Abstract
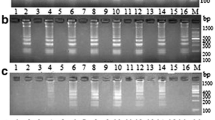
Vibrio vulnificus is an estuarine bacterial pathogen for human. The rapid, specific and sensitive detection of V. vulnificus is urgently needed for early disease diagnosis and timely treatment of V. vulnificus infection. In the study, a loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP) technique was developed for V. vulnificus detection with a set of primers, composed of two out primers and two inner primers targeted to vvhA gene. The optimal amplification temperature was 63°C and the reaction only took 35 min. The amplification products could not only be detected by agarose gel electrophoresis with ladder-like pattern bands, but also could be visualized using calcein with naked eye directly. Forty-five strains were tested for the specificity of LAMP assay, and all the V. vulnificus strains were identified correctly while other strains were negative results. The sensitive of the new LAMP assay was 100-fold more sensitive than the conventional PCR. Meanwhile, all the V. vulnificus strains were detected correctly in spiked, clinical and environmental samples by the new LAMP assay. Compared with other well-known techniques, the new LAMP assay targeted to vvhA gene was extremely rapid, simple, sensitive and specific for V. vulnificus identification.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Böer S I, Heinemeyer E A, Luden K, et al. 2013. Temporal and spatial distribution patterns of potentially pathogenic Vibrio spp. at recreational beaches of the German north sea. Microb Ecol, 65(4): 1052–1067
Endo S, Komori T, Ricci G, et al. 2004. Detection of gp43 of Paracoccidioides brasiliensis by the loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP) method. FEMS Microbiol Lett, 234(1): 93–97
Hara-Kudo Y, Yoshino M, Kojima T, et al. 2005. Loop-mediated isothermal amplification for the rapid detection of Salmonella. FEMS Microbiol Lett, 253(1): 155–161
Iwamoto T, Sonobe T, Hayashi K. 2003. Loop-mediated isothermal amplification for direct detection of Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex, M. avium, and M. intracellulare in sputum samples. J Clin Microbiol, 41(6): 2616–2622
Jaroenram W, Kiatpathomchai W, Flegel T W. 2009. Rapid and sensitive detection of white spot syndrome virus by loop-mediated isothermal amplification combined with a lateral flow dipstick. Mol Cell Probes, 23(2): 65–70
Jones E H, Feldman K A, Palmer A, et al. 2013. Vibrio infections and surveillance in Maryland, 2002–2008. Public Health Rep, 128(6): 537–545
Kim H R, Rho H W, Jeong M H, et al. 1993. Hemolytic mechanism of cytolysin produced from V. vulnificus. Life Sci, 53(7): 571–577
Kim J R, Oh D R, Cha M H, et al. 2008. Protective effect of polygoni cuspidati radix and emodin on Vibrio vulnificus cytotoxicity and infection. J Microbiol, 46(6): 737–743
Lee S E, Ryu P Y, Kim S Y, et al. 2004. Production of Vibrio vulnificus hemolysin in vivo and its pathogenic significance. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 324(1): 86–91
Li Yongjun, Zheng Zejun, Zhao Yulong, et al. 2010. A culture-free method for detection of Vibrio vulnificus from coastal seawater based on loop-mediated isothermal amplification targeting vcgC gene. Acta Oceanol Sin, 29(2): 93–97
Ma Y, Dai T, Serwadda A, et al. 2016. Detecting a novel Eriocheir sinensis reovirus by reverse transcription loop-mediated isothermal amplification assay. Lett Appl Microbiol, 63(5): 363–368
Notomi T, Okayama H, Masubuchi H, et al. 2000. Loop-mediated iso-thermal amplification of DNA. Nucleic Acids Res, 28(12): e63
O’Hara C M, Sowers E G, Bopp C A, et al. 2003. Accuracy of six commercially available systems for identification of members of the family Vibrionaceae. J Clin Microbiol, 41(12): 5654–5659
Richards G P, Nuñez A. 2006. Specificity of a Vibrio vulnificus aminopeptidase toward kinins and other peptidyl substrates. J Bacteriol, 188(6): 2056–2062
Shinoda S, Miyoshi S I, Yamanaka H, et al. 1985. Some properties of Vibrio vulnificus hemolysin. Microbiol Immunol, 29(7): 583–590
Srisuk C, Chaivisuthangkura P, Rukpratanporn S, et al. 2010. Rapid and sensitive detection of Vibrio cholerae by loop-mediated isothermal amplification targeted to the gene of outer membrane protein ompW. Lett Appl Microbiol, 50(1): 36–42
Sugiyama H, Kashimoto T, Ueno S, et al. 2011. Relationship between localization on cellular membranes and cytotoxicity of Vibrio vulnificus hemolysin. PLoS One, 6(10): e26018
Sun Jiachun, Zheng Jing, Wang Guiming, et al. 2012. Apoptotic effect of Vibrio vulnificus cytolysin on A549 human lung adenocarcinoma cells. Mol Med Rep, 5(3): 668–674
Surasilp T, Longyant S, Rukpratanporn S, et al. 2011. Rapid and sensitive detection of Vibrio vulnificus by loop-mediated isothermal amplification combined with lateral flow dipstick targeted to rpoS gene. Mol Cell Probes, 25(4): 158–163
Thompson F L, Iida T, Swings J. 2004. Biodiversity of vibrios. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev, 68(3): 403–431
Yamazaki W, Ishibashi M, Kawahara R, et al. 2008a. Development of a loop-mediated isothermal amplification assay for sensitive and rapid detection of Vibrio parahaemolyticus. BMC Microbiol, 8: 163
Yamazaki W, Seto K, Taguchi M, et al. 2008b. Sensitive and rapid detection of cholera toxin-producing Vibrio cholerae using a loopmediated isothermal amplification. BMC Microbiol, 8: 94
Yano A, Ishimaru R, Hujikata R. 2007. Rapid and sensitive detection of heat-labile I and heat-stable I enterotoxin genes of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli by loop-mediated isothermal amplification. J Microbiol Methods, 68(2): 414–420
Yeh H Y, Shoemaker C A, Klesius P H. 2005. Evaluation of a loop-mediated isothermal amplification method for rapid detection of channel catfish Ictalurus punctatus important bacterial pathogen Edwardsiella ictaluri. J Microbiol Methods, 63(1): 36–44
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Foundation item: The Major PLA Research Project of “The 12th Five-Year Plan” for Medical Science Development under contract No. BWS12J014; the Primary Research & Development Plan of Shandong Province under contract No. 2016GSF121036.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, L., Wang, M., Cong, D. et al. Rapid, specific and sensitive detection of Vibrio vulnificus by loop-mediated isothermal amplification targeted to vvhA gene. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 37, 83–88 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13131-018-1182-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13131-018-1182-8