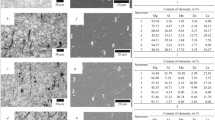
Abstract
Magnesium and its alloys with low specific weight, high specific strength, vast resources, easy recyclability and biodegradation have attracted extensive interest in recent years as an ideal candidate to aluminium and steel alloys. The knowledge of the mechanical properties under high strain rate loading and elevated temperature is necessary for the structural application of magnesium alloy in automotive, aerospace and defence industries. Compressive tests on AZ31B magnesium alloy were carried out at both quasi-static and high strain rate loading in a range between 10−3 s−1 and 3300 s−1 while temperature varies from -30 °C to 200 °C. Strain rate and temperature effect on flow stress, hardening behavior, rate sensitivity, ductility and energy absorption capability of the alloy is discussed. Optical and scanning electron microscopy was performed on selected specimens at quasi-static and high strain rates under room temperature. The Johnson-Cook model is fit to the measured data and predictions from the model are compared with the experimental data.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
K. U. Kainer and B. L. Mordike, Magnesium Alloys and Their Applications, pp.1–8, Wiley, Germany (2000).
J. J. Kim and D. S. Han, Mater. Trans. 49, 894 (2008).
H. Friedrich and S. Schumann, J. Mater. Process. Tech. 117, 276 (2001).
J. C. Mathes, Aircr. Eng. Aerosp. Tec. 13, 323 (1941).
H. E. Friedrich and B. L. Mordike, Magnesium Technology, pp.1–28, Springer, Berlin Heidelberg (2006).
K. U. Kainer and F. Von Buch, Magnesium - Alloys and Technology, pp.1–22, Wiley, Germany (2004).
H. Asgari, J. A. Szpunar, A. G. Odeshi, L. J. Zeng, and E. Olsson, Mat. Sci. Eng. A-Struct. 618, 310 (2014).
S. Kurukuri, M. J. Worswick, D. G. Tari, R. K. Mishra, and J. T. Carter, Philosophical Transactions A, 372, 1 (2014).
J. Xiao, I. R. Ahmad, and D. W. Shu, Mod. Phys. Lett. B 28, (2014).
I. R. Ahmad and D. W. Shu, Mat. Sci. Eng. A-Struct. 592, 40 (2014).
J. Xiao and D. W. Shu, Advances in Engineering Plasticity Xi (eds. G. X. Lu and Q. M. Zhang), pp.141–144, Trans Tech Publications Ltd, Stafa-Zurich (2013).
P. L. Mao, Z. Liu, C. Y. Wang, and Z. Wang, Advanced Structural Materials, pp.325–331, Int Union Mat Res Soc, Qingdao, China (2010).
M. Sanjari, S. A. Farzadfar, S. Yue, and E. Essadiqi, Magnesium Technology 2010, pp.481–486, Magnesium Technology Symposium 2010, Seattle, WA (2010).
D. Hasenpouth, C. Salisbury, A. Bardelcik, M. J. Worswick, 9th International Conference on Mechanical and Physical Behaviour of Materials Under Dynamic Loading, p.1431, Brussels (2009).
Y. Y. Wu, C. W. Tan, Y. B. Yang, F. C. Wang, and H. N. Cai, Rare Metal Mat. Eng. 38, 404 (2009).
T. Yokoyama, J. Phys. Iv 110, 69 (2003).
D. T. Nguyen, High Temp. Mater. Proc. 33, 499 (2014).
F. Feng, S. Y. Huang, Z. H. Meng, J. H. Hu, Y. Lei, M. C. Zhou, D. Wu, and Z. Z. Yang, Mater. Design 57, 10 (2014).
I. Ulacia, C. P. Salisbury, I. Hurtado, and M. J. Worswick, J. Mater. Process. Tech. 211, 830 (2011).
T. Aramoto, H. Tachiya, A. Hori, A. Hojo, and Y. Miyazaki, Int. J. Mod. Phys. B 22, 1135 (2008).
J. Xiao, D. W. Shu, and X. J. Wang, Int. J. Mech. Sci. 89, 381 (2014).
H. Kolsky, Proceedings of the Physical Society. Section B 62, 676 (1949).
U. S. Lindholm, J. Mech. Phys. Solids 12, 317 (1964).
G. E. Dieter, Mechanical Metallurgy, pp.17–52, McGRAWHILL Book Co., United States of America (1961).
S. Ramakrishna, Mater. Design 18, 167 (1997).
G. R. Johnson, W. H. Cook, and H. William, Proceedings of the 7th International Symposium on Ballistics, pp.541–547, The Netherlands, United States of America (1983).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xiao, J., Shu, D.W. Compressive behavior and constitutive analysis of AZ31B magnesium alloy over wide range of strain rates and temperatures. Met. Mater. Int. 21, 823–831 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12540-015-5120-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12540-015-5120-4