Abstract
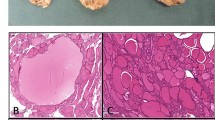
Napsin A and thyroid transcription factor-1 (TTF-1) are useful biomarkers for differentiating lung adenocarcinoma from squamous cell carcinoma and also for differentiating primary lung adenocarcinoma from metastatic lung carcinoma. Pair-boxed 8 (PAX8) can help in distinguishing primary lung carcinoma from metastatic carcinomas and help to determine the primary sites of metastatic carcinomas. Immunohistochemistry for Napsin A, TTF-1, and PAX8 were performed on 193 cases of carcinoma: 50 primary lung carcinoma and 143 carcinomas from other sites. Napsin A and TTF-1 were positive in 54, 52 % of lung carcinomas cases, respectively. While in adenocarcinoma cases, their expressions were 86.7 and 83.3 %, respectively. PAX8 was negative in all lung carcinomas. TTF-1 and PAX8 were positive in 93.3 and 96.7 % of thyroid carcinoma cases and in 87.5 and 93.8 % of papillary carcinoma respectively, and both were positive in 100 % of follicular carcinoma. Napsin A was negative in all thyroid carcinomas. Napsin A and PAX8 were positive in 50 and 93.3 % of renal carcinoma cases and in 81.8 and 100 % of papillary carcinoma, 38.5 and 92.3 % of clear cell carcinoma, and 16.7 and 83.3 % of chromophobe carcinoma respectively. TTF-1 was negative in all renal carcinomas. PAX8 was positive in 80 % of ovarian carcinoma cases; 100 and 60 % of serous mucinous carcinomas, respectively. It was also positive in 100 % of endometrial carcinoma. Napsin A and TTF-1 were negative in both ovarian and endometrial carcinomas. Our data demonstrated that combined use of Napsin A, TTF-1, and PAX8 may help in differentiating between primary lung adenocarcinoma and metastatic lung carcinomas.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bishop JA, Sharma R, Illei PB. Napsin A and thyroid transcription factor-1 expression in carcinomas of the lung, breast, pancreas, colon, kidney, thyroid, and malignant mesothelioma. Hum Pathol. 2010;41(1):20–5.
Brown AF, Sirohi D, Fukuoka J, Cagle PT, Policarpio-Nicolas M, Tacha D, et al. Tissue-preserving antibody cocktails to differentiate primary squamous cell carcinoma, adenocarcinoma, and small cell carcinoma of lung. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2013;137(9):1274–81.
Mukhopadhyay S, Katzenstein AL. Subclassification of non-small cell lung carcinomas lacking morphologic differentiation on biopsy specimens: utility of an immunohistochemical panel containing TTF-1, napsin A, p63, and CK5/6. Am J Surg Pathol. 2011;35(1):15–25.
Stang A, Pohlabeln H, Muller KM, Jahn I, Giersiepen K, Jockel KH. Diagnostic agreement in the histopathological evaluation of lung cancer tissue in a population-based case–control study. Lung Cancer. 2006;52(1):29–36.
Antic T, Gong Y, Sneige N. Tumor type and single cell/mesothelial-like cell pattern of breast carcinoma metastases in pleural and peritoneal effusions. Diagn Cytopathol. 2012;40(4):311–5.
Varadhachary GR, Abbruzzese JL, Lenzi R. Diagnostic strategies for unknown primary cancer. Cancer. 2004;100(9):1776–85.
Ye J, Hameed O, Findeis-Hosey JJ, Fan L, Li F, McMahon LA, et al. Diagnostic utility of PAX8, TTF-1 and Napsin A for discriminating metastatic carcinoma from primary adenocarcinoma of the lung. Biotech Histochem. 2012;87(1):30–4.
Loo PS, Thomas SC, Nicolson MC, Fyfe MN, Kerr KM. Subtyping of undifferentiated non-small cell carcinomas in bronchial biopsy specimens. J Thorac Oncol. 2010;5(4):442–7.
Stoll LM, Johnson MW, Gabrielson E, Askin F, Clark DP, Li QK. The utility of Napsin-A in the identification of primary and metastaticlung adenocarcinoma among cytologically poorly differentiated carcinomas. Cancer Cytopathol. 2010;118(6):441–9.
