Abstract
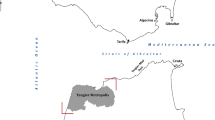
Soil erosion is the dominating factor of damaging roads in Iran. Roads are a critical component of civilization. Developing and maintaining the economic activity that is vital for the quality of modern life would be difficult without roads. Accelerated erosion and increased sediment yields resulting from changes in land use are critical environmental problems, and one of the important changes is road construction. Construction and condition of roadways are associated with direct and indirect impacts on soil erosion. This paper presents the relationship between soil erosion and some characteristics such as distance to roadway, slope, and parent material in Latian Watershed, Tehran Province, Iran. Soil erosion map was interpreted using aerial photos and GIS technology. Buffer zones, subdivided into 12 strips, each 0.2 km wide, which were located alongside roadway. The distribution patterns of various types of erosion were also identified by GIS by overlaying road buffer strips and soil erosion map. The results show that soil erosion landform such as land slide, badland, bank erosion, channel erosion, etc. found in buffer zones along both sides of roads.
الملخص
الإنجراف الهوايي و المائي للتربة هما من اهم اسباب تخريب الطرق في ايران. من جهة اخري الطرق هي من اهم علائم الحضارة. بدون طرق التقدم و تنمية النشاطات الإ قتصادية يكون امر مشكل. التعرية المتزايدة و تشديد الرمال الزاحفة بسبب سوء استخدام الأ راضي هي من اهم تغييرات احداث الطرق.
هذه المقالة درست العلاقة بين تعرية التربة و بعض المواصفات مثل بعد المسافة عن الطريق ، ميزان الإنحدار في مساقط مياه و حوض سد لتيان.
اعدت خارطة تعرية التربة بالإ ستفادة من الصور الجوية و تقنية GIS. علي بعد 2/. كيلومتر من جانبين الطرق 12منطقة احدثت. تحضير خارطة توزيع نماذج مختلفة للتعرية علي جانبين الطريق.
النتائج تدل علي إن هناك انواع مختلفة للتعرية المائية علي جانبين الطريق كزحف التربة و...




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmadi H (1995) Applied geomorphology (1) water erosion. University of Tehran Press, Tehran, pp 688 (in Persian)
Akay, Abdullah E, Erdas O, Reis M, Yuksel A (2008) Estimating sediment yield from a forest road network by using a sediment prediction model and GIS techniques. Build Environ J 43(5):687–695
Ariel E, Gucinski LH (2000) Function, effects, and management of forest roads. For Ecol Manag 133(2000):249–262
Arnaez J, Larrea V, Ortigosa L (2004) Surface runoff and soil erosion on unpaved forest roads from rainfall simulation tests in northeastern Spain. Catena 57(1):1–14
Bååth H, Gällerspång A, Hallsby G, Lundström A, Löfgren P, Nilsson M, Ståhl G (2002) Remote sensing, field survey and long-term forecasting: an efficient combination for local assessments of forest fuels. Biomass Bioenergy 22:145–157
Cao, Longxi Keli Zhang, Wei Zhang (2009) Detachment of road surface soil by flowing water. CATENA 76(2):155–162
Cerdà A (2007) Soil water erosion on road embankments in eastern Spain. Sci Total Environ 378(1–2):151–155
Costa FM, Bacellar LAP (2007) Analysis of the influence of gully erosion in the flow pattern of catchments streams, Southeastern Brazil. Catena 69:230–238
Dunne T (1979) Sediment yield and land use in tropical catchments. J Hydrol 42:281–300
Fahey BD, Coker RJ (1989) Forest road erosion in the granite terrain of southwest Nelson, New Zealand. J Hydrol (NZ) 28:123–141
Forman RTT, Alexander LE (1998) Roads and their major ecological effects. Ann Rev Ecolog Syst 29:207–231
Forman RTT, Deblinger RD (2000) The ecological road effect zone of a Massachusetts (USA) suburban highway. Conserv Biol 14:36–46
Fu B, Newham LTH, Field JB (2009) Modelling erosion and sediment delivery from unsealed roads in southeast Australia. Math Comput Simulat J 79:2679–2688
Maleki M (2009) Quantification of qualitative geomorphology method for water erosion estimation (Case Study: three sub-watersheds of Latian Dam basin). Iran J Nat Resour 61(No. 4):775 (in Persian)
Matthew L, Smith RJ, Nigel LW (2004) Mapping and predicting deforestation patterns in the lowlands of Sumatra. Biodivers Conserv 13:1809–1818
Minten B, Kyle S (1999) The effect of distance and road quality on food collection, marketing margins, and traders’ wages: evidence from the former Zaire. J Dev Econ 60(2):467–495
Mohammadkhan S (2010) Quantifying the sediment and erosion by Geomorphological method (Case Study Latian Watershed), PhD. Thesis. Natural resources Faculty of Tehran University, Tehran (in Persian)
Morschel J, Fox DM, Bruno J-F (2004) Limiting sediment deposition on roadways: topographic controls on vulnerable roads and cost analysis of planting grass buffer strips. Environ Sci Policy 7:39–45
Motha JA, Wallbrink PJ, Hairsine PB, Grayson RB (2004) Unsealed roads as suspended sediment sources in an agricultural catchment in southeastern Australia. J Hydrol 286:1–18
Pan JJ, Zhang TL, Zhao QG (2005) Dynamics of soil erosion in Xingguo County, China, determined using remote sensing and GIS. Pedosphere 15:356–362
Reid LM, Dunne T (1984) Sediment production from forest road surfaces. Water Resour Res 20:1753–1761
Rijsdijk A, Bruijnzeel LAS, Sutoto CK (2007) Runoff and sediment yield from rural roads, trails and settlements in the upper Konto catchment, East Java, Indonesia. Geomorphology J 87(1–2):28–37
Saaty TL (1980) “The analytical hierarchy process”, PK nning, priority resource Allocation. PWS publications, USA
Shi XZ, Wang K, Warner ED, Yu DS, Wang HJ, Yang RW, Liang Y (2008) Relationship between soil erosion and distance to roadways in undeveloped areas of China. CATENA 72(2):305–313
Tang Z, Lei T, Yu J, Shainberg I, Mamedov AI, Ben-Hur M, Levy GJ (2006) Runoff and interrill erosion in sodic soils treated with dry PAM and phosphogypsum. Soil Sci Soc Am J 70:679–690
Todd JH, Volker CR, Roger BH, Murray KC (2004) Road density and landscape pattern in relation to housing density, land ownership, land cover, and soils. Landscape Ecol 20:609–625
Wemple BC, Swanson FJ, Jones JA (2001) Forest roads and geomorphic process interactions, cascade range, Oregon, earth surf. Process Land 26:191–204
Ziegler AD, Giambelluca TW (1997) Importance of rural roads as source areas for runoff in mountainous areas of northern Thailand. J Hydrol 196:204–229
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mohammadkhan, S., Ahmadi, H. & Jafari, M. Relationship between soil erosion, slope, parent material, and distance to road (Case study: Latian Watershed, Iran). Arab J Geosci 4, 331–338 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-010-0197-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-010-0197-z