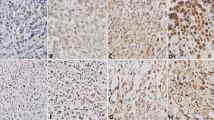
Abstract
Ezrin is a protein that functions as a cross-linker between actin cytoskeleton and plasma membrane. Its clinical role in osteosarcoma is unclear. The aim of this study was to investigate, in osteosarcoma, the prognostic value of ezrin expression at biopsy and changes in expression levels after preoperative chemotherapy. Thirty-eight newly diagnosed osteosarcoma patients aged 6–23 years were included. At diagnosis, 20 patients had localized disease, the others had distant metastases. Median follow-up was 75 months (range 13–135). Ezrin expression was assessed immunohistochemically in biopsy tissue and primary tumour specimens resected after chemotherapy. The influence on survival of changes in ezrin expression after chemotherapy was analysed. Ezrin expression was significantly higher after preoperative chemotherapy and changes compared to biopsy tissue were significantly lower in patients with early progression than in patients with relapse or no further evidence of disease (p = 0.006 and p = 0.002, respectively). Similarly, ezrin expression was higher after preoperative chemotherapy and exhibited less change in expression in deceased patients compared to patients surviving more than 5 years (both p = 0.001). Ezrin expression at biopsy was significantly associated with both histopathological aggressiveness (p < 0.001) and tumour size (p = 0.037). The results of this study provide evidence that changes in overexpression of ezrin due to preoperative chemotherapy could be a useful predictive and prognostic marker in patients with osteosarcoma.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gatta G, Botta L, Rossi S, Aareleid T, Bielska-Lasota M, Clavel J, Dimitrova N, Jakab Z, Kaatsch P, Lacour B, Mallone S, Marcos-Gragera R, Minicozzi P, Sánchez-Pérez MJ, Sant M, Santaquilani M, Stiller C, Tavilla A, Trama A, Visser O, Peris-Bonet R, the EUROCARE Working Group. Childhood cancer survival in Europe 1999-2007: results of EUROCARE-5-a population-based study. Lancet Oncol. 2014;15:35–47.
Jaffe N. Historical perspective on the introduction and use of chemotherapy for the treatment of osteosarcoma. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2014;804:1–30.
Bakhshi S, Radhakrishnan V. Prognostic markers in osteosarcoma. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther. 2010;10:271–87.
Meyers P. Prognostic factors for sarcomas: hard and soft. J Clin Oncol. 2002;20:627–9.
Bianchi E, Artico M, Di Cristofano C, Leopizzi M, Taurone S, Pucci M, Gobbi P, Mignini F, Petrozza V, Pindinello I, Conconi MT, Della RC. Growth factors, their receptor expression and markers for proliferation of endothelial and neoplastic cells in human osteosarcoma. Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol. 2013;26:621–32.
Yang J, Zhang W. New molecular insights into osteosarcoma targeted therapy. Curr Opin Oncol. 2013;25:398–406.
Ługowska I, Woźniak W, Klepacka T, Michalak E, Szamotulska K. A prognostic evaluation of vascular endothelial growth factor in children and young adults with osteosarcoma. Pediatr Blood Cancer. 2011;57:63–8.
Hunter KW. Ezrin, a key component in tumour metastasis. Trends Mol Med. 2004;10:201–4.
Bulut G, Hong SH, Chen K, Beauchamp EM, Rahim S, Kosturko GW, Glasgow E, Dakshanamurthy S, Lee HS, Daar I, Toretsky JA, Khannaand C, Üren A. Small molecule inhibitors of ezrin inhibit the invasive phenotype of osteosarcoma cells. Oncogene. 2012;31:269–81.
Singh V, Lin R, Yang J, Cha B, Sarker R, Tse CM, Donowitz M. AKT and GSK-3 are necessary for direct ezrin binding to NHE3 as part of a C-terminal stimulatory complex: role of a novel Ser-rich NHE3 C-terminal motif in NHE3 activity and trafficking. J Biol Chem. 2014;289:5449–61.
Ardura JA, Wang B, Watkins SC, Vilardaga JP, Friedman PA. Dynamic Na+-H+ exchanger regulatory factor-1 association and dissociation regulate parathyroid hormone receptor trafficking at membrane microdomains. J Biol Chem. 2011;286:35020–9.
