Abstract
Background
The use of biomarkers for prostate cancer screening, diagnosis and prognosis has the potential to improve the clinical management of the patients. Owing to inherent limitations of the biomarker prostate-specific antigen (PSA), intensive efforts are currently directed towards a search for alternative prostate cancer biomarkers, particularly those that can predict disease aggressiveness and drive better treatment decisions.
Methods
A literature search of Medline articles focused on recent and emerging advances in prostate cancer biomarkers was performed. The most promising biomarkers that have the potential to meet the unmet clinical needs in prostate cancer patient management and/or that are clinically implemented were selected.
Conclusions
With the advent of advanced genomic and proteomic technologies, we have in recent years seen an enormous spurt in prostate cancer biomarker research with several promising alternative biomarkers being discovered that show an improved sensitivity and specificity over PSA. The new generation of biomarkers can be tested via serum, urine, or tissue-based assays that have either received regulatory approval by the US Food and Drug Administration or are available as Clinical Laboratory Improvement Amendments-based laboratory developed tests. Additional emerging novel biomarkers for prostate cancer, including circulating tumor cells, microRNAs and exosomes, are still in their infancy. Together, these biomarkers provide actionable guidance for prostate cancer risk assessment, and are expected to lead to an era of personalized medicine.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
R.L. Siegel, K.D. Miller, A. Jemal, Cancer statistics, 2015. CA Cancer J. Clin. 65, 5–29 (2015)
M.K. Fong, R. Hare, A. Jarkowski, A new era for castrate resistant prostate cancer: a treatment review and update. J. Oncol. Pharm. Pract. 18, 343–354 (2012)
D.N. Rodrigues, L.M. Butler, D.L. Estelles, J.S. de Bono, Molecular pathology and prostate cancer therapeutics: from biology to bedside. J. Pathol. 232, 178–184 (2013)
R.D. Loberg, C.J. Logothetis, E.T. Keller, K.J. Pienta, Pathogenesis and treatment of prostate cancer bone metastases: targeting the lethal phenotype. J. Clin. Oncol. 23, 8232–8241 (2005)
J. Romero Otero, B. Garcia Gomez, F. Campos Juanatey, K.A. Touijer, Prostate cancer biomarkers: an update. Urol. Oncol. 32, 252–260 (2014)
H. Lilja, Testing new PSA subforms to enhance the accuracy of predicting cancer risk and disease outcome in prostate cancer. Clin. Chem. 54, 1248–1249 (2008)
H. Lilja, D. Ulmert, A.J. Vickers, Prostate-specific antigen and prostate cancer: prediction, detection and monitoring. Nat. Rev. Cancer 8, 268–278 (2008)
K.C. Cary, M.R. Cooperberg, Biomarkers in prostate cancer surveillance and screening: past, present, and future. Ther. Adv. Urol. 5, 318–329 (2013)
J.I. Epstein, An update of the Gleason grading system. J. Urol. 183, 433–440 (2010)
G.T. Mellinger, D. Gleason, J. Bailar 3rd, The histology and prognosis of prostatic cancer. J. Urol. 97, 331–337 (1967)
M.M. Shen, C. Abate-Shen, Molecular genetics of prostate cancer: new prospects for old challenges. Genes Dev. 24, 1967–2000 (2010)
J.A. Squire, P.C. Park, M. Yoshimoto, J. Alami, J.L. Williams, A. Evans et al., Prostate cancer as a model system for genetic diversity in tumors. Adv. Cancer Res. 112, 183–216 (2011)
J.R. Schoenborn, P. Nelson, M. Fang, Genomic profiling defines subtypes of prostate cancer with the potential for therapeutic stratification. Clin. Cancer Res. 19, 4058–4066 (2013)
S.E. Ilyin, S.M. Belkowski, C.R. Plata-Salaman, Biomarker discovery and validation: technologies and integrative approaches. Trends Biotechnol. 22, 411–416 (2004)
J.R. Prensner, M.A. Rubin, J.T. Wei, A.M. Chinnaiyan, Beyond PSA: the next generation of prostate cancer biomarkers. Sci. Transl. Med. 4, 127rv123 (2012)
