Abstract
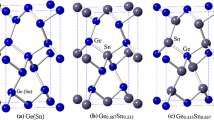
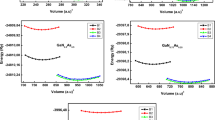
Crystalline structures of elemental solids can be rationalized in terms of the competition between ions and electrons: ions try to increase local symmetry and thus packing fraction, while electrons want to reduce it. If the latter win, layered structures, network, or molecular solids form and the opening of an electronic gap is favoured. In this work, it will be discussed how this competition can affect the thermodynamic behavior of phase change materials (PCMs), in particular that of Ge-Sb-Te alloys: their technologically relevant metastable crystalline structures can be derived from (hypothetical, metallic) simple cubic crystals near half-filling via a symmetry breaking, such as a Peierls distortion in Sb-rich PCMs or ordering of chemical species onto sublattices on the GeTe-Sb2Te3 pseudo-binary line, leading to the formation of σ-bonded networks. Local symmetry and density become even smaller and the gap opens up even more in the glass, for example, when the group IV element germanium undergoes a coordination change from (distorted) octahedral in the crystal to tetrahedral. This coordination change leaves the σ-bonded network intact, as will be demonstrated by analysis of first-principle simulations. Based on local symmetry arguments, simple rules for the number of electron holes and/or vacancies in metastable crystalline structure of PCMs can be derived and the response of Ge-Sb-Te alloys to pressure be predicted: crystalline alloys will amorphise under pressure when there are more Te than Ge atoms and increase their conductivity. Conversely, disordered alloys will crystallize if the number of Ge atoms exceeds that of Te. The possibility to switch the latter PCMs reversibly with pressure will be discussed. Lastly, unusual relaxation dynamics of PCMs are identified from first-principle calculations: when a solid is streched to its amorphisation point, the ionic energy (which is minimized in the crystal) increases with time as opposed to the dominating electronic energy. At the same time, coordination statistics become increasingly distinct with age from those in the crystal, i.e., the glass initially relaxes away from the crystalline phase.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
S.R. Ovshinsky, Phys. Rev. Lett. 21, 1450 (1968)
N. Yamada, E. Ohno, K. Nishiushi, N. Akahira, M. Takao, J. Appl. Phys. 69, 2849 (1991)
A.L. Lacaita, Solid-State Electron. 50, 24 (2006)
M.H.R. Lankhorst, B.W.S.M.M. Ketelaars, R.A.M. Wolters, Nature Mater. 4, 347 (2005)
A.V. Kolobov, P. Fons, A.I. Frenkel, A.L. Ankudinov, J. Tominaga, T. Uruga, Nature Materials 3, 703 (2004)
W. Wełnic, A. Pamungkas, R. Detemple, C. Steimer, S. Blügel, M. Wuttig, Nature Materials 5, 56 (2006)
S. Caravati, M. Bernasconi, T.D. Kühne, M. Krack, M. Parrinello, Appl. Phys. Lett. 91, 171906 (2007)
W. Welnic, M. Wuttig, Mater. Today 11, 20 (2008)
N. Yamada, MRS Bull. 21, 48 (1996)
J. Stuke, G. Zimmerer, Phys. Status Solidi B 49, 513 (1972)
N. Oshima, J. Appl. Phys. 79, 8357 (1996)
Y. Kageyama, H. Iwasaki, M. Harigaya, Y. Ide, Jpn J. Appl. Phys. 35, 500 (1996)
W.K. Njoroge, M. Wuttig, J. Appl. Phys. 90, 3816 (2001)
C.S. Barrett, P. Cucka, K. Haefner, Acta Crystallographica 16, 451 (1963)
N. Yamada, T. Matsunaga, J. Appl. Phys. 88, 7020 (2000)
D.P. Gosain, T. Shimizu, M. Ohmura, M. Suzuki, T. Bando, S. Okano, J. Mat. Sci. 26, 3271 (1991)
M.J. Kang, S.Y. Choi, D. Wamwangi, K. Wang, C. Steimer, M. Wuttig, J. Appl. Phys. 98, 014904 (2005)
S.O. Ryu, S.M. Yoon, N.Y. Lee, IEEE Electron Device Lett. 27, 445 (2006)
K. Shportko, S. Kremers, M. Woda et al., Nature Mater. 7, 653 (2008)