Chiappetta C, Leopizzi M, Censi F, Puggioni C, Petrozza V, Carlo R, Di Cristofano C. Correlation of the Rac1/RhoA pathway with ezrin expression in osteosarcoma. Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol. 2014;22:162–70.
Briggs JW, Ren L, Nguyen R, Chakrabarti K, Cassavaugh J, Rahim S, Bulut G, Zhou M, Veenstra TD, Chen Q, Wei JS, Khan J, Uren A, Khanna C. The ezrin metastatic phenotype is associated with the initiation of protein translation. Neoplasia. 2012;14:297–310.
Köbel M, Gradhand E, Zeng K, Schmitt W, Kriese K, Lantzsch T, Wolters M, Dittmer J, Strauss HGMD, Thomssen C, Hauptmann S. Ezrin promotes ovarian carcinoma cell invasion and its retained expression predicts poor prognosis in ovarian carcinoma. Int J Gynecol Pathol. 2006;25:121–30.
Carneiro A, Bendahl PO, Åkerman M, Domanski HA, Rydholm A, Engellau J, Nilbert M. Ezrin expression predicts local recurrence and development of metastases in soft tissue sarcomas. J Clin Pathol. 2011;64:689–94.
Ma L, Liu YP, Zhang XH, Geng CZ, Li ZH. Relationship of RhoA signaling activity with ezrin expression and its significance in the prognosis for breast cancer patients. Chin Med J. 2013;126:242–7.
Zhu L, Ito T, Nakahara T, Nagae K, Fuyuno Y, Nakao M, Akahoshi M, Nakagawa R, Tu Y, Uchi H, Furue M. Upregulation of S100P, receptor for advanced glycation end products and ezrin in malignant melanoma. J Dermatol. 2013;40:973–9.
Khanna C, Wan X, Bose S, Cassaday R, Olomu O, Mendoza A, Yeung C, Gorlick R, Hewitt SM, Helman LJ. The membrane-cytoskeleton linker ezrin is necessary for osteosarcoma metastasis. Nat Med. 2004;10:182–6.
Pignochino Y, Grignani G, Cavalloni G, Motta M, Tapparo M, Bruno S, Bottos A, Gammaitoni L, Migliardi G, Camussi G, Alberghini M, Torchio B, Ferrari S, Bussolino F, Fagioli F, Picci P, Aglietta M. Sorafenib blocks tumour growth, angiogenesis and metastatic potential in preclinical models of osteosarcoma through a mechanism potentially involving the inhibition of ERK1/2, MCL-1 and ezrin pathways. Mol Cancer. 2009;8:118.
Paige M, Kosturko G, Bulut G, Miessau M, Rahim S, Toretsky JA, Brown ML, Üren A. Design, synthesis and biological evaluation of ezrin inhibitors targeting metastatic osteosarcoma. Bioorg Med Chem. 2014;22:478–87.
Park HR, Jung WW, Bacchini P, Bertoni F, Kim YW, Park YK. Ezrin in osteosarcoma: comparison between conventional high-grade and central low-grade osteosarcoma. Pathol Res Pract. 2006;202:509–15.
Wang YF, Shen JN, Xie XB, Wang J, Huang G. Expression change of ezrin as a prognostic factor in primary osteosarcoma. Med Oncol. 2011;28:636–43.
Khanna C, Khan J, Nguyen P, Prehn J, Caylor J, Yeung C, Trepel J, Meltzer P, Helman L. Metastasis-associated differences in gene expression in a murine model of osteosarcoma. Cancer Res. 2001;61:3750–9.
Leonard P, Sharp T, Henderson S, Hewitt D, Pringle J, Sandison A, Goodship A, Whelan J, Boshoff C. Gene expression array profile of human osteosarcoma. Br J Cancer. 2003;89:2284–8.
Mu Y, Zhang H, Che L, Li K. Clinical significance of microRNA-183/ezrin axis in judging the prognosis of patients with osteosarcoma. Med Oncol. 2014;31:1–7.
