Abstract
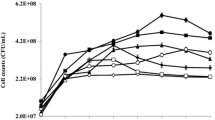
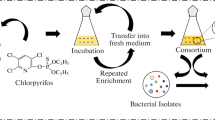
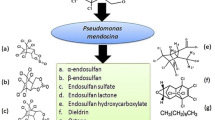
The environmental impact of chlorinated pesticides, including endosulfan, is not only caused by their persistency in the ecosystem but also from their toxic effects on off-target living organisms. In this study, three different strains of microorganisms, namely Afipia genosp, Sphingomonas yanoikuyae Q1 and Methylobacterium rhodesianum that are capable of biodegrading endosulfan at low concentrations (100 µg/L) from a tea cultivation field were reported. The isolated microbial consortium biodegraded 59% of the total endosulfan (63% α-endosulfan, 57% β-endosulfan) at pH 6.5. The same consortium biodegraded 98% of the total endosulfan (96% of α-endosulfan, 97% of β-endosulfan) at pH 8.4. All endosulfan removal performances were observed for a period of 25 days and the experiments were conducted at 25 °C, which was a relatively lower temperature compared to other endosulfan biodegradation studies in the literature. Additional carbon source did not change the overall endosulfan removal. No endosulfan sulfate production was observed during the study.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gupta, P.K., Gupta, R.C.: Pharmacology, toxicology and degradation of endosulfan A review. Toxicology 13(2), 115–130 (1979)
Sun, X., Zhu, L., Wang, J., Wand, J., Su, B., Du, Z., Dua, P.: Effects of endosulfan on the populations of cultivable microorganisms and the diversity of bacterial community structure in Brunisolic soil. Water Air Soil Pollut. 228, 169 (2017)
Falkowska, L., Reindl, A.R., Szumiło, E., Kwaśniak, J., Staniszewska, M., Bełdowska, M., Lewandowska, A., Krause, I.: Mercury and chlorinated pesticides on the highest level of the food web as exemplified by herring from the Southern Baltic and African penguins from the zoo. Water Air Soil Pollut. 224(5), 1549 (2013)
Weber, J., Halsall, C.J., Muir, D., Teixeira, C., Small, J., Solomon, K., Hermanson, M., Hung, H., Bidleman, T.: Endosulfan, a global pesticide: a review of its fate in the environment and occurrence in the Arctic. Sci. Total Environ. 408(15), 2966–2984 (2010)
Bajaj, A., Pathak, A., Mudiam, M.R., Mayilraj, S., Manickam, N.: Isolation and characterization of a Pseudomonas sp. strain IITR01 capable of degrading -endosulfan and endosulfan sulfate. J. Appl. Microbiol. 109(6), 2135–2143 (2010)
ATSDR.: Toxicological profile for endosulfan. U.S. Department of Health and Human Services Public Health Service Agency For Toxic Substances and Disease Registry, 323 (2015)
Mukherjee, I., Mittal, A.: Bioremediation of endosulfan using Aspergillus and Cladosporium oxysporum. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 75, 1034–1040 (2005)
Cotham, W.E.J., Bidleman, T.F.: Degradation of malathion, endosulfan and fenvelarate in seawater and sea water/sediment in microcosms. J. Agric. Food Chem. 37, 824–828 (1989)
Sutherland, T.D., Weir, K.M., Lacey, M.J., Horne, I., Russell, R.J., Oakeshott, J.G.: Enrichment of a microbial culture capable of degrading endosulphate, the toxic metabolite of endosulfan. J. Appl. Microbiol. 92, 541–548 (2002)
Shetty, P.K., Mitra, J., Murthy, N.B.K., Namitha, K.K., Savitha, K.N., Raghu, K.: Biodegradation of cyclodiene insecticide Endosulfan by Mucor thermohyalospora MTCC 1384. Curr. Sci. 79(9), 1381–1383 (2000)
Kaur, I., Mathur, R.P., Tandon, S.N.: Persistence of endosulfan (technical) in water and soil. Environ. Technol. 19, 115–119 (1998)
Taira, K., Hayase, N., Arimura, N., Yamashita, S., Miyazaki, T., Furukawa, K.: Cloning and nucleotide sequence of the 2,3-dihydroxybiphenyl dioxygenase gene from the PCB-degrading strain of Pseudomonas paucimobilis Q1. Biochemistry, 27, 3990–3996 (1998)
Kumar, M., Laksmi, C.V., Khanna, S.: Biodegradation and bioremediation of endosulfan contaminated soil. Biores. Technol. 99, 3116–3122 (2008)
Arshad, M., Hussain, S., Saleem, M.: Optimization of environmental parameters for biodegradation of alpha and beta endosulfan in soil slurry by Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J. Appl. Microbiol. 104(2), 364–370 (2008)
Elsaid, O.E.G., Abdelbagi, A.O., Elsheikhc, E.A.E.: Microbial degradation of endosulfan in carbon free media and selective media. Res. J. Agric. Biol. Sci. 6(3), 257–562 (2010)
Masoud, A.A., Abdel-Wahab Arafa, N.A., El-Bouraie, M.: Patterns and trends of the pesticide pollution of the shallow Nile Delta Aquifer (Egypt). Water Air Soil Pollut. 229, 148 (2018)
