Abstract
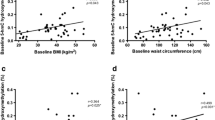
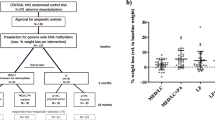
Obesity-associated adipose tissue enlargement is characterized by an enhanced proinflammatory status and an elevated secretion of adipokines such as leptin and cytokines such as tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-alpha. Among the different mechanisms that could underlie the interindividual differences in obesity, epigenetic regulation of gene expression has emerged as a potentially important determinant. Therefore, 27 obese women (age, 32–50 years; baseline body mass index, 34.4 ± 4.2 kg/m2) were prescribed an 8-week low-calorie diet, and epigenetic marks were assessed. Baseline and endpoint anthropometric parameters were measured, and blood samples were drawn. Genomic DNA and RNA from adipose tissue biopsies were isolated before and after the dietary intervention. Leptin and TNF-alpha promoter methylation were measured by MSP after bisulfite treatment, and gene expression was also analyzed. Obese women with a successful weight loss (≥5% of initial body weight, n = 21) improved the lipid profile and fat mass percentage (−12%, p < 0.05). Both systolic (−5%, p < 0.05) and diastolic (−8%, p < 0.01) blood pressures significantly decreased. At baseline, women with better response to the dietary intervention showed lower promoter methylation levels of leptin (−47%, p < 0.05) and TNF-alpha (−39%, p = 0.071) than the non-responder group (n = 6), while no differences were found between responder and non-responder group in leptin and TNF-alpha gene expression analysis. These data suggest that leptin and TNF-alpha methylation levels could be used as epigenetic biomarkers concerning the response to a low-calorie diet. Indeed, methylation profile could help to predict the susceptibility to weight loss as well as some comorbidities such as hypertension or type 2 diabetes.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abete I, Parra D, Martinez JA (2009) Legume-, fish-, or high-protein-based hypocaloric diets: effects on weight loss and mitochondrial oxidation in obese men. J Med Food 12:100–108
Abete I, Parra MD, Zulet MA, Martinez JA (2006) Different dietary strategies for weight loss in obesity: role of energy and macronutrient content. Nutr Res Rev 19:5–17
Ahima RS (2006) Adipose tissue as an endocrine organ. Obesity (Silver Spring) 14(Suppl 5):242S–249S
Ahmadian A, Ehn M, Hober S (2006) Pyrosequencing: history, biochemistry and future. Clin Chim Acta 363:83–94
Bautista LE, Vera LM, Arenas IA, Gamarra G (2005) Independent association between inflammatory markers (C-reactive protein, interleukin-6, and TNF-alpha) and essential hypertension. J Hum Hypertens 19:149–154
Boque N, Campion J, Paternain L, Garcia-Diaz DF, Galarraga M, Portillo MP et al (2009) Influence of dietary macronutrient composition on adiposity and cellularity of different fat depots in Wistar rats. J Physiol Biochem 65:387–395
Bouchard L, Rabasa-Lhoret R, Faraj M, Lavoie ME, Mill J, Perusse L et al (2010) Differential epigenomic and transcriptomic responses in subcutaneous adipose tissue between low and high responders to caloric restriction. Am J Clin Nutr 91:309–320
Bouchard L, Thibault S, Guay SP, Santure M, Monpetit A, St-Pierre J et al (2010) Leptin gene epigenetic adaptation to impaired glucose metabolism during pregnancy. Diab Care 33:2436–2441
Caiafa P, Zampieri M (2005) DNA methylation and chromatin structure: the puzzling CpG islands. J Cell Biochem 94:257–265
Campion J, Milagro FI, Goyenechea E, Martinez JA (2009) TNF-alpha promoter methylation as a predictive biomarker for weight-loss response. Obesity (Silver Spring) 17:1293–1297
Campion J, Milagro FI, Martinez JA (2009) Individuality and epigenetics in obesity. Obes Rev 10:383–392
Campion J, Milagro F, Martinez JA (2010) Epigenetics and obesity. Prog Mol Biol Transl Sci 94:291–347
Esteller M (2008) Epigenetics in cancer. N Engl J Med 358:1148–1159
Fortuno A, Rodriguez A, Gomez-Ambrosi J, Fruhbeck G, Diez J (2003) Adipose tissue as an endocrine organ: role of leptin and adiponectin in the pathogenesis of cardiovascular diseases. J Physiol Biochem 59:51–60
Franco R, Schoneveld O, Georgakilas AG, Panayiotidis MI (2008) Oxidative stress, DNA methylation and carcinogenesis. Cancer Lett 266:6–11
Frommer M, McDonald LE, Millar DS, Collis CM, Watt F, Grigg GW et al (1992) A genomic sequencing protocol that yields a positive display of 5-methylcytosine residues in individual DNA strands. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 89:1827–1831
Godfrey KM, Lillycrop KA, Burdge GC, Gluckman PD, Hanson MA (2007) Epigenetic mechanisms and the mismatch concept of the developmental origins of health and disease. Pediatr Res 61:5R–10R
