Abstract
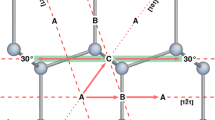
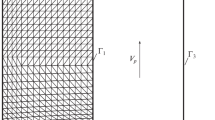
The dislocation width for shuffle 60° dislocation in semiconductors Si and Ge have been calculated by the improved P-N theory in which the discrete effect has been taken into account. Peierls barrier and stress have been evaluated with considering the contribution of strain energy. The discrete effect make dislocation width wider, and Peierls barrier and stress lower. The dislocation width of 60° dislocation in Si and Ge is respectively about 3.84 Å and 4.00 Å (∼1b, b is the Burgers vector). In the case of 60° dislocation, after considering the contribution of strain energy, Peierls barrier and stress are increased. The Peierls barrier for 60° dislocation in Si and Ge is respectively about 15 meV/Å and 12–14 meV/Å, Peierls stress is about 3.8 meV/Å3 (0.6 GPa) and 2.7–3.3 meV/Å3 (0.4–0.5 GPa). The Peierls stress for Si agrees well with the numerical results and the critical stress at 0 K extrapolated from experimental data. Ge behaves similarly to Si.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
J.P. Hirth, J. Lothe, Theory of Dislocations, 2nd edn. (Wiley, New York, 1982)
P.B. Hirsch, Sci. Technol. 1, 666 (1985)
M.S. Duesbery, G.Y. Richardson, Crit, Rev. Solid State Mater. Sci. 17, 1 (1991)
H. Alexander, H. Teichler, in Materials Science and Technology, edited by R.W. Cahn, P. Hassen, E.J. Kramer (VCH Weiheim, Cambridge, 1993), Vol. 4, p. 249
Y.B. Bolkhovityanov et al., Semiconductors 37, 493 (2003)
J. Rabier, J.L. Demenet, Script. Mater. 45, 1259 (2001)
C.X. Li, Q.Y. Meng, G. Li, L.J. Yang, Superlattices Microstruct. 40, 113 (2006)
Y.H. Jing, Q.Y. Meng, W. Zhao, Physica B 404, 2138 (2009)
L. Pizzagalli, J. Godet, S. Brochard, Phys. Rev. Lett. 103, 065505 (2009)
B. Joos, Q. Ren, M.S. Duesbery, Phys. Rev. B 50, 5890 (1994)
R.E. Peierls, Proc. Phys. Soc. 52, 23 (1940)
B. Joos, M.S. Duesbery, Phys. Rev. Lett. 78, 266 (1997)
V.V. Bulatov, E. Kaxiras, Phys. Rev. Lett. 78, 4221 (1997)
S.F. Wang, Phys. Rev. B 65, 094111 (2002)
S.F. Wang, Chin. Phys. 14, 2575 (2005)
S.F. Wang, J. Phys. A Math. Theor. 42, 025208 (2009)
S.F. Wang, R.P. Liu, X.Z. Wu, J. Phys.: Condens. Matter 20, 485207 (2008)
X.Z. Wu, S.F. Wang, Front. Mater. Sci. China 3, 205 (2009)
S.F. Wang, H.L. Zhang. X.Z. Wu, R.P. Liu, J. Phys.: Condens. Matter 22, 055801 (2010)
J.W. Christian, V. Vitek, Rep. Prog. Phys. 33, 307 (1970)
K. Kang, W. Cai, Philos. Mag. 87, 2169 (2007)
S.F. Wang, Phys. Lett. A 313, 408 (2003)
S.F. Wang, Chin. Phys. 15, 1301 (2006)
J. Castaing, P. Veyssiere, L.P. Kubin, J. Rabier, Philos. Mag. A 44, 1407 (1981)
J. Rabier, Phys. Stat. Sol. (A) 204, 2248 (2007)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, H.L. Calculation of shuffle 60° dislocation width and Peierls barrier and stress for semiconductors silicon and germanium. Eur. Phys. J. B 81, 179–183 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1140/epjb/e2011-10932-5
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1140/epjb/e2011-10932-5