Abstract
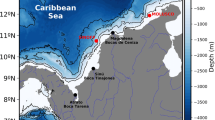
Abnormally low-salinity water originating from the Changjiang River (CR) was observed at the central Yellow Sea (YS) in 2012, which was quite unique compared to other years. In this study, the intrusion process of the Changjiang Diluted Water (CDW) into the YS interior was examined using a hindcast simulation (2003–2012) with particle-tracking experiments. The particles representing the behavior of the CDW were released at the CR mouth from May to August, and then tracked. The simulated salinity patterns coincide fairly well with those derived from observations, particularly showing a large low-salinity structure around the central YS in 2012. A substantial intrusion of freshwater into the YS occurred in 2012, and this accounted for approximately 16% of all the released particles in 2012 which is twice as high as the mean average covering the 10 years. According to the trajectories in 2012, the particles took less than 50 days to travel from the mouth to the YS interior and followed mainly two paths toward the YS. One pathway traveled northward to the central entrance of the YS and then reached the western coast of Korea. This pathway was attributed to the strong easterly winds in late June and early August when three consecutive typhoons passed through the YS, which was a unique pattern that is rarely found in other years. The other pathway involved particles trapped along the Jiangsu coast drifting farther to the north up to the Shandon Peninsula against the anticyclonic tidal residual circulations during the passage of typhoons.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Banas NS, MacCready P, Hickey BM (2009) The Columbia River plume as cross-shelf exporter and along-coast barrier. Cont Shelf Res 29(1):292–301
Bang IK, Lie HJ (1999) A numerical experiment on the dispersion of the Changjiang River plume. J Korean Soc Oceanogr 34:185–199
Batchelder HP, Edwards CA, Powell TM (2002) Individual-based models of copepod populations in coastal upwelling regions: implications of physiologically and environmentally influenced diel vertical migration on demographic success and nearshore retention. Prog Oceanogr 53(2):307–333.
Beardsley RC, Limeburner R, Yu H, Cannon GA (1985) Discharge of the Changjiang (Yangtze river) into the East China sea. Cont Shelf Res 4(1):57–76
Bleck R (2002) An oceanic general circulation model framed in hybrid isopycnic-Cartesian coordinates. Ocean Model 4(1):55–88
Chang PH, Isobe A (2003) A numerical study on the Changjiang diluted water in the Yellow and East China Seas. J Geophys Res 108(C9):3299. doi:10.1029/2002JC001749
Chassignet EP, Hurlburt HE, Smedstad OM, Halliwell GR, Hogan PJ, Wallcraft AJ, Bleck R (2007) The HYCOM (hybrid coordinate ocean model) data assimilative system. J Marine Syst 65(1):60–83
Chen X, Wang X, Guo J (2006) Seasonal variability of the sea surface salinity in the East China Sea during 1990–2002. J Geophys Res 111(C5):C05008. doi:10.1029/2005JC003078
Chapman DC (1985) Numerical treatment of cross-shelf open boundaries in a barotropic coastal ocean model. J Phys Oceanogr 15(8):1060–1075
Choi BH (2002) Digital bathymetric and topographic data for neighboring seas of Korea. J Korean Soc Coast Ocean Eng 14:41–50
Choi BJ, Wilkins JL (2007) The effect of wind on the dispersal of the Hudson River plume. J Phys Oceanogr 37:1878–1897
Dai A, Qian T, Trenberth KE, Milliman JD (2009) Changes in continental freshwater discharge from 1948 to 2004. J Climate 22(10):2773–2792
Fairall CW, Bradley EF, Rogers DP, Edson JB, Young GS (1996) Bulk parameterization of air-sea fluxes for tropical ocean-global atmosphere coupled-ocean atmosphere response experiment. J Geophys Res 101(C2):3747–3764
