Abstract
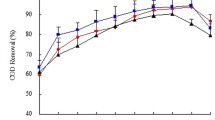
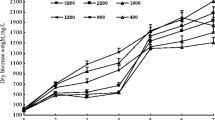
In this study, a semi-continuous photobioreactor was operated for the investigation of nutrient removal efficiency of a unialgal culture, Chlorella vulgarıs. Maximum nitrogen and phosphorous removal efficiencies of 99.6 and 91.2 % were achieved in the photobioreactor. The microalgal slurry obtained from the effluent of the photobioreactor was subjected to biochemical methane potential assay, after application of heat, autoclave, and thermochemical pretreatments to improve anaerobic digestibility and biogas production. Evaluation of pretreatment options indicated that heat pretreatment is the most efficient method in terms of enhancing anaerobic digestibility, at the chemical oxygen demand (COD) loading of 19 ± 0.5 g L−1. This method increased the methane yield by 83.0 %, from 223 to 408 mL CH4 g VS −1added , compared to untreated microalgal slurry reactor with the same COD value. Among reactors with 35 ± 1.5 g L−1 initial COD concentration, autoclave-pretreated microalgal slurry was found to yield the highest methane value of 356 mL CH4 g VS −1added , which was 43.0 % higher than the value observed in the reactor fed with untreated microalgal slurry. The thermochemical pretreatment caused production of inhibitory compounds and resulted in lower biomethane production and COD treatment values, compared to untreated microalgae. Outcomes of this study reveal that coupled micro-algal and anaerobic biotechnology could be a sustainable alternative for integrated nutrient removal and biofuel production applications.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- BM:
-
Basal medium
- BMP:
-
Biochemical methane potential
- CH4 :
-
Methane
- COD:
-
Chemical oxygen demand
- DO:
-
Dissolved oxygen
- GC:
-
Gas chromatograph
- HPLC:
-
High performance liquid chromatography
- N:
-
Nitrogen
- NaOH:
-
Sodium hydroxide
- NH3 :
-
Free ammonia
- NH4 + :
-
Ammonium ion
- NH4 +-N:
-
Ammonium-nitrogen
- NO3 − :
-
Nitrate ion
- NO3 −-N:
-
Nitrate-nitrogen
- OD:
-
Optical density
- P:
-
Phosphorus
- PAR:
-
Photosynthetically active radiation (nm)
- PO4 3− :
-
Phosphate ion
- PO4 3−-P:
-
Orthophosphate-phosphorus
- sCOD:
-
Soluble chemical oxygen demand
- SCP:
-
Semi-continuous cultivation photobioreactor
- S/X:
-
Substrate-to-inoculum ratio
- TAN:
-
Total ammonifiable nitrogen
- tCOD:
-
Total chemical oxygen demand
- TKN:
-
Total Kjeldahl nitrogen
- TN:
-
Total nitrogen
- TP:
-
Total phosphorus
- TS:
-
Total solids
- TSS:
-
Total suspended solids
- VFA:
-
Volatile fatty acids
- VDS:
-
Volatile dissolved solids
- VS:
-
Volatile solids
- VSS:
-
Volatile suspended solids
- vvm:
-
Volume of gas per volume of broth per minute
References
REN21. 2015: Renewables 2015 Global Status Report. Paris (2015)
Jung, H., Baek, G., Kim, J., Seung, S., Lee, C.: Mild-temperature thermochemical pretreatment of green macroalgal biomass: effects on solubilization, methanation, and microbial community structure. Bioresour. Technol. 199, 326–335 (2016)
Mahdy, A., Ballesteros, M., González-Fernández, C.: Enzymatic pretreatment of Chlorella vulgaris for biogas production: influence of urban wastewater as a sole nutrient source on macromolecular profile and biocatalyst efficiency. Bioresour. Technol. 199, 319–325 (2016)
Clarens, A.F., Resurreccion, E.P., White, M.A., Colosi, L.M.: Environmental life cycle comparison of algae to other bioenergy feedstocks. Environ. Sci. Technol. 44, 1813–1819 (2010)
Murphy, C.F., Allen, D.T.: Energy-water nexus for mass cultivation of algae. Environ. Sci. Technol. 45, 5861–5868 (2011)
Mata, T.M., Martins, A.A., Caetano, N.S.: Microalgae for biodiesel production and other applications: a review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 14, 217–232 (2010)
Mussgnug, J.H., Klassen, V., Schlüter, A., Kruse, O.: Microalgae as substrates for fermentative biogas production in a combined biorefinery concept. J. Biotechnol. 150, 51–56 (2010)
Holm-Nielsen, J.B., Al Seadi, T., Oleskowicz-Popiel, P.: The future of anaerobic digestion and biogas utilization. Bioresour. Technol. 100, 5478–5484 (2009)
Passos, F., Solé, M., García, J., Ferrer, I.: Biogas production from microalgae grown in wastewater: effect of microwave pretreatment. Appl. Energy 108, 168–175 (2013)
