Abstract
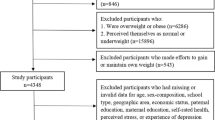
The goal of this study is to systematically examine the associations between perceived weight status and selected health-risk behaviors among Rhode Island adolescents. We utilized the biennial 2007 and 2009 Rhode Island representative Youth Risk Behavior Survey data. The combined statewide sample contained 5,423 randomly selected public high school students. Perceived weight status was classified into very underweight, slightly underweight, about the right weight, slightly overweight, and very overweight according to the question “How do you describe your weight?” Adolescent’s body mass index (BMI) was calculated from self-reported height and weight. BMI percentile was categorized as extremely underweight, underweight, normal, overweight, and obese. Multivariable logistic regression models were used to analyze perceived weight status associated with six categories of priority health-risk factors. Perceived very underweight and very overweight were statistically significantly associated with 17 out of 22 health-risk behaviors. The relationships can be expressed as a “U”-shaped curve in terms of odds ratios in adolescents. There were no such similar consistent patterns between BMI percentile categories and health-risk behaviors. Perceived weight status, rather than BMI percentile categories, has an important influence on health-risk behaviors. Our results may assist health programs to intervene with high-risk students by changing their cognitive behaviors.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmad, N., Biswas, S., Bae, S., Meador, K. E., Huang, R., & Singh, K. P. (2009). Association between obesity and asthma in US children and adolescents. The Journal of asthma, 46(7), 642–646.
Bell, L. M., Byrne, S., Thompson, A., Ratnam, N., Blair, E., Bulsara, M., et al. (2007). Increasing body mass index z-score is continuously associated with complications of overweight in children, even in the healthy weight range. The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism, 92(2), 517–522. doi:10.1210/jc.2006-1714.
Blubberbusters. (2010, November 8, 2010) Height, Weight, and body mass index (BMI) Percentile Calculator for Ages 2 to 20 yrs. Retrieved October 5, 2011, from http://www.blubberbuster.com/height_weight.html.
Caria, M. P., Bellocco, R., Zambon, A., Horton, N. J., & Galanti, M. R. (2009). Overweight and perception of overweight as predictors of smokeless tobacco use and of cigarette smoking in a cohort of Swedish adolescents. Addiction, 104(4), 661–668.
CDC Youth Risk Behavior Survey (YRBS). http://www.cdc.gov/HealthyYouth/yrbs/index.htm. Accessed 2011.
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. (2011a September 13, 2011). About BMI for Children and Teens. Retrieved October 5, 2011, from http://www.cdc.gov/healthyweight/assessing/bmi/childrens_bmi/about_childrens_bmi.html.
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. (2011b September 9, 2010). CDC Growth Charts: United States. Retrieved September 30, 2011, from http://www.cdc.gov/growthcharts/.
Chomitz, V. R., Slining, M. M., McGowan, R. J., Mitchell, S. E., Dawson, G. F., & Hacker, K. A. (2009). Is there a relationship between physical fitness and academic achievement? Positive results from public school children in the northeastern United States. The Journal of School Health, 79(1), 30–37.
Crosnoe, R., & Muller, C. (2004). Body mass index, academic achievement, and school context: examining the educational experiences of adolescents at risk of obesity. Journal of Health and Social Behavior, 45(4), 393–407.
Daniels, J. (2005). Weight and weight concerns: are they associated with reported depressive symptoms in adolescents? Journal of Pediatric Health Care, 19(1), 33–41.
Dave, D., & Rashad, I. (2009). Overweight status, self-perception, and suicidal behaviors among adolescents. Social Science and Medicine, 68(9), 1685–1691.
Deforche, B. I., De Bourdeaudhuij, I. M., & Tanghe, A. P. (2006). Attitude toward physical activity in normal-weight, overweight and obese adolescents. Journal of Adolescent Health, 38(5), 560–568.
Eaton, D. K., Kann, L., Kinchen, S., Shanklin, S., Ross, J., Hawkins, J., et al. (2008). Youth risk behavior surveillance–United States, 2007. MMWR Surveillance Summaries, 57(4), 1–131.
Edwards, N. M., Pettingell, S., & Borowsky, I. W. (2010). Where perception meets reality: Self-perception of weight in overweight adolescents. Pediatrics, 125(3), e452–e458.
