Abstract
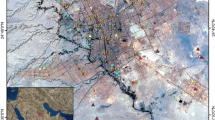
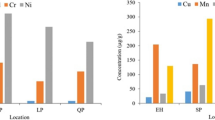
Heavy metals are introduced in human tissue through breathing air, food chain and human skin. They can cause damage to the nervous system and internal organs. In the present study, sixty street dust samples were collected from the central area of Tehran and were digested in the laboratory to determine the content of Zn, Ni, Cd, Cr, Cu and Pb, using inductively coupled plasma optical emission spectrometry (ICP-OES). The level of contamination with the analyzed metals was determined according to the following indices: geo-accumulation index (I geo), enrichment factor (EF), pollution index (PI), integrated pollution index (IPI) and potential ecological risk index (RI). The average concentration of heavy metals found was in the order of Zn > Cu > Pb > Ni > Cr > Cd. The average I geo values for Cd, Cr, Cu, Ni, Pb and Zn were 1.53, −1.88, 2.68, −0.67, 1.62 and 2.70, respectively. Among the investigated heavy metals, zinc and copper had the maximum average EF values and were placed into the “very severe enrichment” class. Potential ecological risk factor (E r) also indicated that Cd had the highest risk, and it was classified as of considerable potential ecological risk. Therefore, it is necessary to pay more attention to the appearance of Cd in the human environment. The calculated potential ecological risk index values also illustrated that the street dust samples presented a “moderate ecological risk.” The calculated IPI values showed that the pollution levels of the street dust samples ranged from high to extremely high.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akoto O, Bismark Eshun F, Darko G, Adei E (2014) Concentrations and health risk assessments of heavy metals in fish from the fosu lagoon International. J Environ Res 8:403–410
Chen C-W, Kao C-M, Chen C-F, Dong C-D (2007) Distribution and accumulation of heavy metals in the sediments of Kaohsiung Harbor. Taiwan Chemosphere 66:1431–1440
Chon H-T, Kim K-W, Kim J-Y (1995) Metal contamination of soils and dusts in Seoul metropolitan city. Korea Environ Geochem Health 17:139–146
Duong TT, Lee B-K (2011) Determining contamination level of heavy metals in road dust from busy traffic areas with different characteristics. J Environ Manag 92:554–562
Faiz Y, Tufail M, Javed MT, Chaudhry M (2009) Road dust pollution of Cd. Cu, Ni, Pb and Zn along Islamabad Expressway, Pakistan Microchemical Journal 92:186–192
Fergusson J, Ryan D (1984) The elemental composition of street dust from large and small urban areas related to city type, source and particle size. Sci Total Environ 34:101–116
Gupta VK, Yola ML, Atar N, Ustundağ Z, Solak AO (2013) A novel sensitive Cu (II) and Cd (II) nanosensor platform: graphene oxide terminated p-aminophenyl modified glassy carbon surface. Sens Actuators B Chem 112:541–548
Hakanson L (1980) An ecological risk index for aquatic pollution control. A Sedimentol Approach Water Res 14:975–1001
Hjortenkrans D, Bergbäck B, Häggerud A (2006) New metal emission patterns in road traffic environments. Environ Monit Assess 117:85–98
Howari F, Abu-Rukah Y, Goodell P (2004) Heavy metal pollution of soils along north Shuna-Aqaba Highway. Jordan Int J Environ Pollut 22:597–607
Kamani H, Hoseini M, Safari GH, Jaafari J, Mahvi AH (2014a) Study of trace elements in wet atmospheric precipitation in Tehran, Iran. Environ Monit Assess 186:5059–5067
Kamani H, Hoseini M, Seyedsalehi M, Mahdavi Y, Jaafari J, Safari GH (2014b) Concentration and characterization of airborne particles in Tehran’s subway system. Environ Sci Pollut Res 21:7319–7328
Kamani H et al (2015) Heavy metal contamination in street dusts with various land uses in Zahedan, Iran. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 94:382–386
Leili M, Naddafi K, Nabizadeh R, Yunesian M, Mesdaghinia A (2008) The study of TSP and PM10 concentration and their heavy metal content in central area of Tehran, Iran. Air Qual Atmos Health 1:159–166
Lu X, Wang L, Lei K, Huang J, Zhai Y (2009) Contamination assessment of copper, lead, zinc, manganese and nickel in street dust of Baoji, NW China. J Hazard Mater 161:1058–1062
Mohmand J et al (2015) Human exposure to toxic metals via contaminated dust: bio-accumulation trends and their potential risk estimation. Chemosphere 132:142–151
