Abstract
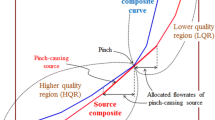
An optimal waste minimisation exchange network was designed for the control of effluent, thermal and gaseous wastes generated from process systems. The model used the concept of pinch technique, which was based on a weighted design superstructure that set design products production targets at 25, 50 and 75% against an operating benchmark status, to optimize the product/waste production from a crude distillation unit of an existing operating refinery. The linear programming model that resulted from the analysis of these waste systems and the composite plots were generated for thermal, gaseous and liquid effluent waste streams. The dynamics of waste recovery systems was investigated in relation to the movement of the pinch position as the process conditions are modified or changed based on design targets of 25, 50 and 75% of the products production scheme. The pinch point was located and the high and low waste generating systems were identified and quantified. The analysis of the composite plots and the solution of the linear programming model showed that a design target that minimized the production of gaseous and liquid wastes was obtained when the deviation of the pinch point favoured movement of product curve away from the waste curve. Thus, a new design model that allows the user to predict and minimize waste from a refinery process system was presented.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rao, J.J., Preventing Pollution around the World, Chem. Eng. Prog., 2001, vol. 97, p. 11.
Moretti, E.C., Reduce VOC and HAP Emissions, Chem. Eng. Prog., 2002, vol. 98, p. 6.
Linnhoff, B. and Ahmad, S., Super Targeting Optimal Synthesis of Energy Management Systems, ASME-AEC, 1986, vol. 2, no. 1, p. 1.
Linnhoff, B. and Hindmarsh, E., Pinch Design Method for Heat Exchanger Networks, Chem. Eng. Sci., 1983, vol. 38, p. 747.
Linnhoff, B. and Turner, J.A., Heat-Recovery Networks, New Insights Yield Big Savings, Chem. Eng., 1981, vol. 88, no. 22, p. 56.
Linnhoff, B., Townsend, D.W., Boland, D., et al., A User Guide on Process Integration for the Efficient Use of Energy, IChemE, 1982, vol. 4, p. 8.
Biegler, L.T., Grossmann, I.E., and Westerberg, A.W., Systematic Methods of Chemical Process Design, New York: Prentice Hall, 1998.
Umeda, T., Harada, T., and Shiroko, K., A Thermodynamic Approach to the Synthesis of Heat Integration Systems in Chemical Processes, Comput. Chem. Eng., 1979, vol. 3, p. 273.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
The article is published in the original.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Abhulimen, K.E., Adeniyi, V.O. & Olafadehan, O.A. Refinery products/waste optimization using a synthesized pinch technique. Theor Found Chem Eng 46, 446–457 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0040579512050090
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0040579512050090