Abstract
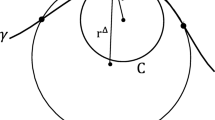
We introduce a new paradigm, the differential invariant signature curve or manifold, for the invariant recognition of visual objects. A general theorem of É. Cartan implies that two curves are related by a group transformation if and only if their signature curves are identical. The important examples of the Euclidean and equi-affine groups are discussed in detail. Secondly, we show how a new approach to the numerical approximation of differential invariants, based on suitable combination of joint invariants of the underlying group action, allows one to numerically compute differential invariant signatures in a fully group-invariant manner. Applications to a variety of fundamental issues in vision, including detection of symmetries, visual tracking, and reconstruction of occlusions, are discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ackerman, M. and Hermann, R. 1975. Sophus Lie's 1880 Transformation Group Paper. Math. Sci. Press: Brookline, MA.
Ackerman, M. and Hermann, R. 1976. Sophus Lie's 1884 Differential Invariant Paper. Math. Sci. Press: Brookline, MA.
Alvarez, L., Lions, P.L., and Morel, J.M. 1992. Image selective smoothing and edge detection by nonlinear diffusion. SIAM J. Numer. Anal., 29:845-866.
Blake, A. and Yuille, A. (Eds.) 1992. Active Vision. MIT Press: Cambridge, MA.
Blaschke, W. 1923. Vorlesungen über Differentialgeometrie. J. Springer: Berlin, Vol. II.
Bruckstein, A.M., Holt, R.J., Netravali, A.N., and Richardson, T.J. 1993. Invariant signatures for planar shape recognition under partial occlusion. CVGIP: Image Understanding, 58:49-65.
Bruckstein, A.M., Katzir, N., Lindenbaum, M., and Porat, M. 1992. Similarity invariant signatures and partially occluded planar shapes. Int. J. Comput. Vision, 7:271-285.
Bruckstein, A.M. and Netravali, A.N. 1995. Ondifferential invariants of planar curves and recognizing partially occluded planar shapes. Ann. Math. Artific. Int., 13:227-250.
Bruckstein, A.M., Rivlin, E., and Weiss, I. 1997. Scale space semilocal invariants. Image and Vision Computing, 15:335-344.
Calabi, E., Olver, P.J., and Tannenbaum, A. 1997. Affine geometry, curve flows, and invariant numerical approximations. Adv. in Math., 124:154-196.
Cartan, É. 1935. La Méthode du Repére Mobile, la Théorie des Groupes Continus, et les Espaces Généralisés. Exposés de Géométrie No. 5, Hermann, Paris.
Caselles, V., Kimmel, R., and Sapiro, G. 1997. Geodesic active contours. Int. J. Computer Vision, 22:61-79.
Cham, T.-J. and Cipolla, R. 1995. Geometric saliency of curve correspondences and grouping of symmetric contours. Preprint, Dept. of Engineering, Univ. of Cambridge.
Channell, P.J. and Scovel, C. 1990. Symplectic integration of Hamiltonian systems. Nonlinearity, 3:231-259.
Cipolla, R. and Blake, A. 1997. Image divergence and deformation from closed curves. Int. J. Robotics Res., 16:77-96.
Dorodnitsyn, V.A. 1994. Symmetry of finite difference equations In CRC Handbook of Lie Group Analysis of Differential Equations, N.H. Ibragimov (Ed.), CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, Vol. 1, pp. 349-403.
Faugeras, O. 1993. On the evolution of simple plane curves of the real projective plane. Comptes Rendus Acad. Sci. (Paris), Série I, 317:565-570.
Faugeras, O. and Keriven, R. 1995. Scale-spaces and affine curvature. In Proc. Europe-China Workshop on Geometrical Modelling and Invariants for Computer Vision, R. Mohr and C. Wu (Eds.), pp. 17-24.
Gage, M. and Hamilton, R.S. 1986. The heat equation shrinking convex plane curves. J. Diff. Geom., 23:69-96.
Grayson, M. 1987. The heat equation shrinks embedded plane curves to round points. J. Diff. Geom., 26:285-314.
Green, M.L. 1978. The moving frame, differential invariants and rigidity theorems for curves in homogeneous spaces. Duke Math. J.45:735-779.
Gross, A.D. and Boult, T.E. 1994. Analyzing skewed symmetries. Int. J. Comput. Vision, 13:91-111.
Guggenheimer, H.W. 1963. Differential Geometry. McGraw-Hill: New York.
Huttenlocher, D.P. and Ullman, S. 1990. Recognising solid objects by alignment with an image. Int. J. Computer Vision, 5:195-212.
Jensen, G.R. 1977. Higher order contact of submanifolds of homogeneous spaces. Lecture Notes in Math., No. 610, Springer-Verlag: New York.
Kass, M., Witkin, A., and Terzopoulos, D. 1988. Snakes: Active contour models. Int. J. Computer Vision, 1:321-331.
Kichenassamy, S., Kumar, A., Olver, P.J., Tannenbaum, A., and Yezzi, T. 1996. Conformal curvature flows: From phase transitions to active vision. Arch. Rat. Mech. Anal., 134:275-301.
Kimia, B., Tannenbaum, A., and Zucker, S. 1995. Shapes, shocks and deformations I: The components of two-dimensional shape and reaction-diffusion space. Int. J. Comp. Vision, 15:189- 224.
Klein, F. and Lie, S. 1871. Über diejenigen ebenen Curven, welche durch ein geschlossenes System von einfach unendlich vielen vertauschbaren linearen Transformationen in sich übergeben. Math. Ann., 4:50-84.
