Summary
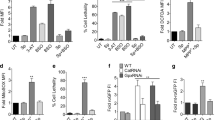
SNpc neurons are uniquely at risk from damage by a variety of ROS, including catechol-quinones formed from autoxidation of DA; as well as Tyr O., TyrOOH, H2O2, O −.2 , NO., HONOO−, and HO.. The high content of Fe2+ in SNPc neurons further promotes HO. formation. Self-preservation ensures that SNpc cells are endowed with a battery of cellular antioxidants, which deactivate these cytotoxic species. Most notable are catalase, superoxide dismutase; and DT-diaphorase, which catalyzes a 2-electron reduction of catechol-quinones. Intra mitochondrial MAO can serve to protect or to damage SNpc neurons, depending on the cellular environ at any time.
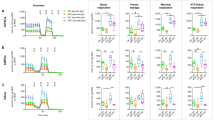
Newer treatment approaches towards PD include the addition of nutrients such as vitamin E and addition of antioxidant drugs that may already be in use as antiparkinsonians: deprenyl, amantadine, DA D2 agonists, apomorphine, NMDA- and adenosine A2A-antagonists. Finally, the potential of neural transplants is explored in the proposal that Sertoli cells, or specific neural cells, or placental blood stem cells will find “routine” use instead of fetal neural cells in the treatment of last-resort for PD.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abin-Carriquiry, J.A., McGregor-Armas, R., Costa, G., Urbanavicius, J. and Dajas, F. (2002). “Presynaptic involvement in the nicotine prevention of dopamine loss provoked by 6-OHDA administration in the substantia nigra”, Neurotoxicity Res., 4, 133–139.
Barzilai, A., Zilkha-Falb, R., Daily, D., Stern, N., Offen, D., Ziv, I., Melamed, E. and Shirvan, A. (2000). “The molecular mechanism of dopamine-induced apoptosis: identification and characterization of genes that mediate dopamine toxicity”, J. Neural Trans. Suppl., 60, 59–76.
Beal, M.F. (1997) “Oxidative damage in neurodegenerative diseases”, Neuroscientist, 3, 21–27.
Beal, M.F., Palomo, T., Kostrzewa, R.M. and Archer, T. (2000) “Neuroprotective and neurorestorative strategies for neuronal injury”, Neurotoxicity Res. 2, 71–84.
Borlongan, C.V., Cameron, D.F., Saporta, S. and Sanberg, P.R. (1997) “Intracerebral transplantation of testis-derived sertoli cells promotes functional recovery in female rats with 6-hydroxydopamine-induced hemiparkinsonism”, Exp. Neurol. 148, 388–392.
Carlsson, A., Waters, N. and Hansson, L.O. (1994) “Neurotransmitter aberrations in schizophrenia: new findings”, In: Fog, R., Gerlach, J. and Hemmingsen, R., eds, Schizophrenia An Integrated View (Munksgard, Copenhagen).
Castagnoli, K., Steyn, S.J., Magnin, G., Van der Schyf, C.J., Fourie, I., Khalil, A. and Castagnoli, Jr, N. (2002) “Studies on the interactions of tobacco leaf and tobacco smoke constituents and monoamine oxidase”, Neurotoxicity Res., 4, 151–160.
Costa, C., Bertazzo, A., Allegri, G., Toffano, G., Curcuruto, O. and Traldi, P. (1992) “Melanin biosynthesis from dopamine: II. A mass spectrometric and collisional spectroscopic investigation”, Pigm. Cell Res. 5, 122–131.
Danysz, W. and Parsons, C. (2002) “Neuroprotective potential of ionotropic glutamate receptor antagonists”, Neurotoxicity Res., 4, 119–126.
Fornstedt, B., Brun, A., Rosengren, E. and Carlsson, A. (1989) “The apparent autoxidation rate of catechols in dopamine-rich regions of human brains increases with the degree of depigmentation of substantia nigra”, J. Neural. Trans. 1, 279–295.
Freed, C.R., Greene, P.E., Breeze, R.E., Tsai, W.Y., DuMouchel, W., Kao, R., Dillon, S., Winfield, H., Culver, S., Trojanowski, J.Q., Eidelberg, D. and Fahn, S. (2001) “Transplantation of embryonic dopamine neurons for severe Parkinson’s disease”, N. Engl. J. Med. 344, 710–719.
Gatto, E.M., Riobó, N., Carreras, M.C. and Poderoso, J.J. (2000) “Nitric oxide overproduction and oxidative stress in human idiopathic Parkinson’s disease” In: Poli, G., Cadenas, E. and Packer, L., eds, Free Radicals in Brain Pathophysiology (Marcel Dekker, New York), pp. 291–312.