C.L. Sawyers, The cancer biomarker problem. Nature 452, 548–552 (2008)
F.C. Lowe, S.J. Trauzzi, Prostatic acid phosphatase in 1993. Its limited clinical utility. Urol. Clin. North Am. 20, 589–595 (1993)
C.J. Ercole, P.H. Lange, M. Mathisen, R.K. Chiou, P.K. Reddy, R.L. Vessella, Prostatic specific antigen and prostatic acid phosphatase in the monitoring and staging of patients with prostatic cancer. J. Urol. 138, 1181–1184 (1987)
D.A. Sartori, D.W. Chan, Biomarkers in prostate cancer: what’s new? Curr. Opin. Oncol. 26, 259–264 (2014)
G.J. Kelloff, P. Choyke, D.S. Coffey, Challenges in clinical prostate cancer: role of imaging. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 192, 1455–1470 (2009)
Y. Mazaheri, A. Shukla-Dave, A. Muellner, H. Hricak, MRI of the prostate: clinical relevance and emerging applications. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 33, 258–274 (2011)
K. Bensalah, F. Montorsi, S.F. Shariat, Challenges of cancer biomarker profiling. Eur. Urol. 52, 1601–1609 (2007)
J. Hernandez, I.M. Thompson, Prostate-specific antigen: a review of the validation of the most commonly used cancer biomarker. Cancer 101, 894–904 (2004)
I.M. Thompson, D.K. Pauler, P.J. Goodman, C.M. Tangen, M.S. Lucia, H.L. Parnes et al., Prevalence of prostate cancer among men with a prostate-specific antigen level < or =4.0 ng per milliliter. N. Engl. J. Med. 350, 2239–2246 (2004)
W.J. Catalona, D.S. Smith, D.K. Ornstein, Prostate cancer detection in men with serum PSA concentrations of 2.6 to 4.0 ng/mL and benign prostate examination. Enhancement of specificity with free PSA measurements. JAMA 277, 1452–1455 (1997)
L.C. Walter, D. Bertenthal, K. Lindquist, B.R. Konety, PSA screening among elderly men with limited life expectancies. JAMA 296, 2336–2342 (2006)
D.D. Brooks, A. Wolf, R.A. Smith, C. Dash, I. Guessous, Prostate cancer screening 2010: updated recommendations from the American Cancer Society. J. Natl. Med. Assoc. 102, 423–429 (2010)
A.M. Wolf, R.C. Wender, R.B. Etzioni, I.M. Thompson, A.V. D’Amico, R.J. Volk et al., American Cancer Society guideline for the early detection of prostate cancer: update 2010. CA Cancer J. Clin. 60, 70–98 (2010)
A.V. D’Amico, M.H. Chen, K.A. Roehl, W.J. Catalona, Preoperative PSA velocity and the risk of death from prostate cancer after radical prostatectomy. N. Engl. J. Med. 351, 125–135 (2004)
R. Etzioni, A. Tsodikov, A. Mariotto, A. Szabo, S. Falcon, J. Wegelin et al., Quantifying the role of PSA screening in the US prostate cancer mortality decline. Cancer Causes Control 19, 175–181 (2008)
A. Christensson, T. Bjork, O. Nilsson, U. Dahlen, M.T. Matikainen, A.T. Cockett et al., Serum prostate specific antigen complexed to alpha 1-antichymotrypsin as an indicator of prostate cancer. J. Urol. 150, 100–105 (1993)
W.J. Catalona, A.W. Partin, K.M. Slawin, M.K. Brawer, R.C. Flanigan, A. Patel et al., Use of the percentage of free prostate-specific antigen to enhance differentiation of prostate cancer from benign prostatic disease: a prospective multicenter clinical trial. JAMA 279, 1542–1547 (1998)
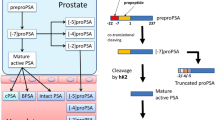
M.A. Khan, L.J. Sokoll, D.W. Chan, L.A. Mangold, P. Mohr, S.D. Mikolajczyk et al., Clinical utility of proPSA and “benign” PSA when percent free PSA is less than 15 %. Urology 64, 1160–1164 (2004)
S. Hori, J.S. Blanchet, J. McLoughlin, From prostate-specific antigen (PSA) to precursor PSA (proPSA) isoforms: a review of the emerging role of proPSAs in the detection and management of early prostate cancer. BJU Int. 112, 717–728 (2013)
S.D. Mikolajczyk, K.M. Marker, L.S. Millar, A. Kumar, M.S. Saedi, J.K. Payne et al., A truncated precursor form of prostate-specific antigen is a more specific serum marker of prostate cancer. Cancer Res. 61, 6958–6963 (2001)