Bishop JA, Benjamin H, Cholakh H, Chajut A, Clark DP, Westra WH. Accurate classification of non-small cell lung carcinoma using a novel microRNA-based approach. Clin Cancer Res. 2013;16(2):610–9.
Hirano T, Gong Y, Yoshida K, Kato Y, Yashima K, Maeda M, et al. Usefulness of TAO2 (napsin A) to distinguish primary lung adenocarcinoma from metastatic lung adenocarcinoma. Lung Cancer. 2003;41(2):155–62.
Ye J, Findeis-Hosey JJ, Yang Q, McMahon LA, Yao JL, Li F, et al. Combination of napsin A and TTF-1immunohistochemistry helps in differentiating primary lung adenocarcinoma from metastatic carcinoma in the lung. Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol. 2011;19(4):313–7.
Gu K, Shah V, Ma C, Zhang L, Yang M. Cytoplasmic immunoreactivity of thyroid transcription factor-1 (clone 8G7G3/1) in hepatocytes true positivity or cross-reaction? Am J Clin Pathol. 2007;128(3):382–8.
DeFelice M, Silberschmidt D, DiLauro R, Xu Y, Wert SE, Weaver TE, et al. TTF-1 phosphorylation is required for peripheral lung morphogenesis, perinatal survival, and tissue-specific gene expression. J Biol Chem. 2003;278(37):35574–83.
Turner BM, Cagle PT, Sainz IM, Fukuoka J, Shen SS, Jagirdar J. Napsin A, a new marker for lung adenocarcinoma, is complementary and more sensitive and specific than thyroid transcription factor 1 in the differential diagnosis of primary pulmonary carcinoma: evaluation of 1674 cases by tissue microarray. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2012;136(2):163–71.
Kim MJ, Shin HC, Shin KC, Ro JY. Best immunohistochemical panel in distinguishing adenocarcinoma from squamous cell carcinoma of lung: tissue microarray assay in resected lung cancer specimens. Ann Diagn Pathol. 2013;17(1):85–90.
Ao MH, Zhang H, Sakowski L, Sharma R, Illei PB, Gabrielson E, et al. The utility of a novel triple marker (combination of TTF1, napsin A, and p40) in the subclassification of non-small cell lung cancer. Hum Pathol. 2014;45(5):926–34.
Sun T, Xie H, Kong L. Role of p40 (ΔNP63), p63, thyroid transcritpion factor-1 and Napsin A in differential diagnosis between lung squamous cell carcinoma and lung adenocarcinoma. Acta Med Mediterr. 2014;30:923–7.
Nitsch R, Di Dato V, di Gennaro A, de Cristofaro T, Abbondante S, De Felice M, et al. Comparative genomics reveals a functional thyroidspecific element in the far upstream region of the PAX8 gene. BMC Genomics. 2010;11:306.
Albadine R, Schultz L, Illei P, Ertoy D, Hicks J, Sharma R, et al. PAX8 (+)/p63 (−) immunostaining pattern in renal collecting duct carcinoma (CDC): a useful immunoprofile in the differential diagnosis of CDC versus urothelial carcinoma of upper urinary tract. Am J Surg Pathol. 2010;34(7):965–9.
Lotan TL, Ye H, Melamed J, Wu XR, Shih Ie M, Epstein JI. Immunohistochemical panel to identify the primary site of invasive micropapillary carcinoma. Am J Surg Pathol. 2009;33(7):1037–41.
Ozcan A, Shen SS, Hamilton C, Anjana K, Coffey D, Krishnan B, et al. PAX 8 expression in non-neoplastic tissues, primary tumors, and metastatic tumors: a comprehensive immunohistochemical study. Mod Pathol. 2011;24(6):751–64.
Laury AR, Perets R, Piao H, Krane JF, Barletta JA, French C, et al. A comprehensive analysis of PAX8 expression in human epithelial tumors. Am J Surg Pathol. 2011;35(6):816–26.
Heidarpour M, Tavanafar Z. Diagnostic utility of PAX8 in differentiation of mullerian from non-mullerian tumors. Adv Biomed Res. 2014;3:96.
