Abstract
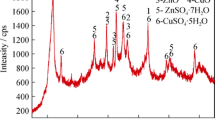
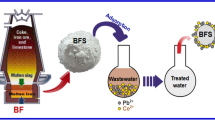
The immobilization of hexavalent chromium in stainless steel slag using blast furnace slag as the immobilizing agent and by performing a hydrothermal treatment was investigated. The results showed that there was no immobilization in the absence of the blast furnace slag. On the other hand, the hexavalent chromium in stainless steel slag could be immobilized through the hydrothermal reaction when blast furnace slag was used at 250 °C for 24 h. A leaching test was performed to evaluate the degree of immobilization of hexavalent chromium in the products formed by the hydrothermal reaction. It was found that the degree of immobilization was very high. Based on the results obtained, the immobilization mechanism of hexavalent chromium in stainless steel slag, resulting from the hydrothermal treatment of blast furnace slag, could be elucidated. Finally, the immobilization of cadmium, lead, and arsenic using blast furnace slag as the immobilization agent was also studied while focusing on the effects of the hydrothermal treatment.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
M. Fujiwara, Bull. Iron Steel Inst. Jpn. 8, 883 (2003).
J.-W. Kim, J.-I. Park, K.-W. Lee, E.-H. Kwon, K.-M. Kim, J.-W. Han, et al. Korean J. Met. Mater. 53, 370 (2015).
J. Y. Yu, S. S. Jung, and I. Sohn, Korean J. Met. Mater. 53, 35 (2015).
V. Bianchi, A. Zantedeschi, A. Montaldi, and F. Majone, Toxicol. Lett. 23, 51 (1984).
Y. J. Kang, Y. H. Kim, and H.-S. Sohn, Met. Mater. Int. 21, 118 (2015).
S. Kubota and Y. Tsuchiya, Water Quality and Standards, p. 74, Oxford, UK (2009).
H. Hatakeda, H. Maruoka, H. Shibata, S. Kitamura, K. Shinoda, and S. Suzuki, Bull. Adv. Mater. Pro. Build. 63, 27 (2007).
A. M. Garbers, Ironmak. Steelmak. 33, 238 (2006).
Z. Huaiwei and H. Xin, Resour. Conserv. Recy. 55, 745 (2011).
T. Tanaka, T. Yoshikawa, and N. Hirai, Ferrum 14, 353 (2009).
R. Inoue and H. Suito, ISIJ Int. 42, 930 (2002).
S.-J. Tae and K. Morita, ISIJ Int. 48, 1311 (2008).
S.-J. Tae and K. Morita, ISIJ Int. 47, 1813 (2007).
T. Akiyama and J. Yagi, Tetsu to Hagané 82, 177 (1996).
K. Byrappa and M. Yoshimura, Handbook of Hydrothermal Technology, 1st ed., pp. 1–52, Noyes Publications, New York, USA (2001).
M. Ito and K. Morita, Tetsu-to-Hagane 91, 421 (2005).
M. Suzuki, T. Yamamoto, S. Kuwata, B. Derin, N. Yamasaki, and T. Tanaka, Mater. Trans. 54, 1741 (2013).
S.-J. Tae, Ph. D. Thesis, pp. 90–102, The University of Tokyo, Tokyo (2008).
N. Hirai, Y. Yamasaki, Y. Nomura, K. Kubota, and T. Tanaka, CAMP-ISIJ 18, 235 (2005).
J. Zhang, J. Provis, D. Feng, and J. Deventer, J. Hazard. Mater. 157, 578 (2008).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tae, SJ., Morita, K. Immobilization of Cr (VI) in stainless steel slag and Cd, As, and Pb in wastewater using blast furnace slag via a hydrothermal treatment. Met. Mater. Int. 23, 576–581 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12540-017-6576-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12540-017-6576-1