T.Y. Chan, S.D. Mikolajczyk, K. Lecksell, M.J. Shue, H.G. Rittenhouse, A.W. Partin et al., Immunohistochemical staining of prostate cancer with monoclonal antibodies to the precursor of prostate-specific antigen. Urology 62, 177–181 (2003)
I. Heidegger, H. Klocker, E. Steiner, V. Skradski, M. Ladurner, R. Pichler et al., [-2]proPSA is an early marker for prostate cancer aggressiveness. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis. 17, 70–74 (2014)
M. Lazzeri, A. Abrate, G. Lughezzani, G.M. Gadda, M. Freschi, F. Mistretta et al., Relationship of chronic histologic prostatic inflammation in biopsy specimens with serum isoform [-2]proPSA (p2PSA), %p2PSA, and prostate health index in men with a total prostate-specific antigen of 4-10 ng/ml and normal digital rectal examination. Urology 83, 606–612 (2014)
M. Lazzeri, A. Haese, A. Abrate, A. de la Taille, J.P. Redorta, T. McNicholas et al., Clinical performance of serum prostate-specific antigen isoform [-2]proPSA (p2PSA) and its derivatives, %p2PSA and the prostate health index (PHI), in men with a family history of prostate cancer: results from a multicentre European study, the PROMEtheuS project. BJU Int. 112, 313–321 (2013)
G. Guazzoni, L. Nava, M. Lazzeri, V. Scattoni, G. Lughezzani, C. Maccagnano et al., Prostate-specific antigen (PSA) isoform p2PSA significantly improves the prediction of prostate cancer at initial extended prostate biopsies in patients with total PSA between 2.0 and 10 ng/ml: results of a prospective study in a clinical setting. Eur. Urol. 60, 214–222 (2011)
A. Houlgatte, S. Vincendeau, F. Desfemmes, J. Ramirez, N. Benoist, K. Bensalah et al., Use of [-2] pro PSA and phi index for early detection of prostate cancer: a prospective of 452 patients. Prog. Urol. 22, 279–283 (2012)
L.J. Sokoll, M.G. Sanda, Z. Feng, J. Kagan, I.A. Mizrahi, D.L. Broyles et al., A prospective, multicenter, National Cancer Institute Early Detection Research Network study of [-2]proPSA: improving prostate cancer detection and correlating with cancer aggressiveness. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomarkers Prev. 19, 1193–1200 (2010)
M.J. Bussemakers, A. van Bokhoven, G.W. Verhaegh, F.P. Smit, H.F. Karthaus, J.A. Schalken et al., DD3: a new prostate-specific gene, highly overexpressed in prostate cancer. Cancer Res. 59, 5975–5979 (1999)
J.B. de Kok, G.W. Verhaegh, R.W. Roelofs, D. Hessels, L.A. Kiemeney, T.W. Aalders et al., DD3(PCA3), a very sensitive and specific marker to detect prostate tumors. Cancer Res. 62, 2695–2698 (2002)
M. Auprich, A. Bjartell, F.K. Chun, A. de la Taille, S.J. Freedland, A. Haese et al., Contemporary role of prostate cancer antigen 3 in the management of prostate cancer. Eur. Urol. 60, 1045–1054 (2011)
E.D. Crawford, K.O. Rove, E.J. Trabulsi, J. Qian, K.P. Drewnowska, J.C. Kaminetsky et al., Diagnostic performance of PCA3 to detect prostate cancer in men with increased prostate specific antigen: a prospective study of 1,962 cases. J. Urol. 188, 1726–1731 (2012)
V. Vlaeminck-Guillem, A. Ruffion, J. Andre, M. Devonec, P. Paparel, Urinary prostate cancer 3 test: toward the age of reason? Urology 75, 447–453 (2010)
I.L. Deras, S.M. Aubin, A. Blase, J.R. Day, S. Koo, A.W. Partin et al., PCA3: a molecular urine assay for predicting prostate biopsy outcome. J. Urol. 179, 1587–1592 (2008)
Tomlins SA, Day JR, Lonigro RJ, Hovelson DH, Siddiqui J, Kunju LP et al., Urine TMPRSS2:ERG Plus PCA3 for Individualized Prostate Cancer Risk Assessment. Eur. Urol. (2015). doi:10.1016/j.eururo.2015.04.039
G.H. Leyten, D. Hessels, S.A. Jannink, F.P. Smit, H. de Jong, E.B. Cornel et al., Prospective multicentre evaluation of PCA3 and TMPRSS2-ERG gene fusions as diagnostic and prognostic urinary biomarkers for prostate cancer. Eur. Urol. 65, 534–542 (2014)