Gurantz D, Cowling RT, Varki N, Frikovsky E, Moore CD, Greenberg BH (2005) IL-1beta and TNF-alpha upregulate angiotensin II type 1 (AT1) receptors on cardiac fibroblasts and are associated with increased AT1 density in the post-MI heart. J Mol Cell Cardiol 38:505–515
Herman JG, Graff JR, Myohanen S, Nelkin BD, Baylin SB (1996) Methylation-specific PCR: a novel PCR assay for methylation status of CpG islands. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93:9821–9826
Keyes MK, Jang H, Mason JB, Liu Z, Crott JW, Smith DE et al (2007) Older age and dietary folate are determinants of genomic and p16-specific DNA methylation in mouse colon. J Nutr 137:1713–1717
Knudson JD, Payne GA, Borbouse L, Tune JD (2008) Leptin and mechanisms of endothelial dysfunction and cardiovascular disease. Curr Hypertens Rep 10:434–439
Kubista M, Andrade JM, Bengtsson M, Forootan A, Jonak J, Lind K et al (2006) The real-time polymerase chain reaction. Mol Aspects Med 27:95–125
Labayen I, Diez N, Parra MD, Gonzalez A, Martinez JA (2004) Time-course changes in macronutrient metabolism induced by a nutritionally balanced low-calorie diet in obese women. Int J Food Sci Nutr 55:27–35
Li LC, Dahiya R (2002) MethPrimer: designing primers for methylation PCRs. Bioinformatics 18:1427–1431
Lomba A, Martinez JA, Garcia-Diaz DF, Paternain L, Marti A, Campion J et al (2010) Weight gain induced by an isocaloric pair-fed high fat diet: a nutriepigenetic study on FASN and NDUFB6 gene promoters. Mol Genet Metab 101:273–278
Lomba A, Milagro FI, Garcia-Diaz DF, Marti A, Campion J, Martinez JA (2010) Obesity induced by a pair-fed high fat sucrose diet: methylation and expression pattern of genes related to energy homeostasis. Lipids Health Dis 9:60
Marti A, Berraondo B, Martinez JA (1999) Leptin: physiological actions. J Physiol Biochem 55:43–49
Marti A, Martinez-Gonzalez MA, Martinez JA (2008) Interaction between genes and lifestyle factors on obesity. Proc Nutr Soc 67:1–8
Martinez JA, Parra MD, Santos JL, Moreno-Aliaga MJ, Marti A, Martinez-Gonzalez MA (2008) Genotype-dependent response to energy-restricted diets in obese subjects: towards personalized nutrition. Asia Pac J Clin Nutr 17(Suppl 1):119–122
Milagro FI, Campion J, Cordero P, Goyenechea E, Gomez-Uriz AM, Abete I, et al. (2011) A dual epigenomic approach for the search of obesity biomarkers: DNA methylation to diet-induced weight loss. FASEB J. doi:10.1096/fj.10-170365
Milagro FI, Campion J, Garcia-Diaz DF, Goyenechea E, Paternain L, Martinez JA (2009) High fat diet-induced obesity modifies the methylation pattern of leptin promoter in rats. J Physiol Biochem 65:1–9
Mutch DM, Temanni MR, Henegar C, Combes F, Pelloux V, Holst C et al (2007) Adipose gene expression prior to weight loss can differentiate and weakly predict dietary responders. PLoS ONE 2:e1344
Odrowaz-Sypniewska G (2007) Markers of pro-inflammatory and pro-thrombotic state in the diagnosis of metabolic syndrome. Adv Med Sci 52:246–250
Okada Y, Sakaue H, Nagare T, Kasuga M (2009) Diet-induced up-regulation of gene expression in adipocytes without changes in DNA methylation. Kobe J Med Sci 54:E241–E249
Richardson B (2003) Impact of aging on DNA methylation. Ageing Res Rev 2:245–261
Shahrzad S, Bertrand K, Minhas K, Coomber BL (2007) Induction of DNA hypomethylation by tumor hypoxia. Epigenetics 2:119–125
Stenvinkel P, Karimi M, Johansson S, Axelsson J, Suliman M, Lindholm B et al (2007) Impact of inflammation on epigenetic DNA methylation—a novel risk factor for cardiovascular disease? J Intern Med 261:488–499
Sullivan KE, Reddy AB, Dietzmann K, Suriano AR, Kocieda VP, Stewart M et al (2007) Epigenetic regulation of tumor necrosis factor alpha. Mol Cell Biol 27:5147–5160
Thaler R, Karlic H, Rust P, Haslberger AG (2009) Epigenetic regulation of human buccal mucosa mitochondrial superoxide dismutase gene expression by diet. Br J Nutr 101:743–749
Viguerie N, Vidal H, Arner P, Holst C, Verdich C, Avizou S et al (2005) Adipose tissue gene expression in obese subjects during low-fat and high-fat hypocaloric diets. Diabetologia 48:123–131
Xiong Z, Laird PW (1997) COBRA: a sensitive and quantitative DNA methylation assay. Nucleic Acids Res 25:2532–2534
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cordero, P., Campion, J., Milagro, F.I. et al. Leptin and TNF-alpha promoter methylation levels measured by MSP could predict the response to a low-calorie diet. J Physiol Biochem 67, 463–470 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13105-011-0084-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13105-011-0084-4