Abstract
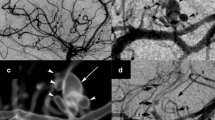
Varicella zoster virus (VZV) vasculopathy is caused by productive virus infection of cerebral arteries, leading to inflammation, pathological vascular remodeling, and ischemic or hemorrhagic stroke. VZV vasculopathy occurs in immunocompetent and immunocompromised individuals and involves both large and small vessels. MRI abnormalities include more deep-seated than superficial lesions, particularly at gray–white matter junctions, and lesions may enhance. Diagnosis is challenging, since stroke can occur months after zoster rash and in the absence of rash or CSF pleocytosis. The best virological test for diagnosis is detection of anti-VZV IgG antibody in the CSF. Pathological studies of VZV-infected arteries from patients with VZV vasculopathy reveal that the arterial adventitia is the initial site of infection, after which virus spreads transmuraly towards the lumen. Histological and immunohistochemical studies of VZV-infected arteries show a thickened intima, disrupted internal elastic lamina, and loss of smooth muscle cells, that likely contribute to weakening of the vessel wall and occlusion. Early in disease, VZV-infected arteries contain CD4+ and CD8+ T cells, macrophages, and rare B cells, in addition to abundant neutrophils in early disease. Importantly, perivascular inflammatory cells underlie the areas of thickened intima, raising the possibility that soluble factors secreted by these cells contribute to arterial remodeling. This review discusses the clinical features of VZV vasculopathy and potential mechanisms of VZV-induced cerebrovascular remodeling and stroke.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amlie-Lefond C, Kleinschmidt-DeMasters BK, Mahalingam R, Davis LE, Gilden D (1995) The vasculopathy of varicella-zoster virus encephalitis. Ann Neurol 37:784–790
Askalan R, Laughlin S, Mayank S, Chan A, MacGregor D, Andrew M, Curtis R, Meaney B, deVeber G (2001) Chickenpox and stroke in childhood: a study of frequency and causation. Stroke 32:1257–1262
Braun KP, Bulder MM, Chabrier S, Kirkham FJ, Uiterwaal CS, Tardieu M, Sébire G (2009) The course and outcome of unilateral intracranial arteriopathy in 79 children with ischaemic stroke. Brain 32:544–557
Dal Canto AJ, Swanson PE, O’Guin AK, Speck SH, Virgin HW (2001) IFN-gamma action in the media of the great elastic arteries: a novel immunoprivileged site. J Clin Invest 107:R15–R22
Devinsky O, Cho ES, Petito CK, Price RW (1991) Herpes zoster myelitis. Brain 114:1181–1196
Ferry G, Lonchampt M, Pennel L, de Nanteuil G, Canet E, Tucker GC (1997) Activation of MMP-9 by neutrophil elastase in an in vivo model of acute lung injury. FEBS Lett 402:111–115
Frid MG, Brunetti JA, Burke DL, Carpetner TC, Davie NJ, Reeves JT, Roedersheimer MT, van Rooijen N, Stenmark KR (2006) Hypoxia-induced pulmonary vascular remodeling requires recruitment of circulating mesenchymal precursors of a monocyte/macrophage lineage. Am J Pathol 168:659–669
Gilden DH, Vafai A, Shtram Y, Becker Y, Devlin M, Wellish M (1983) Varicella-zoster virus DNA in human sensory ganglia. Nature 306:478–480
Gilden D, Beinlich BR, Rubinstien EM, Stommel E, Swenson R, Rubinstein D, Mahalingam R (1994) Varicella-zoster virus myelitis: an expanding spectrum. Neurology 44:1818–1823
Gilden DH, Kleinschmidt-DeMasters BK, Wellish M, Hedley-Whyte ET, Rentier B, Mahalingam R (1996) Varicella zoster virus, a cause of waxing and waning vasculitis: the New England Journal of Medicine case 5–1995 revisited. Neurology 47:1441–1446