E. Schiffer, Biomarkers for prostate cancer. World J. Urol. 25, 557–562 (2007)
S.S. Salami, F. Schmidt, B. Laxman, M.M. Regan, D.S. Rickman, D. Scherr et al., Combining urinary detection of TMPRSS2:ERG and PCA3 with serum PSA to predict diagnosis of prostate cancer. Urol. Oncol. 31, 566–571 (2013)
D. Knezevic, A.D. Goddard, N. Natraj, D.B. Cherbavaz, K.M. Clark-Langone, J. Snable et al., Analytical validation of the Oncotype DX prostate cancer assay - a clinical RT-PCR assay optimized for prostate needle biopsies. BMC Genomics 14, 690 (2013)
P. Blume-Jensen, D.M. Berman, D.L. Rimm, M. Shipitsin, M. Putzi, T.P. Nifong et al., Development and clinical validation of an in situ biopsy-based multimarker assay for risk stratification in prostate cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 21, 2591–2600 (2015)
J.N. Cornu, G. Cancel-Tassin, C. Egrot, C. Gaffory, F. Haab, O. Cussenot, Urine TMPRSS2:ERG fusion transcript integrated with PCA3 score, genotyping, and biological features are correlated to the results of prostatic biopsies in men at risk of prostate cancer. Prostate 73, 242–249 (2013)
M.R. Cooperberg, J.P. Simko, J.E. Cowan, J.E. Reid, A. Djalilvand, S. Bhatnagar et al., Validation of a cell-cycle progression gene panel to improve risk stratification in a contemporary prostatectomy cohort. J. Clin. Oncol. 31, 1428–1434 (2013)
J. Cuzick, D.M. Berney, G. Fisher, D. Mesher, H. Moller, J.E. Reid et al., Prognostic value of a cell cycle progression signature for prostate cancer death in a conservatively managed needle biopsy cohort. Br. J. Cancer 106, 1095–1099 (2012)
S.J. Freedland, L. Gerber, J. Reid, W. Welbourn, E. Tikishvili, J. Park et al., Prognostic utility of cell cycle progression score in men with prostate cancer after primary external beam radiation therapy. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 86, 848–853 (2013)
R.L. Parr, J. Mills, A. Harbottle, J.M. Creed, G. Crewdson, B. Reguly et al., Mitochondria, prostate cancer, and biopsy sampling error. Discov. Med. 15, 213–220 (2013)
M.L. Verschoor, R. Ungard, A. Harbottle, J.P. Jakupciak, R.L. Parr, G. Singh, Mitochondria and cancer: past, present, and future. Biomed Res Int 2013, 612369 (2013)
K. Robinson, J. Creed, B. Reguly, C. Powell, R. Wittock, D. Klein et al., Accurate prediction of repeat prostate biopsy outcomes by a mitochondrial DNA deletion assay. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis. 13, 126–131 (2010)
S. Carlsson, A. Maschino, F. Schroder, C. Bangma, E.W. Steyerberg, T. van der Kwast et al., Predictive value of four kallikrein markers for pathologically insignificant compared with aggressive prostate cancer in radical prostatectomy specimens: results from the European Randomized Study of Screening for Prostate Cancer section Rotterdam. Eur. Urol. 64, 693–699 (2013)
J.D. Voigt, S.M. Zappala, E.D. Vaughan, A.J. Wein, The Kallikrein panel for prostate cancer screening: its economic impact. Prostate 74, 250–259 (2014)
A. Sreekumar, L.M. Poisson, T.M. Rajendiran, A.P. Khan, Q. Cao, J. Yu et al., Metabolomic profiles delineate potential role for sarcosine in prostate cancer progression. Nature 457, 910–914 (2009)
K. Badani, D.J. Thompson, C. Buerki, E. Davicioni, J. Garrison, M. Ghadessi et al., Impact of a genomic classifier of metastatic risk on postoperative treatment recommendations for prostate cancer patients: a report from the DECIDE study group. Oncotarget 4, 600–609 (2013)
E.D. Crawford, K. Ventii, N.D. Shore, New biomarkers in prostate cancer. Oncology (Williston Park) 28, 135–142 (2014)
M.A. Rubin, M. Zhou, S.M. Dhanasekaran, S. Varambally, T.R. Barrette, M.G. Sanda et al., alpha-Methylacyl coenzyme A racemase as a tissue biomarker for prostate cancer. JAMA 287, 1662–1670 (2002)