D. Lencer, M. Salinga, B. Grabowski et al., Nature Mater. 7, 972 (2008)
M. Wuttig, Phys. Status Solidi B 246, 1820 (2009)
G. Lucovsky, R.M. White, Phys. Rev. B 8, 660 (1973)
B. Stegemann, C. Ritter, B. Kaiser, K. Rademann, J. Phys. Chem. B 108, 14292 (2004)
D. Dietzel, C. Ritter, T. Monninghoff et al., Phys. Rev. Lett. 101, 125505 (2008)
M.H. Muser, Europhys. Lett. 66, 97 (2004)
R.E. Peierls, Quantum Theory of Solids (Oxford University Press, Oxford, 1955)
M.P. Marder, Condensed Matter Physics (John Wiley & Sons, New York, 2000)
P. Söderling, O. Eriksson, B. Johansson, J.M. Wills, A.M. Boring, Nature 374, 524 (1995)
D. Shakhvorostov, R.A. Nistor, L. Krusin-Elbaum, G.J. Martyna, D.M. Newns, B.G. Elmegreen, X. Liu, Z.E. Hughes, S. Paul, C. Cabral Jr, S. Raoux, D.B. Shrekenhamer, D.N. Basov, Y. Song, M.H. Müser, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 106, 10907 (2009)
J.-P. Gaspard, A. Pellegatti, F. Marinelli, C. Bichara, Phil. Mag. B 77, 727 (1988)
T. Matsunaga, R. Kojima, N. Yamada, K. Kifune, Y. Kubota, Y. Tabata, M. Takata, Inorg. Chem. 45, 2235 (2006)
J.K. Burdett, T.M. McLarnan, J. Chem. Phys. 75, 5764 (1981)
J.K. Burdett, S. Lee, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 105, 1079 (1983)
J.A. Venables, C.A. English, Acta Crystallogr. B 30, 929 (1974)
In the Pa3 phase, N2 molecules occupy face center cubic lattice positions. Each director of one of the four molecules in the unit cell points parallel to its own space diagonal of the cubic elementary cell
W.H. Beamer, C.R. Maxwell, J. Chem. Phys. 14, 569 1946
H. Iwasaki, T. Kikegawa, Acta Crystallogr. B 53, 353 (1997)
S.P. Rudin, A.Y. Liu, J.K. Freericks, A. Quandt, Phys. Rev. B 63, 224107 (2001)
A. Decker, G.A. Landrum, R. Dronskowski, Z. Anorg. Allg. Chem. 628, 295 (2002)
M. Wuttig, D. Lusebrink, D. Wamwangi, W. Welnic, M. Gilleßen, R. Dronskowski, Nature Mater. 6, 122 (2007)
T.A. Anderson, H.B. Krause, Acta Cryst. B 30, 1307 (1973)
E. Prodan, W. Kohn, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 102, 11635 (2005)
A.H. Edwards, A.C. Pineda, P.A. Schultz et al., Phys. Rev. B 73, 045210 (2006)
S. Caravati, M. Bernasconi, T.D. Kühne et al., J. Phys.: Condens. Matter 21, 255501 (2009)
A. Ormeci, H. Rosner, Z. Kristallogr 219, 370 (2004)
S. Baroni, A. Dal Corso, S. de Gironcoli, P. Giannozzi, C. Cavazzoni, G. Ballabio, S. Scandolo, G. Chiarotti, P. Focher, A. Pasquarello, K. Laasonen, A. Trave, R. Car, N. Marzari, A. Kokalj, PWSCF: Plane Wave Self Consistent Field ab initio package, http://www.pwscf.org retrieved on 2009.01.04
X. Gonze, J.-M. Beuken, R. Caracas et al., Science 25, 478 (2002)
X. Gonze, G.-M. Rignanese, M. Verstraete et al., Zeit. Kristallogr. 220, 558 (2005)
A.D. Becke, J. Chem. Phys. 98, 5648 (1993)
C. Lee, W. Yang, R.G. Parr, Phys. Rev. B 37, 785 (1988)
N. Troullier, J.L. Martins, Phys. Rev. B 43, 1993 (1991)
J. Akola, R.O. Jones, Phys. Rev. B 76, 235201 (2007)
R.A. Nistor, Simulation of charge transfer and orbital rehybridization, Ph.D. thesis, University of Western Ontario, London, Ontario (2009)
J.Y. Raty, V. Godlevsky, Ph. Ghosez, C. Bichara, J.P. Gaspard, J.R. Chelikowsky, Phys. Rev. Lett. 85, 1950 (2000)
A.V. Kolobov, J. Haines, A. Pradel, M. Ribes, P. Fons, J. Tominaga, Y. Katayama, T. Hammouda, T. Uruga, Phys. Rev. Lett. 97, 035701 (2006)
S. Caravati, M. Bernasconi, T.D. Kühne et al., Phys. Rev. Lett. 102, 205502 (2009)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Müser, M. Elementary considerations on the local symmetry in optoelectronic materials and their phase change behavior. Eur. Phys. J. B 74, 291–302 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1140/epjb/e2010-00072-y
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1140/epjb/e2010-00072-y