Moore F, Esmaeili K, Keshavarzi B (2011) Assessment of heavy metals contamination in stream water and sediments affected by the Sungun porphyry copper deposit, East Azerbaijan Province, Northwest Iran. Water Qual Expo Health 3:37–49
Muller G (1969) Index of geoaccumulation in sediments of the Rhine River. GeoJournal 2:108–118
Nude PM, Foli G, Yidana SM (2011) Geochemical assessment of impact of mine spoils on the quality of stream Sediments within the Obuasi mines environment, Ghana. Int J Geosci 2:259–266
Rafiei B, Bakhtiari Nejad M, Hashemi M, Khodaei A (2010) Distribution of heavy metals around the Dashkasan Au mine. Int J Environ Res 4:647–654
Roubicek V, Raclavska H, Juchelkova D, Filip P (2008) Wear and environmental aspects of composite materials for automotive braking industry. Wear 265:167–175
Rudnick R, Gao S (2003) Composition of the continental crust. Treatise Geochem 3:1–64
Saeedi M, Li LY, Salmanzadeh M (2012) Heavy metals and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons: pollution and ecological risk assessment in street dust of Tehran. J Hazard Mater 227:9–17
Saeedi M, Salmanzadeh M, Jamshidi-Zanjani A, Li L (2014) Response to the comments of Zhang et al.(2014) on “Heavy metals and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons: pollution and ecological risk assessment in street dust of Tehran”. J Hazard Mater 279:389–391
Sayadi M, Sayyed MRG (2011) Comparative assessment of baseline concentration of the heavy metals in the soils of Tehran (Iran) with the comprisable reference data. Environ Earth Sci 63:1179–1188
Schwar M, Moorcroft J, Laxen D, Thompson M, Armorgie C (1988) Baseline metal-in-dust concentrations in Greater London. Sci Total Environ 68:25–43
Selvam AP, Priya SL, Banerjee K, Hariharan G, Purvaja R, Ramesh R (2012) Heavy metal assessment using geochemical and statistical tools in the surface sediments of Vembanad Lake, Southwest Coast of India. Environ Monit Assess 184:5899–5915
Sezgin N, Ozcan HK, Demir G, Nemlioglu S, Bayat C (2004) Determination of heavy metal concentrations in street dusts in Istanbul E-5 highway. Environ Int 29:979–985
Shi X, Wang J (2013) Comparison of different methods for assessing heavy metal contamination in street dust of Xianyang City, NW China. Environ Earth Sci 68:2409–2415
Šmuc NR, Vrhovnik P, Dolenec T, Serafimovski T, Tasev G, Dolene M (2009) Assessment of the heavy metal contamination in the surficial sediments of Lake Kalimanci (Macedonia): a preliminary study. RMZ Mater Geoenviron 56:437–447
Sun Y, Zhou Q, Xie X, Liu R (2010) Spatial, sources and risk assessment of heavy metal contamination of urban soils in typical regions of Shenyang, China. J Hazard Mater 174:455–462
Thorpe A, Harrison RM (2008) Sources and properties of non-exhaust particulate matter from road traffic: a review. Sci Total Environ 400:270–282
USEPA (1996) Method 3050B: Acid digestion of sediments, sludges and soils (revision 2):1-12
Wei B, Yang L (2010) A review of heavy metal contaminations in urban soils, urban road dusts and agricultural soils from China. Microchem J 94:99–107
Weissmannová HD, Pavlovský J, Chovanec P (2015) Heavy metal contaminations of Urban soils in Ostrava, Czech Republic: assessment of metal pollution and using principal component analysis. Int J Environ Res 9
Yaylalı-Abanuz G (2011) Heavy metal contamination of surface soil around Gebze industrial area, Turkey. Microchem J 99:82–92
Yola ML, Eren T, İlkimen H, Atar N, Yenikaya C (2014) A sensitive voltammetric sensor for determination of Cd (II) in human plasma. J Mol Liq 197:58–64
Zhang J, Kaeseberg T, Krebs P, Hua P (2014) Comments on “Heavy metals and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons: pollution and ecological risk assessment in street dust of Tehran”. J Hazard Mater 273:124–126
Zhu W, Bian B, Li L (2008) Heavy metal contamination of road-deposited sediments in a medium size city of China. Environ Monit Assess 147:171–181
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the School of Public Health, Tehran University of Medical Science for the financial support of this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Editorial responsibility: M. Abbaspour
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kamani, H., Mahvi, A.H., Seyedsalehi, M. et al. Contamination and ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in street dust of Tehran, Iran. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 14, 2675–2682 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-017-1327-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-017-1327-x