Sutherland, T.D., Horne, I., Lacey, M.J., Harcourt, R.L., Russell, R.J., Oakeshott, J.G.: Enrichment of an endosulfan-degrading mixed bacterial culture. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 66, 2822–2828 (2000)
Stefan, R.I., Atlas, R.M.: Polymerase chain reaction. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 45, 137–161 (1991)
Saitou, N., Nei, M.: The neighbor-joining method: a new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol. Biol. Evol. 4, 406–425 (1987)
EPA Method 508.1., Determination of Chlorinated Pesticides, Herbicides, and Organohalides by Liquid-Solid Extraction and Electron Capture Gas Chromatography -Revision 2.0.38 pp
Kwon, G.S., Sohn, H.Y., Shin, K.S., Kim, E., Seo, B.: Biodegradation of the organochlorine insecticide, endosulfan, and the toxic metabolite, endosulfan sulfate, by Klebsiella oxytoca KE-8. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 67, 845–850 (2005)
Lee, J.B., Sohn, H.Y., Shin, K.S., Jo, M.S., Kim, J.E.,. Lee, S.W., Shin, J.W., Kum, E.J., Kwon, G.S.: Isolation of a soil bacterium capable of biodegradation and detoxification of endosulfan and endosulfan sulfate. J. Agric. Food Chem. 54, 8824–8828 (2006)
Bergey, D.H., Holt, J.G.: Bergey’s Manual of Systematic Bacteriology. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Philadelphia p. 787 (1994)
Bodour, A.A., Wang, J.M., Brusseau, M.L., Maier, R.M.: Temporal change in culturable phenanthrene degraders in response to long-term exposure to phenanthrene in a soil column system. Environ. Microbiol. 5, 888–895 (2003)
Moosvi, S.A., McDonald, I.R., Pearce, D.A., Kelly, D.P., Wood, A.P.: Molecular detection and isolation from Antarctica of methylotrophic bacteria able to grow with methylated sulfur compounds. Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 28, 541–554 (2005)
Wittich, R.M., Wilkes, H., Sinnwell, V., Francke, W., Fortnagel, P.: Metabolism of dibenzo-p-dioxin by Sphingomonas sp. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. strain RW1, 58, 1005–1010 (1992)
Mohn, W.W.: Bacteria obtained from a sequencing batch reactor that are capable of growth on dehydroabietic acid. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 61, 2145–2150 (1995)
Imai, R., Nagata, Y., Fukuda, M., Takagi, M., Yano, K.: Molecular cloning of a Pseudomonas paucimobilis gene encoding a 17-kilodalton polypeptide that eliminates HCl molecules from gamma-hexachlorocyclohexane. J. Bacteriol. 173, 6811–6819 (1991)
Nohynek, L., Nurmiaho-Lassila, E., Suhonen, E., Busse, H., Mohammadi, M., Hantula, J.: Description of chlorophenol-degrading Pseudomonas sp. strains KF1T, KF3, and NKF1 as a new species of the genus Sphingomonas, Sphingomonas subarctica sp. nov.. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 46, 1042–1055 (1996)
Ka, J., Holben, W., Tiedje, J.: Genetic and phenotypic diversity of 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid (2,4-D)-degrading bacteria isolated from 2,4-D treated field soils. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 60, 1106–1115 (1994)
Khan, A., Wang, R., Cao, W., Franklin, W., Cerniglia, C.: Reclassification of a polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon-metabolizing bacterium, Beijerinckia sp. strain B1, as Sphingomonas yanoikuyae by fatty acid analysis, protein pattern analysis, DNADNA hybridization, and 16S ribosomal DNA sequencing. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 46, 466–469 (1996)
Green, P.N., Bousfield, I.J.: A taxonomic study of some gram-negative facultative methylotrophic bacteria. J. Gen. Microbiol. 128, 623–638 (1982)
Goswami, S., Singh, D.K.: Biodegradation of a and b endosulfan in broth medium and soil microcosm by bacterial strain Bordetella sp. Biodegradation B9, 20, 199–207 (2009)
Kataoka, R., Takagi, K.: Biodegradability and biodegradation pathways of endosulfan and endosulfan sulfate. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 97(8), 3285–3292 (2013)
Awasthi, N., Manickam, N., Kumar, A.: Biodegradation of endosulfan by a bacterial coculture. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 59(6), 928–934 (1997)
Kumar, M., Philip, L.: Endosulfan mineralization by bacterial isolates and possible degradation pathway identification. Bioremediat. J. 10(4), 179–190 (2006)
Bhalerao, T.S., Puranik, P.R.: Biodegradation of organochlorine pesticide, endosulfan, by a fungal soil isolate, Aspergillus niger. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 59(4), 315–321 (2007)
Singh, N.S., Singh, D.K.: Biodegradation of endosulfan and endosulfan sulfate by Achromobacter xylosoxidans strain C8B in broth medium. Biodegradation 22(5), 845–857 (2011)
