Abstract
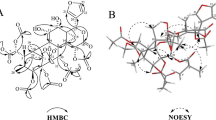
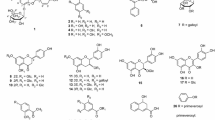
A new neolignan, linderin A (1), together with six known lignans, (+)-xanthoxyol (2), pluviatilol (3), actiforin (4), (+)-syringaresinol (5), (+)-(7S,8R,8′R)-acuminatolide (6), and (+)-9′-O-trans-feruloyl-5,5′-dimethoxylariciresinol (7) were isolated from the stems of Lindera obtusiloba Blume (Lauraceae). Their chemical structures were elucidated by a combination of spectroscopic analysis and chemical reaction, and the absolute configuration of 1 was determined by Mosher’s esterification. The effect of compounds 1–7 on tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α, interleukin(IL)-6, and their inhibitory activity of histamine release were examined using human mast cells. Among the lignans tested, compounds 1, 3, 4, 6, and 7 inhibited release of histamine from mast cells. Especially, compounds 1 and 4 suppressed the gene expressions of pro-inflammatory cytokines, TNF-α, and IL-6 in human mast cells. Our findings suggest that the lignan constituents in L. obtusiloba may contribute to its anti-allergic inflammatory effects.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Choi, E.J., S. Lee, H.H. Kim, T.S.K. Singh, J.K. Choi, H.G. Choi, W.M. Suh, S.H. Lee, and S.H. Kim. 2011. Suppression of dust mite extract and 2,4-dinitrochlorobenzene-induced atopic dermatitis by the water extract of Lindera obtusiloba. Journal of Ethnopharmacology 137: 802–807.
Hironobu, T., Y. Seiko, K. Shoichi, A. Hiroshi, and F. Yoshiyasu. 2002. Lignans and sesquiterpenes from Magnolia praecocissima. Chemical and Pharmaceutical Bulletin 50: 541–543.
Kim, S.H., C.D. Jun, K. Suk, B.J. Choi, H. Lim, S. Park, S.H. Lee, H.Y. Shin, D.K. Kim, and T.Y. Shin. 2006. Gallic acid inhibits histamine release and pro-inflammatory cytokine production in mast cells. Toxicological Sciences 91: 123–131.
Kim, S.H., S. Lee, K. Suk, H. Bark, C.D. Jun, D.K. Kim, C.H. Choi, and T. Yoshimura. 2007. Discoidin domain receptor 1 mediates collagen-induced nitric oxide production in J774A.1 murine macrophages. Free Radical Biology and Medicine 42: 343–352.
Kubo, I., Jamalamadaka, V., Kamisawa, T., Takahashi, K., Tabata, K., Kusumi, K. 1996. Absolute stereochemistry of tanabalin, an insect antifeedant clerodane from Tanacetum balsamita. Chemistry Letters, 441–442.
Kuo, P.C., M.C. Lin, G.F. Chen, T.J. Yiu, and J.T.C. Tzen. 2011. Identification of methanol-soluble compounds in sesame and evaluation of antioxidant potential of its lignans. Journal of Agriculture and Food Chemistry 59: 3214–3219.
Kwon, H.C., S.U. Choi, J.O. Lee, K.H. Bae, O.P. Zee, and K.R. Lee. 1999. Two new lignans from Lindera obtusiloba Blume. Archives of Pharmacal Research 22: 417–422.
Kwon, H.C., N.I. Baek, S.U. Choi, and K.R. Lee. 2000. New cytotoxic butanolides from Lindera obtusiloba. Chemical and Pharmaceutical Bulletin 48: 614–616.
Lee, J., E.K. Seo, D.S. Jang, T.J. Ha, J.P. Kim, J.W. Nam, G. Bae, Y.M. Lee, D.S. Yang, and J.S. Kim. 2009. Two new stereoisomers of neolignan and lignan from the flower buds of Magnolia fargesii. Chemical and Pharmaceutical Bulletin 57: 298–301.
Yook, C.S. 1989. Medicinal Plants of Korea. Seoul: Jinmyeong Publishing Co.
Park, J.C., Y.B. Yu, and J.H. Lee. 1996. Isolation and structure elucidation of flavonoid glycosides from Lindera obtusiloba Blume. J. Korean. Soc. Food Nutr. 25: 76–79.
Su, B.N., E.J. Park, Z.H. Mbwambo, B.D. Santarsiero, A.D. Mesecar, H.H.S. Fong, J.M. Pezzuto, and A.D. Kinghon. 2002. New chemical constituents of Euphorbia quinquecostata and absolute configuration assignment by a convenient Mosher ester procedure carried out in NMR tubes. Journal of Natural Products 65: 1278–1282.
Takanu, N., D.H. Choi, K. Mikame, T. Okunishi, S. Suzuki, H. Ohashi, T. Umezawa, and M. Shimada. 2001. Lignans of Chamaecyparis obtusa. Journal of Wood Science 47: 476–482.
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by the Yeungnam University research grants in 2013.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Choi, H.G., Choi, Y.H., Kim, J.H. et al. A new neolignan and lignans from the stems of Lindera obtusiloba Blume and their anti-allergic inflammatory effects. Arch. Pharm. Res. 37, 467–472 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-013-0239-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-013-0239-7