M.A. Rubin, T.A. Bismar, O. Andren, L. Mucci, R. Kim, R. Shen et al., Decreased alpha-methylacyl CoA racemase expression in localized prostate cancer is associated with an increased rate of biochemical recurrence and cancer-specific death. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomarkers Prev. 14, 1424–1432 (2005)
Z. Jiang, G.R. Fanger, B.A. Woda, B.F. Banner, P. Algate, K. Dresser et al., Expression of alpha-methylacyl-CoA racemase (P504s) in various malignant neoplasms and normal tissues: astudy of 761 cases. Hum. Pathol. 34, 792–796 (2003)
P. Cairns, K. Okami, S. Halachmi, N. Halachmi, M. Esteller, J.G. Herman et al., Frequent inactivation of PTEN/MMAC1 in primary prostate cancer. Cancer Res. 57, 4997–5000 (1997)
B.S. Carver, C. Chapinski, J. Wongvipat, H. Hieronymus, Y. Chen, S. Chandarlapaty et al., Reciprocal feedback regulation of PI3K and androgen receptor signaling in PTEN-deficient prostate cancer. Cancer Cell 19, 575–586 (2011)
Bostrom PJ, Bjartell AS, Catto JW, Eggener SE, Lilja H, Loeb S et al., Genomic predictors of outcome in prostate cancer. Eur. Urol. (2015). doi:10.1016/j.eururo.2015.04.008
K. Sircar, M. Yoshimoto, F.A. Monzon, I.H. Koumakpayi, R.L. Katz, A. Khanna et al., PTEN genomic deletion is associated with p-Akt and AR signalling in poorer outcome, hormone refractory prostate cancer. J. Pathol. 218, 505–513 (2009)
A. Krohn, T. Diedler, L. Burkhardt, P.S. Mayer, C. De Silva, M. Meyer-Kornblum et al., Genomic deletion of PTEN is associated with tumor progression and early PSA recurrence in ERG fusion-positive and fusion-negative prostate cancer. Am. J. Pathol. 181, 401–412 (2012)
K.A. Leinonen, O.R. Saramaki, B. Furusato, T. Kimura, H. Takahashi, S. Egawa et al., Loss of PTEN is associated with aggressive behavior in ERG-positive prostate cancer. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomarkers Prev. 22, 2333–2344 (2013)
M. Yoshimoto, A.M. Joshua, I.W. Cunha, R.A. Coudry, F.P. Fonseca, O. Ludkovski et al., Absence of TMPRSS2:ERG fusions and PTEN losses in prostate cancer is associated with a favorable outcome. Mod. Pathol. 21, 1451–1460 (2008)
L.H. Broersen, G.W. van Pelt, R.A. Tollenaar, W.E. Mesker, Clinical application of circulating tumor cells in breast cancer. Cell. Oncol. 37, 9–15 (2014)
D.C. Danila, G. Heller, G.A. Gignac, R. Gonzalez-Espinoza, A. Anand, E. Tanaka et al., Circulating tumor cell number and prognosis in progressive castration-resistant prostate cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 13, 7053–7058 (2007)
M.J. Kim, N.Y. Choi, E.K. Lee, M.S. Kang, Identification of novel markers that outperform EpCAM in quantifying circulating tumor cells. Cell. Oncol. 37, 235–243 (2014)
G. Attard, J.F. Swennenhuis, D. Olmos, A.H. Reid, E. Vickers, R. A’Hern et al., Characterization of ERG, AR and PTEN gene status in circulating tumor cells from patients with castration-resistant prostate cancer. Cancer Res. 69, 2912–2918 (2009)
J.S. de Bono, H.I. Scher, R.B. Montgomery, C. Parker, M.C. Miller, H. Tissing et al., Circulating tumor cells predict survival benefit from treatment in metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 14, 6302–6309 (2008)
D.P. Bartel, MicroRNAs: target recognition and regulatory functions. Cell 136, 215–233 (2009)
A. Gordanpour, R.K. Nam, L. Sugar, A. Seth, MicroRNAs in prostate cancer: from biomarkers to molecularly-based therapeutics. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis. 15, 314–319 (2012)
D.R. Hurst, M.D. Edmonds, D.R. Welch, Metastamir: the field of metastasis-regulatory microRNA is spreading. Cancer Res. 69, 7495–7498 (2009)
S. Saini, S. Majid, R. Dahiya, Diet, microRNAs and prostate cancer. Pharm. Res. 27, 1014–1026 (2010)
S. Saini, S. Majid, S. Yamamura, L. Tabatabai, S.O. Suh, V. Shahryari et al., Regulatory role of mir-203 in prostate cancer progression and metastasis. Clin. Cancer Res. 17, 5287–5298 (2011)