Gilden DH, Gesser R, Smith J, Wellish M, Laguardia JJ, Cohrs RJ, Mahalingam R (2001) Presence of VZV and HSV-1 DNA in human nodose and celiac ganglia. Virus Genes 23:145–147
Gilden D, Cohrs RJ, Mahalingam R, Nagel MA (2009) Varicella zoster virus vasculopathies: diverse clinical manifestations, laboratory features, pathogenesis, and treatment. Lancet Neurol 8:731–740
Gilden D, Cohrs RJ, Mahalingam R, Nagel MA (2010) Neurological disease produced by varicella zoster virus reactivation without rash. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol 342:243–253
Gray F, Mohr M, Rozenberg F, Belec L, Lescs MC, Dournon E, Sinclair E, Scaravilli F (1992) Varicella-zoster virus encephalitis in acquired immunodeficiency syndrome: report of four cases. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol 18:502–514
Gray F, Bélec L, Lescs MC, Chrétien F, Ciardi A, Hassine D, Flament-Saillour M, de Truchis P, Clair B, Scaravilli F (1994) Varicella-zoster virus infection of the central nervous system in the acquired immune deficiency syndrome. Brain 117:987–999
Hartney T, Birari R, Venkataraman S, Villegas L, Martinez M, Black SM, Stenmark KR, Nozik-Grayck E (2011) Xanthine oxidase-derived ROS upregulate Egr-1 via ERK1/2 in PA smooth muscle cells: model to test impact of extracellular ROS in chronic hypoxia. PLoS One 6:e27531
Haug A, Mahalingam R, Cohrs RJ, Schmid DS, Corboy JR, Gilden D (2010) Recurrent polymorphonuclear pleocytosis with increased red blood cells caused by varicella zoster virus infection of the central nervous system: case report and review of the literature. J Neurol Sci 292:85–88
Hsieh CC, Yen MH, Yen CH, Lau YT (2001) Oxidized low-xdensity lipoprotein induces apoptosis via generation of reactive oxygen species in vascular smooth muscle cells. Cardiovasc Res 49:135–145
Hyman RW, Ecker JR, Tenser RB (1983) Varicella-zoster virus RNA in human trigeminal ganglia. Lancet 2:814–816
Itoh Y, Nagase H (1995) Preferential inactivation of tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases-1 that is bound to the precursor of matrix metalloproteinase 9 (progelatinase B) by human neutrophil elastase. J Biol Chem 270:16518–16521
Kang JH, Ho JD, Chen YH, Lin HC (2009) Increased risk of stroke after a herpes zoster attack: a population-based follow-up study. Stroke 40:3443–3448
Kennedy PG, Grinfeld E, Gow JW (1998) Latent varicella-zoster virus is located predominantly in neurons in human trigeminal ganglia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 95:4658–4662
Li J, Li W, Su J, Liu W, Altura BT, Altura BM (2003) Hydrogen peroxide induces apoptosis in cerebral vascular smooth muscle cells: possible relation to neurodegenerative diseases and strokes. Brain Res Bull 62:101–106
Lin HC, Chien CW, Ho JD (2010) Herpes zoster ophthalmicus and the risk of stroke: a population-based follow-up study. Neurology 74:792–797
Mahalingam R, Wellish M, Wolf W, Dueland AN, Cohrs R, Vafai A, Gilden D (1990) Latent varicella-zoster viral DNA in human trigeminal and thoracic ganglia. N Engl J Med 323:627–631
Mathias M, Nagel MA, Khmeleva N, Boyer PJ, Choe A, Durairaj VD, Bennett JL, Mandava N, Gilden D (2013) VZV multifocal vasculopathy with ischemic optic neuropathy, acute retinal necrosis, and temporal artery infection in the absence of zoster rash. J Neurol Sci 325:180–182
Morgello S, Block GA, Price RW, Petito CK (1988) Varicella-zoster virus leukoencephalitis and cerebral vasculopathy. Arch Pathol Lab Med 112:173–177
Nagel MA, Forghani B, Mahalingam R, Wellish MC, Cohrs RJ, Russman AN, Katzan I, Lin R, Gardner CJ, Gilden DH (2007) The value of detecting anti-VZV IgG antibody in CSF to diagnose VZV vasculopathy. Neurology 68:1069–1073