Salas S, de Pinieux G, Gomez-Brouchet A, Larrousserie F, Leroy X, Aubert S, Decouvelaere AV, Giorgi R, Fernandez C, Bouvieret C. Ezrin immunohistochemical expression in cartilaginous tumours: a useful tool for differential diagnosis between chondroblastic osteosarcoma and chondrosarcoma. Virchows Arch. 2009;454:81–7.
Xu-Dong S, Zan S, Shui-er Z, Li-na T, Wen-xi Y, Feng L, Yang Y. Expression of ezrin correlates with lung metastasis in Chinese patients with osteosarcoma. Clin Invest Med. 2009;32:180–8.
Ferrari S, Zanella L, Alberghini M, Palmerini E, Staals E, Bacchini P. Prognostic significance of immunohistochemical expression of ezrin in non-metastatic high-grade osteosarcoma. Pediatr Blood Cancer. 2008;50:752–6.
Salas S, Bartoli C, Deville JL, Gaudart J, Fina F, Calisti A, Bollini G, Curvale G, Gentet JC, Duffaud F, Figarella-Branger D, Bouvier C. Ezrin and alpha-smooth muscle actin are immunohistochemical prognostic markers in conventional osteosarcomas. Virchows Arch. 2007;451:999–1007.
Kim MS, Song WS, Cho WH, Lee SY, Jeon DG. Ezrin expression predicts survival in stage IIB osteosarcomas. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2007;459:229–36.
Le Guellec S, Moyal ECJ, Filleron T, Delisle MB, Chevreau C, Rubie H, Castex MP, Sales de Gauzy J, Bonnevialle P, Gomez-Brouchet A. The β5/focal adhesion kinase/glycogen synthase kinase 3β integrin pathway in high-grade osteosarcoma: a protein expression profile predictive of response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy. Hum Pathol. 2013;44:2149–58.
Wang Z, He ML, Zhao JM, Qing HH, Wu Y. Meta-analysis of associations of the ezrin gene with human osteosarcoma response to chemotherapy and prognosis. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2013;14:2753–8.
Lun DX, Hu YC, Xu ZW, Xu LN, Wang BW. The prognostic value of elevated ezrin in patients with osteosarcoma. Tumour Biol. 2014;35:1263–6.
Park HR, Cabrini RL, Araujo ES, Paparella ML, Brandizzi D, Park YK. Expression of ezrin and metastatic tumour antigen in osteosarcomas of the jaw. Tumori. 2009;95:81.
Boldrini E, Peres SV, Morini S, de Camargo B. Immunoexpression of ezrin and CD44 in patients with osteosarcoma. J Pediatr Hematol Oncol. 2010;32:E213–7.
Ren L, Khanna C. Role of ezrin in osteosarcoma metastasis. In: Kleinerman ES, editor. Current advances in osteosarcoma. Springer International Publishing; 2014. pp. 181–201.
Shang X, Wang Y, Zhao Q, Wu K, Li X, Ji X, He R, Zhang W. siRNAs target sites selection of ezrin and the influence of RNA interference on ezrin expression and biological characters of osteosarcoma cells. Mol Cell Biochem. 2012;364:363–71.
Wang Y, Shen J, Shang X, Wang J, Li J, Yin J, Zou C. Ezrin mRNA target site selection for DNAzymes using secondary structure and hybridization thermodynamics. Tumour Biol. 2011;324:809–17.
Abdou AG, Kandil M, Asaad NY, Dawoud MM, Shahin AA, Abd Eldayem AF. The prognostic role of ezrin and HER2/neu expression in osteosarcoma. Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol. 2016;24(5):355–63.
Li J, Wei K, Yu H, Jin D, Wang G, Yu B. Prognostic value of ezrin in various cancers: a systematic review and updated meta-analysis. Sci Rep. 2015;5:17903.
Acknowledgment
The study was financially supported by the research grant of National Science Centre (grant number: N N407 144838).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Financial support
The study was funded by the research grant of National Science Centre: grant number: N N407 144838.
Conflicts of interest
None
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lugowska, I., Mierzejewska, E., Lenarcik, M. et al. The clinical significance of changes in ezrin expression in osteosarcoma of children and young adults. Tumor Biol. 37, 12071–12078 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-016-5091-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-016-5091-1