Abstract
The limestone forest of Mt. Exianling on Hainan Island, China, was inventoried, and their floristic composition and biogeographical affinities discussed. Botanical surveys recorded 1121 vascular plant species belonging to 620 genera and 171 families; of which 81 represented significant records including 11 new species. Mt. Exianling is characterized by phanerophytes making up ca. 79% of the total flora, and those with mesophyllous leaves comprising ca. 64%. Ecological species groups were discerned from field observations: species exclusive to limestone habitats make up 2.4% of the total flora. Based on their distributions, 11 biogeographic elements at the generic level are recognized. Our work on Mt. Exianling revealed closer affinity to tropical Asian floras than to temperate elements of eastern Asian floras, with ca. 90% of the seed plant genera being tropical; this limestone forest is essentially tropical and is part of the tropical Asian flora at its northern margin. Unfortunately, Exianling has been subject to environmental threats from mining activities in the past two decades. Kadoorie Conservation China has heavily involved in the conservation of Exianling limestone forest and partially financed the above floristic studies. A nature reserve station was constructed in 2009, and now Exianling is being gazetted as a formal provincial nature reserve. Recently, activities in exploiting of the gold mining in Exianling has been stopped by the nature reserve.

Similar content being viewed by others
Literature Cited
Chin, S. C. 1977 The limestone hill flora of Malaya, I. Gard. Bull. Singapore 30: 165–219.
Chin, S. C. 1979. The limestone hill flora of Malaya, II. Gard. Bull. Singapore 32: 64–203.
Chung, K. F., Leong, W. C., Rubite, R. R., et al. 2014. Phylogenetic analyses of Begonia sect. Coelocentrum and allied limestone species of China shed light on the evolution of Sino-Vietnamese karst flora. Botanical Studies 55:1.
Clements, R., Sodhi, N.S., Schilthuizen, M., et al. 2006. Limestone karsts of Southeast Asia: imperiled arks of biodiversity. BiosCience 56:733–742.
Gong, Z.T., Zhang, G.L. & Qi, Z.P. 2004. Outline of the soil series in Hainan Island, pp. 5. Science Press, Beijing. [In Chinese.]
Guangdong Institute of Botany. 1976. Vegetation of Guangdong, pp. 41–98. Science Press, Beijing. [In Chinese.]
Henry. 1886. Ling-nam or interior views of southern China, including explorations in the hitherto untraveled island of Hainan. London.
IUCN. 2016. The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. http://www.iucnredlist.org. Accessed 27 Dec 2016
Lee, K.S. & Lu, G. 2007. Birds of Exianling area, Hainan; with a new record for Hainan. Tropical Forestry 35 Supplement: 24–27. [In Chinese with English abstract.]
Li, Z.X. & Xing F.W. 1990. Some newly recorded plants from Hainan (II). Acta Botanica Austro Sinica. 6: 31–37. [In Chinese with English abstract.]
Liang, C. F., Liang, J. Y. & Liu, L. F. 1985. A report on the exploration of the flora of Longgang. Guihaia 5(3): 191–209. [In Chinese with English abstract.]
Liu, L. H. 1987. Rain forest. In: C. Y. Wu (editor), Vegetation of Yunnan. Science Press, Beijing. [In Chinese.]
Liu, H., Zhang, Ye, G. & Chen, H. 1994. Floristic analysis of the Longhua natural reserve. Acta Bot. Austrosinica 9: 1–16. [In Chinese with English abstract.]
Lu, G. & Chen, Q. 2007. Report of Orchidaceae at Exianling area, Hainan. Tropical Forestry 35 Supplement: 19–21. [In Chinese with English abstract.]
Qin, X.S. 2006. Studies on the limestone flora and phytogeography of Hainan Island. PhD dissertation, South China Botanical Garden, the Chinese Academy of Sciences, Guangzhou. [In Chinese with English abstract.]
——, Yan, Y. H., Wang, F.G., et al. 2005. Flora characteristics of Pteridophytes in limestone regions in Hainan Island. Acta Scientiarum Naturalium Universitatis Sunyatseni. 44 (Sup. 2): 201–208. [In Chinese with English abstract.]
——, Zhang, R.J., Chen, H.F., et al. 2007. General state of knowledge of thevascular-plant flora of limestone regions on Hainan Island. Tropical Forestry. 35 (Sup.): 6–9. [In Chinese with English abstract.]
——, He, K.S., Liu, L.W., et al. 2012. Floristic and ecological characteristics of the community with Impatiens hainanensis in Exianling limstone mountain, Hainan. Journal of South China Agricultural University 33(3):361–367.[In Chinese with English abstract.]
——, —— & Xing, F.W. 2014. Flora of seed plants in the limestone areas of Hainan. 35(3):90–99. [In Chinese with English abstract.]
Raunkiaer, C. 1934. The life forms of plants and statistical plant geography. Oxford Univ. Press, Oxford.
Schimper, A. F. W. 1903. Plant-geography upon a physiological basis. Oxford Univ. Press, Oxford.