Alzate, M.E., Muñoz, R., Rogalla, F., Fdz-Polanco, F., Pérez-Elvira, S.I.: Biochemical methane potential of microalgae: influence of substrate to inoculum ratio, biomass concentration and pretreatment. Bioresour. Technol. 123, 488–494 (2012)
Chen, P.H., Oswald, W.J.: Thermochemıcal treatment for algal fermentation. Environ. Int. 24, 889–897 (1998)
Keymer, P., Ruffell, I., Pratt, S., Lant, P.: High pressure thermal hydrolysis as pre-treatment to increase the methane yield during anaerobic digestion of microalgae. Bioresour. Technol. 131, 128–133 (2013)
Demirer, G.N., Chen, S.: Anaerobic biogasification of undiluted dairy manure in leaching bed reactors. Waste Manag 28, 112–119 (2008)
Cai, T., Park, S.Y., Li, Y.: Nutrient recovery from wastewater streams by microalgae: status and prospects. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 19, 360–369 (2013)
Wang, L., Min, M., Li, Y., Chen, P., Chen, Y., Liu, Y., Wang, Y., Ruan, R.: Cultivation of green algae Chlorella sp. in different wastewaters from municipal wastewater treatment plant. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 162, 1174–1186 (2010)
Alcántara, C., García-Encina, P.A., Muñoz, R.: Evaluation of mass and energy balances in the integrated microalgae growth-anaerobic digestion process. Chem. Eng. J. 221, 238–246 (2013)
Passos, F., Ferrer, I.: Microalgae conversion to biogas: thermal pretreatment contribution on net energy production. Environ. Sci. Technol. 48, 7171–7178 (2014)
Tan, C.H., Show, P.L., Chang, J.S., Ling, T.C., Lan, J.C.W.: Novel approaches of producing bioenergies from microalgae: a recent review. Biotechnol. Adv. 33, 1219–1227 (2014)
Wiley, P.E., Campbell, J.E., McKuin, B.: Production of biodiesel and biogas from algae: a review of process train options. Water Environ. Res. 83, 326–338 (2011)
Demuez, M., Mahdy, A., Tomás-Pejó, E., González-Fernández, C., Ballesteros, M.: Enzymatic cell disruption of microalgae biomass in biorefinery processes. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 112, 1955–1966 (2015)
González-Fernández, C., Sialve, B., Bernet, N., Steyer, J.P.: Impact of microalgae characteristics on their conversion to biofuel. Part II: focus on biomethane production. Biofuels. Bioprod. Biorefining. 6, 246–256 (2012)
Domozych, D.S.: Algal cell walls. In: eLS. Wiley, Chichester (2011). doi:10.1002/9780470015902.a0000315.pub3
Passos, F., Uggetti, E., Carrère, H., Ferrer, I.: Pretreatment of microalgae to improve biogas production: a review. Bioresour. Technol. 172, 403–412 (2014)
Rodriguez, C., Alaswad, A., Mooney, J., Prescott, T., Olabi, A.G.: Pre-treatment techniques used for anaerobic digestion of algae. Fuel Process. Technol. 138, 765–779 (2015)
Mendez, L., Mahdy, A., Timmers, R.A., Ballesteros, M., González-Fernández, C.: Enhancing methane production of Chlorella vulgaris via thermochemical pretreatments. Bioresour. Technol. 149, 136–141 (2013)
Ometto, F., Quiroga, G., Pšenička, P., Whitton, R., Jefferson, B., Villa, R.: Impacts of microalgae pre-treatments for improved anaerobic digestion: thermal treatment, thermal hydrolysis, ultrasound and enzymatic hydrolysis. Water Res. 65, 350–361 (2014)
He, S., Fan, X., Katukuri, N.R., Yuan, X., Wang, F., Guo, R.-B.: Enhanced methane production from microalgal biomass by anaerobic bio-pretreatment. Bioresour. Technol. 204, 145–151 (2016)
González-Fernández, C., Sialve, B., Bernet, N., Steyer, J.P.: Comparison of ultrasound and thermal pretreatment of Scenedesmus biomass on methane production. Bioresour. Technol. 110, 610–616 (2012)
Passos, F., García, J., Ferrer, I.: Impact of low temperature pretreatment on the anaerobic digestion of microalgal biomass. Bioresour. Technol. 138, 79–86 (2013)
Schwede, S., Rehman, Z.-U., Gerber, M., Theiss, C., Span, R.: Effects of thermal pretreatment on anaerobic digestion of Nannochloropsis salina biomass. Bioresour. Technol. 143, 505–511 (2013)
Vlyssides, A.G., Karlis, P.K.: Thermal-alkaline solubilization of waste activated sludge as a pre-treatment stage for anaerobic digestion. Bioresour. Technol. 91, 201–206 (2004)
Calicioglu, O., Demirer, G.N.: Integrated nutrient removal and biogas production by Chlorella vulgaris cultures. J. Renew. Sustain. Energy 7, 1–14 (2015)
APHA: Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater. APHA, Washington (2005)
Davidsson, A., La Cour Jansen, J.: Pre-treatment of wastewater sludge before anaerobic digestion—hygienisation, ultrasonic treatment and enzyme dosing. Vatten 62, 335–340 (2006)