Everett Jones, S., & Lollar, D. J. (2008). Relationship between physical disabilities or long-term health problems and health risk behaviors or conditions among US high school students. The Journal of School Health, 78(5), 252–257. quiz 298–259.
Farhat, T., Iannotti, R. J., & Simons-Morton, B. G. (2010). Overweight, obesity, youth, and health-risk behaviors. American Journal of Preventive Medicine, 38(3), 258–267.
Foti, K., & Lowry, R. (2010). Trends in perceived overweight status among overweight and non overweight adolescents. Archives of Pediatrics and Adolescent Medicine, 164(7), 636–642.
Halpern, C. T., Udry, J. R., Campbell, B., & Suchindran, C. (1999). Effects of body fat on weight concerns, dating, and sexual activity: a longitudinal analysis of black and white adolescent girls. Developmental Psychology, 35(3), 721–736.
Hollar, D., Messiah, S. E., Lopez-Mitnik, G., Hollar, T. L., Almon, M., & Agatston, A. S. (2010). Effect of a two-year obesity prevention intervention on percentile changes in body mass index and academic performance in low-income elementary school children. American Journal of Public Health, 100(4), 646–653.
Huang, L., Tao, F. B., Wan, Y. H., Xing, C., Hao, J., Su, P. Y., et al. (2011). Self-reported weight status rather than BMI may be closely related to psychopathological symptoms among Mainland Chinese adolescents. Journal of Tropical Pediatrics, 57(4), 307–311.
Jiang, Y., Perry, D., Garneau, D., Kim, H., & Sienko, D. (2008). Disability and Health Risks Among Rhode Island Public High School Students in 2007. 4. Retrieved from publications website: http://www.health.ri.gov/publications/healthriskreports/youth/2007Disability.pdf.
Kim, D. S. (2009). Body image dissatisfaction as an important contributor to suicidal ideation in Korean adolescents: gender difference and mediation of parent and peer relationships. Journal of Psychosomatic Research, 66(4), 297–303.
Kim, D. S., Cho, Y., Cho, S. I., & Lim, I. S. (2009). Body weight perception, unhealthy weight control behaviors, and suicidal ideation among Korean adolescents. Journal of School Health, 79(12), 585–592.
Kuczmarski RJ, Ogden CL, Guo SS, et al. (2002). 2000 CDC growth charts for the United States: Methods and development. Vital and Health Statistics Series 11 (246). doi:GN63.A225 2001.
Kurth, B. M., & Ellert, U. (2008). Perceived or true obesity: Which causes more suffering in adolescents? Findings of the German health interview and examination survey for children and adolescents (KiGGS). Deutsches Ärzteblatt International, 105(23), 406–412.
Leatherdale, S. T., Wong, S. L., Manske, S. R., & Colditz, G. A. (2008). Susceptibility to smoking and its association with physical activity, BMI, and weight concerns among youth. Nicotine & Tobacco Research, 10(3), 499–505.
Lo, W. S., Ho, S. Y., Mak, K. K., Wong, Y. M., Lai, Y. K., & Lam, T. H. (2009). Prospective effects of weight perception and weight comments on psychological health among Chinese adolescents. Acta Paediatrica, 98(12), 1959–1964.
Maximova, K., McGrath, J. J., Barnett, T., O’Loughlin, J., Paradis, G., & Lambert, M. (2008). Do you see what I see? Weight status misperception and exposure to obesity among children and adolescents. International Journal of Obesity, 32(6), 1008–1015.
Mei, Z., Grummer-Strawn, L. M., Pietrobelli, A., Goulding, A., Goran, M. I., & Dietz, W. H. (2002). Validity of body mass index compared with other body-composition screening indexes for the assessment of body fatness in children and adolescents. The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, 75(6), 978–985.
Neumark-Sztainer, D., Story, M., Dixon, L. B., & Murray, D. M. (1998). Adolescents engaging in unhealthy weight control behaviors: are they at risk for other health-compromising behaviors? American Journal of Public Health, 88(6), 952–955.
Neumark-Sztainer, D., Story, M., French, S. A., Hannan, P. J., Resnick, M. D., & Blum, R. W. (1997). Psychosocial concerns and health-compromising behaviors among overweight and nonoverweight adolescents. Obesity Research, 5(3), 237–249.
Pasch, K. E., Nelson, M. C., Lytle, L. A., Moe, S. G., & Perry, C. L. (2008). Adoption of risk-related factors through early adolescence: associations with weight status and implications for causal mechanisms. Journal of Adolescent Health, 43(4), 387–393.
