Abstract
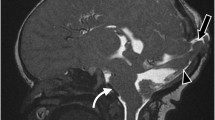
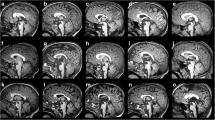
Partial rhombencephalosynapsis (PRECS) has been recently reported in association with Chiari II (CII). However, its existence as a true malformation is challenged due to the anatomical changes potentially induced by CII. The aim of this report was to investigate the contribution of midbrain/hindbrain tractography in this setting. A 13-year-old boy with a known CII malformation and operated myelomeningocele was referred for brain imaging after a first complex partial seizure. In addition to the classical features of CII, MRI showed partially fused cerebellar hemispheres and multiple supratentorial abnormalities. Diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) color map and tractography showed absent transverse fibers on the midsection of the cerebellum, scarce fibers of the middle cerebellar peduncle (MCP), absence of the middle pontine crossing tract, and fibers running vertically in the medial part of the cerebellum. Vertical mediocerebellar fibers are a feature of classical RECS and the paucity or absence of MCP fibers is mainly described in CII. In our patient, DTI and FT therefore demonstrated structural characteristics of both RECS and CII confirming their potential coexistence and suggesting possible shared embryological pathway.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Naidich TP, McLone DG, Fulling KH. The Chiari II malformation: part IV. The hindbrain deformity. Neuroradiology. 1983;25(4):179–97.
Truwit CL, Barkovich AJ, Shanahan R, Maroldo TV. MR imaging of rhombencephalosynapsis: report of three cases and review of the literature. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 1991;12(5):957–65.
Jellinger KAK. Rhombencephalosynapsis. Acta Neuropathol. 2002;103(3):305–6.
Poretti AA, Bartholdi DD, Gobara SS, Alber FDF, Boltshauser EE. Gomez–Lopez–Hernandez syndrome: an easily missed diagnosis. Eur J Med Genet. 2008;51(3):197–208.
Sukhudyan BB, Jaladyan VV, Melikyan GG, Schlump JUJ, Boltshauser EE, Poretti AA. Gómez–López-Hernández syndrome: reappraisal of the diagnostic criteria. Eur J Pediatr. 2010;169(12):1523–8.
Demaerel PP, Morel CC, Lagae LL, Wilms GG. Partial rhombencephalosynapsis. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2004;25(1):29–31.
Chemli JJ, Abroug MM, Tlili KK, Harbi AA. Rhombencephalosynapsis diagnosed in childhood: clinical and MRI findings. Eur J Paediatr Neurol. 2007;11(1):35–8.
Sener RN. Unusual MRI findings in rhombencephalosynapsis. Comput Med Imaging Graph. 2000;24(4):277–82.
Sener RN, Dzelzite S. Rhombencephalosynapsis and a Chiari II malformation. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 2003;27(2):257–9.
Wan SMSMY, Khong PLSMY, Ip PSMY, Ooi GCSMY. Partial rhombencephalosynapsis and Chiari II malformation. Hong Kong Med J. 2005;11(4):299–302.
Ramkumar PGP, Kanodia AKA, Ananthakrishnan GG, Roberts RR. Chiari II malformation mimicking partial rhombencephalosynapsis? A case report. Cerebellum. 2010;9(1):111–4.
Toelle SP, Yalcinkaya C, Kocer N, Deonna T, Overweg-Plandsoen WCWCG, Bast TWCG, et al. Rhombencephalosynapsis: clinical findings and neuroimaging in 9 children. Neuropediatrics. 2002;33(4):209–14.
Jellinger KAK. Rhombencephalosynapsis with and without associated malformations. Acta Neuropathol. 2009;117(2):219.
Boltshauser E. Cerebellum-small brain but large confusion: a review of selected cerebellar malformations and disruptions. Am J Med Genet A. 2004;126A(4):376–85.
Miller EE, Widjaja EE, Blaser SS, Dennis MM, Raybaud CC. The old and the new: supratentorial MR findings in Chiari II malformation. Childs Nerv Syst. 2008;24(5):563–75.
Striano PP, Morana GG, Pezzella MM, Bellini TT, Rossi AA. Rhombencephalosynapsis in a patient with mental retardation, epilepsy, and dysmorphisms. Neurol Sci. 2011;32(1):193–4.
Basser PJ, Pierpaoli C. A simplified method to measure the diffusion tensor from seven MR images. Magn Reson Med. 1998;39(6):928–34.
Widjaja E, Blaser S, Raybaud C. Diffusion tensor imaging of midline posterior fossa malformations. Pediatr Radiol. 2006;36(6):510–7.
Herweh C, Akbar M, Wengenroth M, Blatow M, Mair-Walther J, Rehbein N, et al. DTI of commissural fibers in patients with Chiari II-malformation. Neuroimage. 2009;44(2):306–11.
Herweh CC, Akbar MM, Wengenroth MM, Heiland SS, Bendszus MM, Stippich CC. Reduced anisotropy in the middle cerebellar peduncle in Chiari-II malformation. Cerebellum. 2010;9(3):303–9.
Rollins NKN. Clinical applications of diffusion tensor imaging and tractography in children. Pediatr Radiol. 2007;37(8):769–80.
Barth PGP. Rhombencephalosynapsis. Handb Clin Neurol. 2008;87:53–65.
Utsunomiya H, Takano K, Ogasawara T, Hashimoto T, Fukushima T, Okazaki M. Rhombencephalosynapsis: cerebellar embryogenesis. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 1998;19(3):547–9.
Sidman RL, Rakic P. Development of the human central nervous system. In: Haymaker W, Adams RD, editors. Histology and histopathology of the nervous system. Springfield: Thomas; 1982. p. 3–145.
Herrup K, Kuemerle B. The compartmentalization of the cerebellum. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1997;20:61–90.
Barkovich AJ, Millen KJK, Dobyns WBW. A developmental and genetic classification for midbrain–hindbrain malformations. Brain. 2009;132(Pt 12):3199–230.
Tubbs RS, Shoja MM, Ardalan MRM, et al. Hindbrain herniation: a review of embryological theories. Ital J Anat Embryol. 2008;113:37–46.
Sarnat HB. Molecular genetic classification of central nervous system malformations. J Child Neurol. 2000;15(10):675–87.
Chizhikov VV, Lindgren AG, Mishima Y, Roberts RW, Aldinger KA, Miesegaes GR, Currle DS, Monuki ES, Millen KJ. Lmx1a regulates fates and location of cells originating from the cerebellar rhombic lip and telencephalic cortical hem. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2010;107(23):10725–30.
Conflict of Interest
The authors state that there is no conflict of interest (e.g., consultancies, stock ownership, equity interests, patent licensing arrangements), real or perceived. No honorarium, grant, or other form of payment was given to anyone to produce the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Merlini, L., Fluss, J., Korff, C. et al. Partial Rhombencephalosynapsis and Chiari Type II Malformation in a Child: a True Association Supported by DTI Tractography. Cerebellum 11, 227–232 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12311-011-0300-3
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12311-011-0300-3