmark, but in the case of an irreversible process with null net current, the degree-degree distribution has to be considered to identify the irreversible nature of the series.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
G. Weiss, J. Appl. Prob. 12, 831 (1975)
R. Kawai, J.M.R. Parrondo, C. Van den Broeck, Phys. Rev. Lett. 98, 080602 (2007)
J.M.R. Parrondo, C. Van den Broeck, R. Kawai, New. J. Phys. 11, 073008 (2009)
E. Roldan, J.M.R. Parrondo, Phys. Rev. Lett. 105, 15 (2010)
E. Roldan, J.M.R. Parrondo, Entropy production and Kullback-Leibler divergence between stationary trajectories of discrete systems, http://arxiv.org/abs/1201.5613
A.C. Yang, S.S. Hseu, H.W. Yien, A.L. Goldberger, C.-K. Peng, Phys. Rev. Lett. 90, 10 (2003)
M. Costa, A.L. Goldberger, C.-K. Peng, Phys. Rev. Lett. 95, 198102 (2005)
M.D. Costa, C.K. Peng, A.L. Goldberger, Cardiovasc. Eng. 8, (2008)
C.S. Daw, C.E.A. Finney, M.B. Kennel, Phys. Rev. E 62, 2 (2000)
M.B. Kennel, Phys. Rev. E 69, 056208 (2004)
C. Diks, J.C. van Houwelingen, F. Takens, J. DeGoede, Phys. Lett. A 201, 221 (1995)
P. Gaspard, J. Stat. Phys. 117, (2004)
C. Cammarota, E. Rogora, Chaos Solitons Fractals 32, 1649 (2007)
D. Andrieux, P. Gaspard, S. Ciliberto, N. Garnier, S. Joubaud, A. Petrosyan, Phys. Rev. Lett. 98, 150601 (2007)
Q. Wang, S.R. Kulkarni, S. Verdú, IEEE Transactions on Information Theory 51, 9 (2005)
T.M. Cover, J.A. Thomas, Elements of Information Theory (Wiley, New Jersey, 2006)
B. Luque, L. Lacasa, J. Luque, F. Ballesteros, Phys. Rev. E 80, 046103 (2009)
L. Lacasa, B. Luque, F. Ballesteros, J. Luque, J.C. Nuno, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 105, 4973 (2008)
L. Lacasa, B. Luque, J. Luque, J.C. Nuno, Europhys. Lett. 86, 30001 (2009)
L. Lacasa, R. Toral, Phys. Rev. E 82, 036120 (2010)
B. Luque, L. Lacasa, F.J. Ballesteros, A. Robledo, PLoS One 6, 9 (2011)
J.B. Elsner, T.H. Jagger, E.A. Fogarty, Geophys. Res. Lett. 36, 16 (2009)
C. Liu, W.-X. Zhou, W.-K. Yuan, Physica A 389, 13 (2010)
Y. Yang, J. Wang, H. Yang, J. Mang, Physica A 388, 4431 (2009)
G. Gutin, T. Mansour, S. Severini, Physica A 390, 12 (2011)
M.E.J. Newmann, SIAM Rev. 45, 167 (2003)
P. Gaspard, Physica A 369, 1 (2006)
A. Porporato, J.R. Rigby, E. Daly, Phys. Rev. Lett. 98, 9 (2007)
J.C. Sprott, G. Rowlands, Int. J. Bifurc. Chaos 11, 1865 (2001)
E.J. Kostelich, T. Schreiber, Phys. Rev. E 48, 1752 (1993)
M.J. Hinich, P. Rothman, Macroecon. Dyn. 2, 1 (1998)
Y.T. Chen, R.Y. Chou, C.M. Kuan, J. Econom. 95, 199 (2000)
H.A. Makse, S. Havlin, M. Schwartz, H.E. Stanley, Phys. Rev. E 53, 5 (1996)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lacasa, L., Nuñez, A., Roldán, É. et al. Time series irreversibility: a visibility graph approach. Eur. Phys. J. B 85, 217 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1140/epjb/e2012-20809-8
Received:
Revised:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1140/epjb/e2012-20809-8