Zhang P, Han YP, Huang L, Li Q, Ma DL. Value of Napsin A and thyroid transcription factor-1 in the identification of primary lung adenocarcinoma. Oncol Lett. 2010;1(5):899–903.
Siami K, McCluggage WG, Ordonez NG, Euscher ED, Malpica A, Sneige N, et al. Thyroid transcription factor-1 expression in endometrial and endocervical adenocarcinomas. Am J Surg Pathol. 2007;31(11):1759–63.
Bowen NJ, Logani S, Dickerson EB, Kapa LB, Akhtar M, Benigno BB, et al. Emerging roles for PAX8 in ovarian cancer and endosalpingeal development. Gynecol Oncol. 2007;104(2):331–7.
Nonaka D, Tang Y, Chiriboga L, Rivera M, Ghossein R. Diagnostic utility of thyroid transcription factors Pax8 and TTF-2 (FoxE1) in thyroid epithelial neoplasms. Mod Pathol. 2008;21(2):192–200.
Laury AR, Hornick JL, Perets R, Krane JF, Corson J, Drapkin R, et al. PAX 8 reliably distinguishes ovarian serous tumors from malignant mesothelioma. Am J Surg Pathol. 2010;34(5):627–35.
Wiseman W, Michael CW, Roh MH. Diagnostic utility of PAX8 and PAX2 immunohistochemistry in the identification of metastatic Müllerian carcinoma in effusions. Diagn Cytopathol. 2011;39(9):651–6.
Terry J, Leung S, Laskin J, Leslie KO, Gown AM, Ionescu DN. Optimal immunohistochemical markers for distinguishing lung adenocarcinomas from squamous cell carcinomas in small tumor samples. Am J Surg Pathol. 2010;34(12):1805–11.
Kim GY, Lim SJ, Kim WS, Lee GK. A minimal immunohistochemical panel for subtyping poorly differentiated non-small cell lung carcinoma: a tissue microarray study simulating small biopsy conditions. J Lung Cancer. 2012;11(1):21–32.
Downey P, Cummins R, Moran M, Gulmann C. If it’s not CK5/6 positive, TTF-1 negative it’s not a squamous cell carcinoma of lung. APMIS. 2008;116(6):526–9.
Tacha D, Zhou D, Cheng L. Expression of PAX8 in normal and neoplastic tissues: a comprehensive immunohistochemical study. Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol. 2011;19(4):293–9.
Ozcan A, de la Roza G, Ro JY, Shen SS, Truong LD. PAX2 and PAX8 expression in primary and metastatic renal tumors: a comprehensive comparison. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2012;136(12):1541–51.
Knoepp SM, Kunju LP, Roh MH. Utility of PAX8 and PAX2 immunohistochemistry in the identification of renal cell carcinoma in diagnostic cytology. Diagn Cytopathol. 2012;40(8):667–72.
Liliac L, Carcangiu ML, Canevari S, Căruntu ID, Ciobanu Apostol DG, Danciu M, et al. The value of PAX8 and WT1 molecules in ovarian cancer diagnosis. Rom J Morphol Embryol. 2013;54(1):17–27.
Wang M, Ma H, Pan Y, Xiao W, Li J, Yu J, et al. PAX2 and PAX8 reliably distinguishes ovarian serous tumors from mucinous tumors. Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol. 2015;23(4):280–7.
Tong GX, Devaraj K, Hamele-Bena D, Yu WM, Turk A, Chen X, et al. Pax8: a marker for carcinoma of Müllerian origin in serous effusions. Diagn Cytopathol. 2011;39(8):567–74.
Xiang L, Kong B. PAX8 is a novel marker for differentiating between various types of tumor, particularly ovarian epithelial carcinomas. Oncol Lett. 2013;5(3):735–8.
Conflict of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
El-Maqsoud, N.M.R.A., Tawfiek, E.R., Abdelmeged, A. et al. The diagnostic utility of the triple markers Napsin A, TTF-1, and PAX8 in differentiating between primary and metastatic lung carcinomas. Tumor Biol. 37, 3123–3134 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-015-3964-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-015-3964-3