Lei, Z., Keren, D., and Cooper, D.B. 1995. Recognition of complex free-form objects based on mutual algebraic invariants for pairs of patches of data. Preprint, Brown University.
Lie, S. 1880. Theorie der Transformationsgruppen I. Math. Ann., 16:441-528; also Gesammelte Abhandlungen, Vol. 6, B.G. Teubner, Leipzig, 1927, pp. 1-94; see (Ackerman and Hermann, 1975) for an English translation.
Lie, S. 1884. Über Differentialinvarianten. Math. Ann.24:537-578; also Gesammelte Abhandlungen, B.G. Teubner, Leipzig, 1927, Vol. 6, pp. 95-138; see (Ackerman and Hermann, 1976) for an English translation.
Marsden, J.E. 1992. Lectures on Mechanics. Cambridge Univ. Press: London.
Moons, T., Pauwels, E., van Gool, L., and Oosterlinck, A. 1995. Foundations of semi-differential invariants. Int. J. Comput. Vision, 14:25-48.
Mumford, D. 1991. Mathematical theories of shape: Do they model perception? In Geometrical Methods in Computer Vision, SPIE Proceedings, San Diego, Vol. 1570, pp. 2-10.
Mundy, J.L. and Zisserman, A. (Eds.) 1992. Geometric Invariance in Computer Vision. MIT Press: Cambridge, MA.
Mundy, J.L., Zisserman, A., and Forsyth, D. (Eds.) 1994. Applications of Invariance in Computer Vision. Springer-Verlag: New York.
Olver, P.J. 1995. Equivalence, Invariants, and Symmetry. Cambridge University Press.
Olver, P.J., Sapiro, G., and Tannenbaum, A. 1994a. Classification and uniqueness of invariant geometric flows. Comptes Rendus Acad. Sci. (Paris), Sërie I, 319:339-344.
Olver, P.J., Sapiro, G., and Tannenbaum, A. 1994b. Differential invariant signatures and flows in computer vision: A symmetry group approach. In Geometry-Driven Diffusion in Computer Vision, B.M. Ter Haar Romeny (Ed.), Kluwer Acad. Publ. Dordrecht, Netherlands, pp. 255-306.
Olver, P.J., Sapiro, G., and Tannenbaum, A. 1995. Affine invariant edge maps and active contours. Preprint, University of Minnesota.
Olver, P.J., Sapiro, G., and Tannenbaum, A. 1997. Invariant geometric evolutions of surfaces and volumetric smoothing. SIAM J. Appl. Math., 57:176-194.
Osher, S.J. and Sethian, J.A. 1988. Front propagation with curvature dependent speed: Algorithms based on Hamilton-Jacobi formulations. J. Comp. Phys., 79:12-49.
Pauwels, E., Moons, T., Van Gool, L.J., Kempenaers, P., and Oosterlinck, A. 1995. Recognition of planar shapes under affine distortion, Int. J. Comput. Vision, 14:49-65.
ter Haar Romeny, B. (Ed.) 1994. Geometry-Driven Diffusion in Computer Vision. Kluwer, Holland.
Rothwell, C.A., Zisserman, A., Forsyth, D.A., and Mundy, J.L. 1995. Planar object recognition using projective shape representation. Int. J. Comput. Vision, 16:57-99.
Sapiro, G. and Tannenbaum, A. 1994. On affine plane curve evolution. J. Func. Anal., 119:79-120.
Sato, J. and Cipolla, R. 1995. Invariant signatures and outlier detection. Preprint, Dept. of Engineering, Univ. of Cambridge.
Shah, J. 1995. Recovery of shapes by evolution of zero crossings, preprint. Department of Mathematics, Northeastern University, Boston.
Shokin, Yu. I. 1983. The Method of Differential Approximation.Springer-Verlag: New York.
Sturmfels, B. 1993. Algorithms in Invariant Theory. Springer-Verlag: New York.
van Beckum, F.P.H. and van Groesen, E. 1987. Discretizations conserving energy and other constants of the motion. In Proc. ICIAM 87, Paris, pp. 17-35.
Van Gool, L., Moons, T., Pauwels, E., and Oosterlinck, A. 1994. Semi-differential invariants. In Applications of Invariance in Computer Vision, J.L. Mundy and A. Zisserman (Eds.), Springer-Verlag: New York, pp. 157-192.
Van Gool, L., Moons, T., Pauwels, E., and Oosterlinck, A. 1995. Vision and Lie's approach to invariance. Image and Vision Comp., 13:259-277.
Weiss, I. 1993a. Geometric invariants and object recognition. Int. J. Comp. Vision, 10:207-231.
Weiss, I. 1993b. Noise-resistant invariants of curves. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Machine Intelligence, 15:943-948.
Weyl, H. 1946. Classical Groups. Princeton Univ. Press: Princeton, N.J.
Wilczynski, E.J. 1906. Projective Differential Geometry of Curves and Ruled Surfaces.B.G. Teubner: Leipzig.
Yezzi, A., Kichenassamy, S., Kumar, A., Olver, P.J., and Tannenbaum, A. 1997. A geometric snake model for segmentation of medical imagery. IEEE Trans. Medical Imaging, 16:199-209.
Yezzi, A., Kichenassamy, S., Olver, P., and Tannenbaum, A. 1996. A gradient surface approach to 3D segmentation. Proceedings of IS&T.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Calabi, E., Olver, P.J., Shakiban, C. et al. Differential and Numerically Invariant Signature Curves Applied to Object Recognition. International Journal of Computer Vision 26, 107–135 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1007992709392
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1007992709392