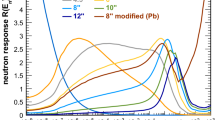
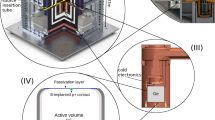
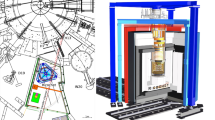
Abstract.
The contribution to \(\gamma\)-ray background from secondary neutrons, originating from cosmic muon interactions in Pb-Cu composite shield, has been measured via \((\mathrm{n},\mathrm{n}^{\prime} \gamma)\) reactions in Cu and Ge. The minimization of background plays a key role in improving the sensitivity of rare event experimental searches like neutrinoless double beta decay and neutron background is often a major concern. It is important to understand secondary neutron production from cosmic muons, especially in materials like Cu and Pb, which often form a part of the detector or shields. The direct contribution of fast neutrons generated from cosmic muon interactions to the \(\gamma\)-ray background via \((\mathrm{n},\mathrm{n}^{\prime} \gamma)\) reactions is investigated for the first time. Measurements are carried out in the low background HPGe detector setup, TiLES, using Pb-Cu composite shield as target material for muon interactions. Simulations have been carried out with GEANT4.10.00 and GEANT4.10.05, each with two different Physics lists. The observed intensities of \((\mathrm{n},\mathrm{n}^{\prime} \gamma)\) for Cu are significantly under-predicted by GEANT4.10.00, while GEANT4.10.05 shows good agreement with the experimental data.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
R. Henning, Rev. Phys. 1, 29 (2016)
S. Dell’Oro et al., Adv. High Energy Phys. 29, 2162659 (2016)
R. Agnese et al., Phys. Rev. Lett. 111, 251301 (2013)
D.S. Akerib et al., Phys. Rev. Lett. 118, 021303 (2014)
D.M. Mei, A. Hime, Phys. Rev. D 73, 053004 (2006)
N. Dokania et al., JINST 10, T12005 (2015)
H.M. Kluck, PhD Thesis, Karlsruhe Institute of Technology (2013)
O.M. Horn, PhD Thesis, Karlsruhe Institute of Technology (2007)
A. Da Silva et al., Nucl. Instrum. Methods A 324, 553 (1995)
F. Boehm et al., Phys. Rev. D 62, 092005 (2000)
I. Abt et al., Astropart. Phys. 90, 1 (2017)
L. Reichhart et al., Astropart. Phys. 47, 67 (2013)
M. Aglietta, Proceedings of the Twenty-sixth International Cosmic Ray conference, Salt lake City, Vol. 2 (AIP, NY, 1999) p. 44
C. Zhang, D.M. Mei, Phys. Rev. D 90, 122003 (2014)
Y.F. Wang et al., Phys. Rev. D 4764, 013012 (2001)
V.A. Kudryavstev et al., Nucl. Instrum. Methods 505, 688 (2003)
A. Lindote et al., Astropart. Phys. 31, 366 (2009)
V. Nanal, EPJ Web of Conferences 112, 1375 (2017)
N. Dokania et al., Nucl. Instrum. Methods A 745, 119 (2014)
N. Dokania et al., Eur. Phys. J. A 53, 74 (2017)
D.M. Mei et al., Phys. Rev. C 77, 054614 (2008)
G. Gupta et al., Proc. DAE-BRNS Symp. Nucl. Phys. 61, 1026 (2016)
G. Cocconi, V. Cocconi Tongiorgi, Phys. Rev. 84, 29 (1951)
D. Heck, Forschungzentrum Karlsruhe Report FZKA 6019, (1998)
D.F. Smart, M.A. Shea, Adv. Space Res. 36, 2012 (1998)
S. Agostinelli et al., Nucl. Instrum. Methods A 506, 250 (2003)
J. Allison et al., Nucl. Instrum. Methods A 835, 186 (2016)
The CMS Collaboration, Phys. Lett. B 692, 83 (2010)
L.A. Currie, Anal Chem. 40, 586 (1968)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by C. Broggini
Data Availability Statement
This manuscript has no associated data or the data will not be deposited. [Authors’ comment: All data generated during this study are contained in this published article.]
Publisher’s Note
The EPJ Publishers remain neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Krishnamoorthy, H., Gupta, G., Garai, A. et al. Study of \(\gamma\)-ray background from cosmic muon induced neutrons. Eur. Phys. J. A 55, 136 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1140/epja/i2019-12822-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1140/epja/i2019-12822-3