Yen, H.W., Brune, D.E.: Anaerobic co-digestion of algal sludge and waste paper to produce methane. Bioresour. Technol. 98, 130–134 (2007)
Clark, P.B., Hillman, P.F.: Enhancement of anaerobic digestion using duckweed (Lemna minor) enriched with ıron. Water Environ. J. 10, 92–95 (1996)
de Morais, M.G., Costa, J.A.V.: Carbon dioxide fixation by Chlorella kessleri, C. vulgaris, Scenedesmus obliquus and Spirulina sp. cultivated in flasks and vertical tubular photobioreactors. Biotechnol. Lett. 29, 1349–1352 (2007)
de Godos, I., Vargas, V.A., Guzman, H.O., Soto, R., Garcia, B., Garcia, P.A., Muñoz, R.: Assessing carbon and nitrogen removal in a novel anoxic–aerobic cyanobacterial–bacterial photobioreactor configuration with enhanced biomass sedimentation. Water Res. 61, 77–85 (2014)
Becker, E.W.: Microalgae: Biotechnology and Microbiology. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (2008)
Green, F.B., Lundquist, T.J., Oswald, W.J.: Energetics of advanced ıntegrated wastewater pond systems. Water Sci. Technol. 31, 9–20 (1995)
Li, C., Yang, H., Li, Y., Cheng, L., Zhang, M., Zhang, L., Wang, W.: Novel bioconversions of municipal effluent and CO2 into protein riched Chlorella vulgaris biomass. Bioresour. Technol. 132, 171–177 (2013)
Wang, Y., Guo, W., Cheng, C.L., Ho, S.H., Chang, J.S., Ren, N.: Enhancing bio-butanol production from biomass of Chlorella vulgaris JSC-6 with sequential alkali pretreatment and acid hydrolysis. Bioresour. Technol. 200, 557–564 (2016)
Appels, L., Degrève, J., Van der Bruggen, B., Van Impe, J., Dewil, R.: Influence of low temperature thermal pre-treatment on sludge solubilisation, heavy metal release and anaerobic digestion. Bioresour. Technol. 101, 5743–5748 (2010)
Kim, J., Park, C., Kim, T.-H., Lee, M., Kim, S., Kim, S.-W., Lee, J.: Effects of various pretreatments for enhanced anaerobic digestion with waste activated sludge. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 95, 271–275 (2003)
Costanzo, W., Jena, U., Hilten, R., Das, K.C., Kastner, J.R.: Low temperature hydrothermal pretreatment of algae to reduce nitrogen heteroatoms and generate nutrient recycle streams. Algal Res. 12, 377–387 (2015)
Passos, F., Carretero, J., Ferrer, I.: Comparing pretreatment methods for improving microalgae anaerobic digestion: thermal, hydrothermal, microwave and ultrasound. Chem. Eng. J. 279, 667–672 (2015)
Hendriks, A.T.W.M., Zeeman, G.: Pretreatments to enhance the digestibility of lignocellulosic biomass. Bioresour. Technol. 100, 10–18 (2009)
Pettersen, R.: The chemical composition of wood. Chem. Solid Wood 207, 1–9 (1984)
Tchobanoglous, G., Burton, F.L., Stensel, H.D.: Wastewater Engineering: Treatment, Disposal and Reuse. McGraw-Hill Inc., New York (2003)
Ariunbaatar, J., Panico, A., Esposito, G., Pirozzi, F., Lens, P.N.L.: Pretreatment methods to enhance anaerobic digestion of organic solid waste. Appl. Energy 123, 143–156 (2014)
Samson, R., Leduy, A.: Influence of mechanical and thermochemical pretreatments on anaerobic digestion of Spirulina maxima algal biomass. Biotechnol. Lett. 5, 671–676 (1983)
Montingelli, M.E., Tedesco, S., Olabi, A.G.: Biogas production from algal biomass: a review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 43, 961–972 (2015)
Ras, M., Lardon, L., Bruno, S., Bernet, N., Steyer, J.-P.: Experimental study on a coupled process of production and anaerobic digestion of Chlorella vulgaris. Bioresour. Technol. 102, 200–206 (2011)
Jegede, A.O.: Anaerobic digestion of cyanobacteria and chlorella to produce methane for biofuel. Int. J. Agric. Biol. Eng. 5, 1–8 (2012)
Demirer, G.N., Chen, S.: Two-phase anaerobic digestion of unscreened dairy manure. Process Biochem. 40, 3542–3549 (2005)
Lusk, P.: Methane Recovery from Animal Manures The Current Opportunities Casebook. National Renewable Energy Laboratory, NREL/SR, 580-25145, Washington (1998)
Speece, R.E.: Anaerobic Biotechnology and Odor/Corrosion Control for Municipalities and Industries. Archea Press, Nashville (2008)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Calicioglu, O., Demirer, G.N. Biogas Production from Waste Microalgal Biomass Obtained from Nutrient Removal of Domestic Wastewater. Waste Biomass Valor 7, 1397–1408 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12649-016-9546-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12649-016-9546-9