Gatto, E.M., Riobó, N., Carreras, M.C., Poderoso, J.J. and Micheli, F.E. (2002) “Neuroprotection in Parkinson's disease; a commentary”, Neurotoxicity Res. 4, 141–145.
Harada, S., Tachikawa, H. and Kawanishi, Y. (2001) “Glutathione-S-transferase M1 gene deletion may be associated with susceptibility to certain forms of schizophrenia”, Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 281, 267–271.
Herrera-Marschitz, M. and Ungerstedt, U. (1984a) “Evidence that apomorphine and pergolide induce rotation in rats by different actions on D1 and D2 receptor sites”, Eur. J. Pharmacol. 98, 165–176.
Herrera-Marschitz, M. and Ungerstedt, U. (1984b) “Evidence that striatal efferents relate to different dopamine receptors”, Brain Res. 323, 269–278.
Hurtado-Guzman, C., Martinez-Alvarado, P., Paris, I., Dagnino-Subiabre, A., Caviedes, P., Caviedes, R., Cassels, B.K. and Segura-Aguilar, J. (2002) “Neurotoxicity of some MAO inhibitors in adult rat hypothalamic cell cultures”, Neurotoxicity Res. 4, 161–163.
Kochman, A., Koka, C. and Metodiewa, D. (2002) “Submolecular adventures of brain tyrosine: What are we searching for now?”, Amino Acids 22, in press.
Kostrzewa, R.M. (2001) “Review on apoptosis vs. necrosis of substantia nigra pars compacta in Parkinson’s disease”, Neurotoxicity Res. 2, 239–250.
Pehar, M., Martinez-Palma, L., Peluffo, H., Kamaid, A., Cassina, P. and Barbeito, L. (2002) “Peroxynitrite-induced cytotoxicity in cultured astrocytes is associated with morphological changes and increased nitrotyrosine immunoreactivity”, Neurotoxicity Res., 4, 87–93.
Rodriguez, A.I., Willing, A.E., Cameron, D.F., Saporta, S. and Sanberg, P.R. (2002) “Neurobehavioral assessment of transplanted porcine sertoli cells into the intact rat striatum”, Neurotoxicity Res. 4, 103–109.
Sanberg, P.R., Borlongan, C.V., Othberg, A.I., Saporta, S., Freeman, T.B. and Cameron, D.F. (1997) “Testis-derived sertoli cells have a trophic effect on dopamine neurons and alleviate hemiparkinsonism in rats”, Nature Med., 3, 1129–1132.
Sanberg, P.R., Willing, A.E. and Cahill, D.W. (2002) “Novel cellular approaches to repair of neurodegenerative disease”, Neurotoxicity Res., 4, 95–101.
Segura-Aguilar, J. (2000) “One and two-electron reduction of catecholamitie ortho-quinones”, In: Creveling, C.R., ed., Role of Catechol-Quinone Species in Cellular Toxicity (F.P. Graham Publishing, Johnson City TN), pp. 11–29.
Segura-Aguilar, J., Baez, S., Widersten, M., Welch, C.J. and Mannervik, B. (1997) “Human class mu glutathione transferases, in particular isoenzyme M2-2, catalyze detoxication of the dopamine metabolite aminochrome”, J. Biol. Chem., 272, 5727–5731.
Segura-Aguilar, J., Diaz-Veliz, G., Mora S. and Herrera-Marschitz, M. (2002) “Inhibition of DT-diaphorase is a requirement for Mn3+ to produce a 6-OH-dopamine like rotational behaviour”, Neurotoxicity Res. 4, 127–131.
Smythies, J. (2002) “The adrenochrome hypothesis of schizophrenia revisited” Neurotoxicity Res., 4.
Tatton, W.G. and Chalmers-Redman, R.M. (1996) “Modulation of gene expression rather than monoamine oxidase inhibition: (−)-deprenyl-related compounds in controlling neurodegeneration”, Neurology, 47, S171-S183.
Willing, A.E., Saporta, S., Lixian, J., Milliken, M., Poulos, S., Bowersox, S.S. and Sanberg, P.R. (2002) “Behavioral effects of LBS-neuron implantation on seizure susceptibility following middle cerebral artery occlusion in the rat”, Neurotoxicity Res., 4, 111–118.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kostrzewa, R.M., Segura-Aguilar, J. Neurotoxicological and neuroprotective elements in Parkinson’s disease. neurotox res 4, 83–86 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1080/10298420290015890
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1080/10298420290015890