Awasthi, N., Ahuja, R., Kumar, A.: Factors influencing the degradation of soil-applied endosulfan isomers. Soil Biol. Biochem. 32, 1697–1705 (2000)
Hussain, S., Arshad, M., Saleem, M., Zahir, Z.A.: Screening of soil fungi for in vitro degradation of endosulfan. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 23, 939–945 (2007)
Awasthi, N., Singh, A.K., Jain, R.K., Khangarot, B.S., Kumar, A.: Degradation and detoxification of endosulfan isomers by a defined co-culture of two Bacillus strains. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 62, 279–283 (2003)
Siddique, T., Okeke, B.C., Arshad, M., Frankenberger, W.T.J.: Biodegradation kinetics of endosulfan by Fusarium ventricosum and a Pandoraea species. J. Agric. Food Chem. 51(27), 8015–8019 (2003)
Kumar, K., Devi, S.S., Krishnamurthi, K., Kanade, G.S., Chakrabarti, T.: Enrichment and isolation of endosulfan Degrading and detoxifying bacteria. Chemosphere 68, 317–322 (2007)
Thangadurai, P., Suresh, S.: Biodegradation of endosulfan by soil bacterial cultures. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 94, 38–47 (2014)
Mukherjee, I., Gopal, M.: Degradation of beta-endosulfan by Aspergillus niger. Toxicol. Environ. Chem. 46, 217–221 (1994)
Katayama, A., Matsumura, F.: Degradation of organochlorine pesticides, particularly endosulfan, by Trichoderma harzianum. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 12(6), 1059–1065 (1993)
Kullman, S., Matsumura, F.: Metabolic pathways utilized by Phanerochaete chrysosporium for degradation of the cyclodiene pesticide endosulfan, Appl, Environ, Microbiol,, 593–600 (1996)
Guha, A., Kumari, B., Bora, T.C., Deka, P.C., Roy, M.K.: Bioremediation of endosulfan by Micrococcus sp. Indian J. Environ. Health 42, 9–12 (2000)
Lee, S.E., Kim, J.S., Kennedy, I.R., Park, J.W., Kwon, G.S., Koh, S.C., Kim, J.E.: Biotransformation of an organochlorine insecticide, endosulfan by Anabaena species. J. Agric. Food Chem. 51(5), 1336–1340 (2003)
Park, B.S., Lee, S.E.: Biotransformation of β-endosulfan by Anabaena sp. PCC 7120. Agric. Chem. Biotechnol. 47(1), 38–41 (2004)
Sethunathan, N., Megharaj, M., Chen, Z.L., Williams, B.D., Lewis, G., Naidu, R.: Algal degradation of a known endocrine disrupting insecticide, α-endosulfan, and its metabolite, endosulfan sulfate, in liquid medium and soil. J. Agric. Food Chem. 52, 3030–3035 (2004)
Weir, K.M., Sutherland, T.D., Horne, I., Russell, R.J., Oakeshott, J.G.: A single monooxygenase, Ese, is involved in the metabolism of the organochlorides endosulfan and endosulfate in an Arthrobacter sp. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 72, 3524–3530 (2006)
Kalyani, S., Sharma, J., Singh, S., Dureja, P.: Enrichment and isolation of endosulfan-degrading microorganism from tropical acid soil. J. Environ. Sci. Health B 44, 663–672 (2009)
Li, W., Dai, Y., Xue, B., Li, Y., Peng, X., Zhang, J., Yan, Y.: Biodegradation and detoxification of endosulfan in aqueous medium and soil by Achromobacter xylosoxidans strain CS5. J. Hazard. Mater. 167, 209–216 (2009)
Kong, L., Zhu, S., Zhu, L., Xie, H., Su, K., Yan, T., Wang, J., Wang, J., Wang, F., Sun, F.: Biodegradation of organochlorine pesticide endosulfan by bacterial strain Alcaligenes faecalis JBW4. J. Environ. Sci. 25(11), 2257–2264 (2013)
Narkhede, C.P., Patil, A.R., Koli, S., Suryawanshi, R., Wagh, N.D., Salunke, B.K., Patil, S.V.: Studies on endosulfan degradation by local isolate Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 4(2), 259–265 (2015)
Ito, K., Kawashima, F., Takagi, K., Kataoka, R., Kotake, M., Kiyota, H., Yamazaki, K., Sakakibara, F., Okada, S.: Isolation of endosulfan sulfate-degrading Rhodococcus koreensis strain S1-1 from endosulfan contaminated soil and identification of a novel metabolite, endosulfan diol monosulfate. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 473(4), 1094–1099 (2016)
Chauhan, A., Pathak, A., Ewida, A.Y., Griffiths, Z., Stothard, P.: Whole genome sequence analysis of an Alachlor and Endosulfan degrading Pseudomonas strain W15Feb9B isolated from Ochlockonee River. Florida. Genomics Data 8, 134–138 (2016)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bilgin, A., Sanin, S.L. Isolation and Identification of Endosulfan Degrading Native Bacterial Consortium from Agricultural Soils. Waste Biomass Valor 11, 3303–3313 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12649-019-00662-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12649-019-00662-5