Haidvogel DB, Arango H, Budgell WP, Cornuelle BD, Curchitser E, Di Lorenzo E, Levin J (2008) Ocean forecasting in terrainfollowing coordinates: Formulation and skill assessment of the Regional Ocean Modeling System. J Comput Phys 227(7):3595–3624
Kim HC, Yamaguchi H, Yoo S, Zhu J, Okamura K, Kiyomoto Y, Ishizaka J (2009) Distribution of Changjiang diluted water detected by satellite chlorophyll-a and its interannual variation during 1998–2007. J Oceanogr 65(1):129–135
Kwon KM (2007) A numerical experiment on the currents along the eastern boundary of the Yellow Sea in Summer 2007. M.D. Thesis, Kunsan National University, 89 p
Lee JH, Pang IC, Moon IJ, Ryu JH (2011) On physical factors that controlled the massive green tide occurrence along the southern coast of the Shandong Peninsula in 2008: a numerical study using a particle-tracking experiment. J Geophys Res 116:C12036. doi:10.1029/2011JC007512
Lie HJ, Cho CH, Lee JH, Lee S (2003) Structure and eastward extension of the Changjiang River plume in the East China Sea. J Geophys Res 108:3077. doi:10.1029/2001JC001194
Liu SM, Zhang J, Chen SZ, Chen HT, Hong GH, Wei H, Wu QM (2003) Inventory of nutrient compounds in the Yellow Sea. Cont Shelf Res 23(11):1161–1174
Marchesiello P, McWilliams JC, Shchepetkin A (2001) Open boundary conditions for long-term integration of regional oceanic models. Ocean Model 3(1):1–20
Moon JH, Pang IC, Yoon JH (2009a) Response of the Changjiang diluted water around Jeju Island to external forcings: a modeling study of 2002 and 2006. Cont Shelf Res 29(13):1549–1564.
Moon JH, Hirose N, Yoon JH (2009b) Comparison of wind and tidal contributions to seasonal circulation of the Yellow Sea. J Geophys Res 116:C08016. doi:10.1029/2009JC005314
Moon JH, Hirose N, Pang IC, Hyun KH (2012) Modeling offshore freshwater dispersal from the Changjiang River and controlling factors during summer. Terr Atmos Ocean Sci 23:247–260
Oh KH, Lee JH, Lee S, Pang IC (2014) Intrusion of low-salinity water into the Yellow Sea Interior in 2012. Ocean Sci J 49(4):343–356
Rabouille C, Conley DJ, Dai MH, Cai WJ, Chen CTA, Lansard B, McKee B (2008) Comparison of hypoxia among four riverdominated ocean margins: the Changjiang (Yangtze), Mississippi, Pearl, and Rhone rivers. Cont Shelf Res 28(12):1527–1537
Shchepetkin AF, McWilliams JC (2005) The regional oceanic modeling system (ROMS): a split-explicit, free-surface, topographyfollowing-coordinate oceanic model. Ocean Model 9(4):347–404
Umlauf L, Burchard H (2003) A generic length-scale equation for geophysical turbulence models. J Mar Res 61(2):235–265
Visser AW (1997) Using random walk models to simulate the vertical distribution of particles in a turbulent water column. Mar Ecol- Prog Ser 158:275–281.
Wu H, Shen J, Zhu J, Zhang J, Li L (2014) Characteristics of the Changjiang plume and its extension along the Jiangsu Coast. Cont Shelf Res 76:108–123
Wang BD, Wang XL, Zhan R (2003) Nutrient conditions in the Yellow Sea and the East China Sea. Estuar Coast Shelf S 58(1):127–136
Xuan J, Yang Z, Huang D, Wang T, Zhou F (2015) Tidal residual current and its role in the mean flow on the Changjiang Bank. J Marine Syst 154:66–81
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hong, JS., Moon, JH., Lee, JH. et al. Modeling the largest inflow of Changjiang freshwater into the Yellow Sea in 2012 with particle-tracking experiment. Ocean Sci. J. 51, 549–562 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12601-016-0057-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12601-016-0057-1