I. Giusti, V. Dolo, Extracellular vesicles in prostate cancer: new future clinical strategies? Biomed Res Int 2014, 561571 (2014)
Y. Xi, G. Nakajima, E. Gavin, C.G. Morris, K. Kudo, K. Hayashi et al., Systematic analysis of microRNA expression of RNA extracted from fresh frozen and formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded samples. RNA 13, 1668–1674 (2007)
J.A. Weber, D.H. Baxter, S. Zhang, D.Y. Huang, K.H. Huang, M.J. Lee et al., The microRNA spectrum in 12 body fluids. Clin. Chem. 56, 1733–1741 (2010)
S. Dijkstra, P.F. Mulders, J.A. Schalken, Clinical use of novel urine and blood based prostate cancer biomarkers: a review. Clin. Biochem. 47, 889–896 (2014)
J. Szczyrba, E. Loprich, S. Wach, V. Jung, G. Unteregger, S. Barth et al., The microRNA profile of prostate carcinoma obtained by deep sequencing. Mol. Cancer Res. 8, 529–538 (2010)
A. Schaefer, M. Jung, H.J. Mollenkopf, I. Wagner, C. Stephan, F. Jentzmik et al., Diagnostic and prognostic implications of microRNA profiling in prostate carcinoma. Int. J. Cancer 126, 1166–1176 (2010)
P.S. Mitchell, R.K. Parkin, E.M. Kroh, B.R. Fritz, S.K. Wyman, E.L. Pogosova-Agadjanyan et al., Circulating microRNAs as stable blood-based markers for cancer detection. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 105, 10513–10518 (2008)
F. Moltzahn, A.B. Olshen, L. Baehner, A. Peek, L. Fong, H. Stoppler et al., Microfluidic-based multiplex qRT-PCR identifies diagnostic and prognostic microRNA signatures in the sera of prostate cancer patients. Cancer Res. 71, 550–560 (2011)
R.J. Bryant, T. Pawlowski, J.W. Catto, G. Marsden, R.L. Vessella, B. Rhees et al., Changes in circulating microRNA levels associated with prostate cancer. Br. J. Cancer 106, 768–774 (2012)
S. Mathivanan, H. Ji, R.J. Simpson, Exosomes: extracellular organelles important in intercellular communication. J Proteomics 73, 1907–1920 (2010)
D. Duijvesz, T. Luider, C.H. Bangma, G. Jenster, Exosomes as biomarker treasure chests for prostate cancer. Eur. Urol. 59, 823–831 (2011)
G. Tavoosidana, G. Ronquist, S. Darmanis, J. Yan, L. Carlsson, D. Wu et al., Multiple recognition assay reveals prostasomes as promising plasma biomarkers for prostate cancer. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 108, 8809–8814 (2011)
J. Nilsson, J. Skog, A. Nordstrand, V. Baranov, L. Mincheva-Nilsson, X.O. Breakefield et al., Prostate cancer-derived urine exosomes: a novel approach to biomarkers for prostate cancer. Br. J. Cancer 100, 1603–1607 (2009)
S. Khan, J.M. Jutzy, M.M. Valenzuela, D. Turay, J.R. Aspe, A. Ashok et al., Plasma-derived exosomal survivin, a plausible biomarker for early detection of prostate cancer. PLoS ONE 7, e46737 (2012)
A. Cannistraci, A.L. Di Pace, R. De Maria, D. Bonci, MicroRNA as new tools for prostate cancer risk assessment and therapeutic intervention: results from clinical data set and patients’ samples. Biomed Res Int 2014, 146170 (2014)
M.A. Cortez, C. Bueso-Ramos, J. Ferdin, G. Lopez-Berestein, A.K. Sood, G.A. Calin, MicroRNAs in body fluids--the mix of hormones and biomarkers. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 8, 467–477 (2011)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The manuscript complies with ethical standards.
Funding
The author is supported by the National Cancer Institute at the National Institutes of Health (Grant Number RO1CA177984).
Conflict of interest
The author declares that there are no conflicts of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Saini, S. PSA and beyond: alternative prostate cancer biomarkers. Cell Oncol. 39, 97–106 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13402-016-0268-6
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13402-016-0268-6