Shimizu, T. 1964. Studies on the limestone flora of Japan and Taiwan. Part II. J. Fac. Textile Sci. Technol. Shinsu Univ., A 12: 1–88.
The Local Chronicles Compilation Committee of Changjing Li Minority Autonomous County, 1998 Hainan. Changjiang County Annals.
Thin, N. N. 1997. The vegetation of Cucphuong national park, Vietnam. Sida 17: 719–759.
Tian, H.Z. 2013. Comparison of Orchidaceae flora in 38 regions of China. Acta Bot. Boreal. -Occident. Sin. 33(4):0808–0823.[In Chinese with English abstract.]
Wang, Q.L. 2012. Taxonomic revision of the Acanthaceae from Hainan Province. Master of Botany dissertation, College of Horticulture and Landscape Architecture, Hainan University, Haikou. [In Chinese with English abstract.]
Wang, H., Zhu, H. & Li, B.G. 1997. Vegetation on limestone in Xishuangbanna, southwest China. Guihaia 17: 101–117. [In Chinese with English abstract.]
Wang, F.G., Qin, X.S. & Chen, H.F. 2006. Endemic plants in limestone region on Hainan Island. Journal of Tropical and Subtropical Botany. 14(1): 45–54.[In Chinese with English abstract.]
Wei, H.J., Shu, J.P., Huang, K.R., et al. 2016. New records of pteridophytes distributed in Hainan. Acta Bot. Boreal. -Occident. Sin. 36(3):0627–0630.[In Chinese with English abstract.]
Whitmore, T. C. 1984. Tropical rain forests of the Far East, 2nd ed. Clarendon Press, Oxford.
Wu, C. Y. 1980. Vegetation of China, pp. 363–397. Science Press, Beijing. [In Chinese.]
—— 1991. The areal-types of Chinese genera of seed plants. Acta Bot. Yunnan Suppl. IV: 1–139.
Xing, F.W. Zhou, J. S. & Wang, F.G. 2012. Inventory of plant species diversity of Hainan. Huazhong University of Science & Technology Press, Wuhan. [In Chinese.]
Yuan, Q. 2016. Wild flower resources in karst region of Exianling, Hainan Island and their use in landscape. Journal of Tropical Biology. 7(2):185–189.[In Chinese with English abstract.]
Zhang, R.J. 2007. Study on limestone phytocoenology of Hainan, China. PhD dissertation, South China Botanical Garden, the Chinese Academy of Sciences, Guangzhou. [In Chinese with English abstract.]
—— 2015. Hainan Exianling: the tropical rainforest on limestone. Forest & Humankind (2):46–49. [In Chinese.]
——, —— & Xing, F.W. 2005. Features of Lasiococca comberi var. pseudoverticillaita Community in limestone areas in Changjiang, Hainan Island. Acta Scientiarum Naturalium Universitatis Sunyatseni 44(Sup.): 283–290. [In Chinese with English abstract.]
——, Qin, X.S., Chen H.F., et al. 2007. Study on the community of Euphorbia hainanensis in the limestone shrubland of Exianling Moutains, Hainan Province. Guihaia 27(5): 725–729. [In Chinese with English abstract.]
Zhong, Y.F., Wu, H.Z., Song, X.Q., et al. 2014. Species diversity and the relationship with habitat community characteristics of Impatiens hainanensis, endemic to Hainan Island. Chinese Journal of Tropical Crops 35(2):355–361.[In Chinese with English abstract.]
Zhu, H. 2002. Ecology and biogeography of the limestone vegetation in southern Yunnan, SW China. Kunming: Yunnan Science & Technology Press, 1–67.
—— 2005. Reclassifiction of monsoon tropical forests in southern Yunnan, SW China. Acta Phytoecologica Sinica 29(1):170–174. [In Chinese with English abstract.]
——, Wang, H., Li, B., et al. 2003. Biogeography and floristic affinities of the limestone flora in southern Yunnan, China. Ann. Missouri Bot. Gard. 90: 444–465.
Acknowledgements
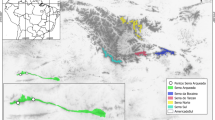
The authors would like to thank the Forestry Department of Hainan Province for granting permission for conducting fieldwork. We thank Li Fei of Kadoorie Farm and Botanic Garden for kindly producing Fig. 1, and Chen Qing of Bawangling National Nature Reserve for assistance in fieldwork. The villagers of Nanlang provided much logistic supports for fieldwork and lodging. The senior author is grateful to Philip Lo of Kadoorie Farm and Botanic Garden for his assistance and advice in conducting this study. This project was funded by The National Natural Science Foundation of China (41001028, 41471046), and Kadoorie Farm and Botanic Garden.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Appendix
Appendix
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, R., Qin, X., Chen, H. et al. Phytogeography and Floristic Affinities of the Limestone Flora of Mt. Exianling, Hainan Island, China. Bot. Rev. 83, 38–58 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12229-017-9176-3
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12229-017-9176-3