Perry, D., Jiang, Y., & Silvia, A. M. (2009). Sexual Orientation and Health Risks Among Rhode Island Public High School Students in 2007. 4. Retrieved from publications website: http://www.health.ri.gov/publications/healthriskreports/youth/20070SexualOrientation.pdf.
Potter, B. K., Pederson, L. L., Chan, S. S., Aubut, J. A., & Koval, J. J. (2004). Does a relationship exist between body weight, concerns about weight, and smoking among adolescents? An integration of the literature with an emphasis on gender. Nicotine Tobacco Research, 6(3), 397–425.
Rhode Island Youth Risk Behavior Survey (YRBS). http://www.health.ri.gov/data/youthriskbehaviorsurvey/index.php. Accessed 2011.
Richards, K. C., Campania, C., & Muse-Burke, J. L. (2010). Self-care and well-being in mental health professionals: The mediating effects of self-awareness and mindfulness. Journal of Mental Health Counseling, 32(3), 247.
Rigby, A. S. (2000). Statistical methods in epidemiology. v. Towards an understanding of the kappa coefficient. Disability and Rehabilitation, 22(8), 339–344.
SAS Institute. (2004). SAS institute User’s Guide, Version 9.1. Gary.SchoolMentalHealth.org. http://www.schoolmentalhealth.org/Resources/ESMH/DefESMH.html.
Strauss, R. S. (1999a). Comparison of measured and self-reported weight and height in a cross-sectional sample of young adolescents. International Journal of Obesity and Related Metabolic Disorders, 23(8), 904–908.
Strauss, R. S. (1999b). Self-reported weight status and dieting in a cross-sectional sample of young adolescents: National health and nutrition examination survey III. Archives of Pediatrics and Adolescent Medicine, 153(7), 741–747.
Taras, H., & Potts-Datema, W. (2005). Childhood asthma and student performance at school. Journal of School Health, 75(8), 296–312.
ter Bogt, T. F., van Dorsselaer, S. A., Monshouwer, K., Verdurmen, J. E., Engels, R. C., & Vollebergh, W. A. (2006). Body mass index and body weight perception as risk factors for internalizing and externalizing problem behavior among adolescents. The Journal of Adolescent Health, 39(1), 27–34.
Weiss, R., Shaw, M., Savoye, M., & Caprio, S. (2009). Obesity dynamics and cardiovascular risk factor stability in obese adolescents. Pediatric Diabetes, 10(6), 360–367.
Whetstone, L. M., Morrissey, S. L., & Cummings, D. M. (2007). Children at risk: the association between perceived weight status and suicidal thoughts and attempts in middle school youth. Journal of School Health, 77(2), 59–66. quiz 98–59.
Winter, A. L., de Guia, N. A., Ferrence, R., & Cohen, J. E. (2002). The relationship between body weight perceptions, weight control behaviours and smoking status among adolescents. Canadian Journal of Public Health, 93(5), 362–365.
Xie, B., Chou, C. P., Spruijt-Metz, D., Reynolds, K., Clark, F., Palmer, P. H., et al. (2006). Weight perception, academic performance, and psychological factors in Chinese adolescents. American Journal of Health Behavior, 30(2), 115–124.
Zimmermann, M. B., Gubeli, C., Puntener, C., & Molinari, L. (2004). Detection of overweight and obesity in a national sample of 6–12-y-old Swiss children: accuracy and validity of reference values for body mass index from the US centers for disease control and prevention and the international obesity task force. The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, 79(5), 838–843.
Acknowledgments
The Rhode Island Departments of Health; Elementary and Secondary Education; Mental Health, Retardation, and Hospitals; and the Executive Office of Health and Human Services provided funding and other support for the 2007 and 2009 Rhode Island Youth Risk Behavior Survey. The Rhode Island Department of Health contracted with Market Decisions, LLC, of Portland Maine to administer the 2007 and 2009 YRBS in high schools statewide.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jiang, Y., Risica, P.M., Arias, W. et al. Perceived Weight Status Effect on Adolescent Health-Risk Behaviors: Findings from 2007 and 2009 Rhode Island Youth Risk Behavioral Survey. School Mental Health 4, 46–55 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12310-011-9068-3
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12310-011-9068-3