Abstract
-
Part 1: Characterisation factors (DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.1065/lca2004.12.194.1) Part 2: Damage scores (DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.1065/lca2004.12.194.2)
-
Preamble. In this series of two papers, a methodology to calculate damages to human health caused by indoor emissions from building materials is presented and applied. Part 1 presents the theoretical foundation of the indoor emission methodology developed, as well as characterisation factors calculated for 36 organic compounds, radon and gamma radiation. Part 2 calculates damage scores of building materials with the characterisation factors presented in part 1. The relevancy of including indoor air emission in the full damage scores at a material level and a dwelling level is also quantified and discussed.
Goal, Scope and Background
Methodologies based on life cycle assessment have been developed to calculate the environmental impact of dwellings. Human health damage due to exposure to substances emitted to indoor air are not included in these methodologies. In order to compare this damage with human health damages associated with the rest of the life cycle of the dwelling, a methodology has been developed to calculate damages to human health caused by pollutants emitted from building materials.
Methods
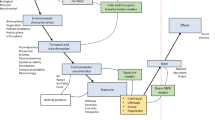
Fate, exposure and health effects are addressed in the calculation procedure. The methodology is suitable for organic substances, radon and elements emitting gamma radiation. The (Dutch reference) dwelling used in the calculation was divided in three compartments: crawl space, first floor and second floor. Fate factors have been calculated based on indoor and outdoor intake fractions, dose conversion factors or extrapolation from measurements. Effect factors have been calculated based on unit risk factors, (extrapolated) effect doses or linear relationship between dose and cancer cases. Damage factors are based on disability adjusted life years (DALYs).
Results and Discussion
Characterisation factors have been calculated for 36 organic compounds, radon and gamma radiation emitted by building materials applied in a Dutch reference dwelling. For organic compounds and radon, the characterisation factors of emissions to the second floor are 10–20% higher than the characterisation factors of emissions to the first floor. For the first and second floor, the characterisation factors are dominated by damage to human health as a result of indoor exposure. The relative contribution of carcinogenic and non-carcinogenic effects to the characterisation factors is generally within one order of magnitude, and up to three orders of magnitude for formaldehyde.
Conclusion
Health effects due to indoor exposure to pollutants emitted from building materials appear to be dominant in the characterisation factors over outdoor exposure to such pollutants. The health effects of emissions of organic compounds and gamma radiation in the crawl space are very small compared to the health effects of emissions into the other compartments. Using the characterisation factors calculated in this study, it is possible to calculate the human health damage due to emissions of substances and radiation emitted to indoor air and compare this damage with damages to human health associated with the rest of the life cycle of the material. This is the subject of part II of this research.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Meijer, A., Huijbregts, M. & Reijnders, L. Human Health Damages due to Indoor Sources of Organic Compounds and Radioactivity in Life Cycle Impact Assessment of Dwellings - Part 1: Characterisation Factors (8 pp). Int J Life Cycle Assessment 10, 309–316 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1065/lca2004.12.194.1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1065/lca2004.12.194.1