Nagel MA, Cohrs RJ, Mahalingam R, Wellish MC, Forghani B, Schiller A, Safdieh JE, Kamenkovich E, Ostrow LW, Levy M, Greenberg B, Russman AN, Katzan I, Gardner CJ, Häusler M, Nau R, Saraya T, Wada H, Goto H, de Martino M, Ueno M, Brown WD, Terborg C, Gilden DH (2008) The varicella zoster virus vasculopathies: clinical, CSF, imaging, and virologic features. Neurology 70:853–860
Nagel MA, Traktinskiy I, Azarkh Y, Kleinschmidt-DeMasters B, Hedley-Whyte T, Russman A, VanEgmond EM, Stenmark K, Frid M, Mahalingam R, Wellish M, Choe A, Cordery-Cotter R, Cohrs RJ, Gilden D (2011) Varicella zoster virus vasculopathy: analysis of virus-infected arteries. Neurology 77:364–370
Nagel MA, Russman AN, Feit H, Traktinskiy I, Khmeleva N, Schmid DS, Skarf B, Gilden D (2013a) VZV ischemic optic neuropathy and subclinical temporal artery infection without rash. Neurology 80:220–222
Nagel MA, Bennett JL, Khmeleva N, Choe A, Rempel A, Boyer PJ, Gilden D (2013b) Multifocal VZV vasculopathy with temporal artery infection mimics giant cell arteritis. Neurology 80:2017–2021
Nagel MA, Choe A, Khmeleva N, Overton L, Rempel A, Wyborny A, Traktinskiy I, Gilden D (2013c) Search for varicella zoster virus and herpes simplex virus-1 in normal human cerebral arteries. J Neurovirol 19(2):181–5
Nagel MA, Traktinskiy I, Stenmark KR, Frid MG, Choe A, Gilden D (2013d) Varicella-zoster virus vasculopathy: immune characteristics of virus-infected arteries. Neurology 80:62–68
Okada G, Nakanishi Y (1989) Activation of matrix metalloproteinase 3 (stromelysin) and matrix metalloproteinase 2 ('gelatinase') by human neutrophil elastase and cathepsin I. FEBS Lett 249:353–356
Petito CK, Cho ES, Lemann W, Navia BA, Price RW (1986) Neuropathology of acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS): an autopsy review. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 45:635–646
Ryder JW, Croen K, Kleinschmidt-DeMasters BK, Ostrove JM, Straus SE, Cohn DL (1986) Progressive encephalitis three months after resolution of cutaneous zoster in a patient with AIDS. Ann Neurol 192:182–188
Salazar R, Russman AN, Nagel MA, Cohrs RJ, Mahalingam R, Schmid DS, Kleinschmidt-DeMasters BK, VanEgmond EM, Gilden D (2011) Varicella zoster virus ischemic optic neuroxpathy and subclinical temporal artery involvement. Arch Neurol 68:517–520
Stenmark KR, Frid MG, Yeager M, Li M, Riddle S, McKinsey T, El Kasmi KC (2012) Targeting the adventitial microenvironment in pulmonary hypertension: a potential approach to therapy that considers epigenetic change. Pulm Circ 2:3–14
Stevens DA, Ferrington RA, Jordan GW, Merigan TC (1975) Cellular events in zoster vesicles: relation to clinical course and immune parameters. J Infect Dis 131:509–515
Weber DS, Taniyama Y, Rocic P (2004) Phosphoinositide-dependent kinase 1 and p21-activated protein kinase mediate reactive oxygen species-dependent regulation of platelet-derived growth factor-induced smooth muscle cell migration. Circ Res 94:1219–1226
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by Public Health Service grant NS067070 to M.A.N. from the National Institutes of Health. I thank Marina Hoffman for editorial review and Lori DePriest for manuscript preparation.
Conflict of interest
The author has no conflicts of interest to report.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nagel, M.A. Varicella zoster virus vasculopathy: clinical features and pathogenesis. J. Neurovirol. 20, 157–163 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13365-013-0183-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13365-013-0183-9