Abstract
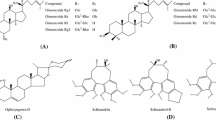
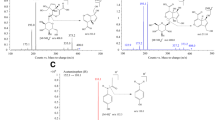
The pharmacokinetics, tissue distribution, metabolism, and excretion of ginsenosides Rg1 were studied in Wistar rats, by measuring the concentrations of Rg1 and its metabolites in the blood, tissues, bile, urine, and feces after dosing. After intravenous (i.v.) administration, the elimination half-lives of Rg1 and its metabolites were 1.82, 5.87, and 6.87 h, and the area under the curves were 1595.7, 597.5, and 805.6 ng· h/mL, respectively. After oral administration, the elimination half-lives of Rg1 and its metabolites were 2.25, 6.73, 5.44, and 5.06 h, and the area under the curves were 2363.5, 4185.5, 3774.3, and 396.2 ng· h/mL, respectively. After i.v. administration, Rg1 and its metabolites were well distributed to the tissues analyzed except for the brain. The maximum concentration of Rg1 was reached in all tissues at 5 min post dose, and it was eliminated from most of the tissues except for the kidney faster than it was eliminated from the blood. The maximum concentration of the metabolites was reached in all tissues between 4 and 6 h post dose. After i.v. administration, the recovery of the Rg1 prototype in the urine and bile was 27.96% and 60.77%, respectively. The metabolism of Rg1 in the intestine was via a hydrolization pathway, with the 6- and 20-glucoside bond hydrolyzed gradually under the catalysis of β-glucosaccharase, and then the metabolites were reabsorbed into the blood. Finally, the total recovery of the Rg1 prototype and its metabolites in the urine and feces were 51.31% and 47.46%, respectively.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Attele, A. S., Wu, J. A., and Yuan, C. S., Ginseng Pharmacology multiple constituents and multiple actions. Biochem. Pharmacol., 58, 1685–1693 (1999).
Bae, E. A., Han, M. J., Choo, M. K., Park, S. Y., and Kim, D. H., Metabolism of 20 (S)- and 20 (R)-Ginsenoside Rg3 by human intestinal bacteria and its relation to in vitro biological activities. Biol. Pharm. Bull., 25, 58–63 (2002).
Chen, G. T., Yang, M., Lu, Z. Q., Zhang, J., Huang, H., Liang, Y., Guan, S., Song, Y., Wu, L., and Guo, D. A., Microbial transformation of 20(S)-protopanaxatriol type saponins by Absidia eoerulea. J. Nat. Prod., 70, 1203–1206 (2007).
Chen, X., Cardiovascular protection by ginsenosides and their nitric oxide releasing action. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol., 23, 728–732 (1996).
Gillis, C. N., Panax ginseng pharmacology: a nitric oxide link. Biochem. Pharmacol., 54, 1–8 (1997).
Han, M., Han, L. M., Wang, Q. S., Bai, Z. H., and Fang, X. L., Mechanism of oral absorption of panax notoginseng saponins. Yao Xue Xue Bao, 41, 498–505 (2006).
Hasegawa, H., Sung, J. H., Matsumiya, S., and Uchiyama, M., Main ginseng saponin metabolites formed by intestinal bacteria. Planta Med., 62, 453–457 (1996).
Kim, J. Y., Germolec, D. R., and Luster, M. I., Panax ginseng as a potential immunomodulator: studies in mice. Immunopharmacol. Immunotoxicol., 12, 257–276 (1990).
Lee, Y. J., Chung, E., Lee, K. Y., Lee, Y. H., Huh, B., and Lee, S. K., Ginsenoside-Rg1, one of the major active molecules from Panax ginseng, is a functional ligand of glucocorticoid receptor. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol., 133, 135–140 (1997).
Ma, Y. Q., Li, T., and Xiao, J. C., Research of the pharmacokinetics about 3H labeled ginsenoside Rg1 in rat. Chin. Tradit. Herb. Drugs, 18, 21–24 (1987).
Odani, T., Tanizawa, H., and Takino, Y., Studies on absorption, distribution, excretion and metabolism of ginseng saponins. II. The absorption, distribution and excretion of ginsenoside Rg1. Chem. Pharm. Bull., 31, 292–298 (1983).
Shibata, S., Tanaka, O., and Shoji, J., Chemistry and pharmacology of Panax notoginseng. Econo. Med. Plant. Res., Academic Press, New York, pp. 217–284, (1985).
Wakabayashi, C., Murakami, K., Hasegawa, H., Murata, J., and Saiki, I., An intestinal bacterial metabolite of ginseng protopanax saponins has the ability to induce apoptosis in tumor cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun., 246, 725–730 (1998).
Wang, Y., Liu, T. H., and Wang, Y. P., Studies on the metabolism of ginsenosides Rg1 by intestinal bacterial and its absorbed metabolites in rat and human serum. Acta Pharmacol. Sin., 35, 284–288 (2000).
Xu, Q. F., Fang, X. L., and Chen, D. F., Pharmacokinetics and bioavailabilities of ginsenosides Rb1 and Rg1 from Panax notoginseng in rats. J. Ethnopharmacol., 84, 187–192 (2003).
Yamaguchi, Y., Higashi, M., and Kobayashi, H., Effects of oral and intraventricular administration of ginsenosides Rg1 on the performance impaired by scopolamine in rats. Biomed. Res., 17, 487–490 (1996).
Zhang, J. W., Wang, G. J., and Sun, J. G., Progress in pharmacodynamics and pharmacokinetics of ginsenoside Rgl. J. Chin. Pharm. Univ., 38, 283–288 (2007).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Feng, L., Wang, L., Hu, C. et al. Pharmacokinetics, tissue distribution, metabolism, and excretion of ginsenoside Rg1 in rats. Arch. Pharm. Res. 33, 1975–1984 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-010-1213-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-010-1213-2