Abstract.
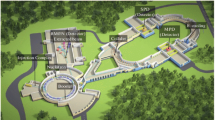
The HERMES Collaboration installed a new Recoil Detector to upgrade the existing spectrometer to study hard exclusive processes which provide access to generalised parton distributions (GPDs) and hence to the orbital angular momentum of quarks. The HERMES Recoil Detector mainly consists of three components: a silicon detector surrounding the target cell inside the beam vacuum, a scintillating fibre tracker and a photon detector with three layers of tungsten and scintillator bars in three different orientations. All three detectors are located inside a solenoidal magnet which provides a 1T longitudinal magnetic field. The Recoil Detector was installed in January 2006 and data taking will last until July of 2007.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
HERMES Collaboration (K. Ackerstaff), Nucl. Instrum. Methods A 417, 230 (1998).
X. Ji, Phys. Rev. Lett. 78, 610 (1997)
V.A. Korotkov, W.-D. Nowak, Nucl. Phys. A 711, 175 (2002).
R. Kaiser, HERMES Internal Note 02-033 (2002).
http://www.micronsemiconductor.co.uk/pdf/ttt.pdf.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yu, W. The HERMES Recoil Detector. Eur. Phys. J. A 31, 509–511 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1140/epja/i2006-10248-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1140/epja/i2006-10248-8