Abstract
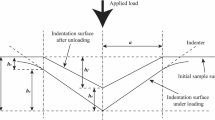
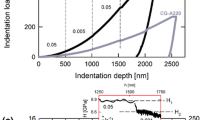
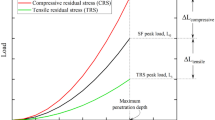
Nanoindentation has been widely used to measure mechanical properties for instance elastic modulus and hardness due to relatively simple sample preparation and experimental procedure. Primary limitation of nanoindentation is that it does not measure quantitative mechanical properties such as yield strength, ultimate tensile strength and fracture strain unlike uni-axial tensile testing. We investigate the tensile stress-strain curve of electroplated copper using a single nanoindentation with a Berkovich indenter. Micro-tensile testing and nanoindentation were performed for three electroplated copper samples with different microstructures by post heat treatments. We find a linear relationship between the strain-hardening exponent as measured by micro-tensile testing and the log value of the characteristic length for the indentation size effect as measured by nanoindentation. By defining a representative flow stress-strain point corresponding to the Berkovich indenter along with the elastic modulus measured by nanoindentation, we obtain complete tensile stress-strain curves for electroplated copper that are in good agreement with those measured by micro-tensile testing.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
J. Chen, L. Lu, and K. Lu, Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. Mater. 54, 1913 (2006).
X. H. Chen and L. Lu, Scripta Mater. 57, 133 (2007).
M. Dao, L. Lu, R. J. Asaro, J. T. M. De Hosson, and E. Ma, Acta Mater. 55, 4041 (2007).
M. Dao, L. Lu, Y. F. Shen, and S. Suresh, Acta Mater. 54, 5421 (2006).
D. C. Jang, X. Y. Li, H. J. Gao, and J. R. Greer, Nat. Nanotechnol. 7, 594 (2012).
D. C. Jang, C. Cai, and J. R. Greer, Nano Lett. 11, 1743 (2011).
L. Lu, X. Chen, X. Huang, and K. Lu, Science 323, 607 (2009).
L. Lu, S. X. Li, and K. Lu, Scripta Mater. 45, 1163 (2001).
L. Lu, R. Schwaiger, Z. W. Shan, M. Dao, K. Lu, and S. Suresh, Acta Mater. 53, 2169 (2005).
L. Lu, Y. F. Shen, X. H. Chen, L. H. Qian, and K. Lu, Science 304, 422 (2004).
L. Lu, Z. S. You, and K. Lu, Scripta Mater. 66, 837 (2012).
Y. F. Shen, L. Lu, M. Dao, and S. Suresh, Scripta Mater. 55, 319 (2006).
Y. F. Shen, L. Lu, Q. H. Lu, Z. H. Jin, and K. Lu, Scripta Mater. 52, 989 (2005).
A. Singh, L. Tang, M. Dao, L. Lu, and S. Suresh, Acta Mater. 59, 2437 (2011).
H. Van Swygenhoven, M. Spaczer, and A. Caro, Acta Mater. 47, 3117 (1999).
J. R. Weertman, D. Farkas, K. Hemker, H. Kung, M. Mayo, and H. Van Swygenhoven, et al. MRS Bull. 24, 44 (1999).
X. H. Chen, L. Lu, and K. Lu, Scripta Mater. 64, 311 (2011).
Y. C. Kim, H. J. Ahn, D. Kwon, and J. Y. Kim, Met. Mater. Int. 22, 12 (2016).
Y. C. Kim, M. J. Choi, D. Kwon, and J. Y. Kim, Met. Mater. Int. 21, 850 (2015).
Y. H. Lee, S. M. Ahn, J. Y. Kim, C. P. Park, and H. K. Jane, Korean J. Met. Mater. 53, 162 (2015).
Y. H. Lee, J. S. Park, Y. I. Kim, and Y. H. Huh, Korean J. Met. Mater. 53, 90 (2015).
J.-Y. Kim, K.-W. Lee, J.-S. Lee, and D. Kwon, Surface and Coatings Technology 201, 4278 (2006).
S. Jayaraman, G. T. Hahn, W. C. Oliver, and P. C. Bastias, International Journal of Solids and Structures 35, 365 (1998).
J. G. Swadener, E. P. George, and G. M. Pharr, J. Mech. Phys. Solids 50, 681 (2002).
ASTM E8, Standard Test Methods for Tension Testing of Metallic Materials, ASTM International, PA, USA (2015).
J. H. Hollomon, T. Am. I. Min. Met. Eng. 162, 268 (1945).
N. J. Petch, J. Iron Steel I. 174, 25 (1953).
E. O. Hall, P. Phys. Soc. Lond. B 64, 747 (1951).
W. D. Nix and H. J. Gao, J. Mech. Phys. Solids 46, 411 (1998).
Y. Huang, F. Zhang, K. C. Hwang, W. D. Nix, G. M. Pharr, and G. Feng, J. Mech. Phys. Solids 54, 1668 (2006).
K. Durst, B. Backes, and M. Goken, Scripta Mater. 52, 1093 (2005).
J. Y. Kim, S. K. Kang, J. R. Greer, and D. Kwon, Acta Mater. 56, 3338 (2008).
H. Gao, Y. Huang, W. D. Nix, and J. W. Hutchinson, J. Mech. Phys. Solids 47, 1239 (1999).
Y. Huang, H. Gao, W. D. Nix, and J. W. Hutchinson, J. Mech. Phys. Solids 48, 99 (2000).
A. A. Elmustafa and D. S. Stone, J. Mech. Phys. Solids 51, 357 (2003).
D. Tabor, The Hardness of Metals, pp. 105–106, Oxford, New York, USA (1951).
K. L. Johnson, Contact Mechanics, pp.171–179, Cambridge University Press, UK (1987).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, SH., Kim, YC., Lee, S. et al. Evaluation of tensile stress-strain curve of electroplated copper film by characterizing indentation size effect with a single nanoindentation. Met. Mater. Int. 23, 76–81 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12540-017-6461-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12540-017-6461-y