Abstract
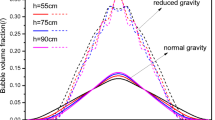
The gas-liquid two-phase flow has been widely applied to the field of space technology, such as thermal energy and power generation, long duration life support systems, transportation for propulsion, etc. (Microgravity Sci. Technol. 21, 175-183 (2009); Microgravity Sci. Technol. 22, 87-96 (2010); etc.). Through reviewing previous researches, it can be found that a dynamic viscosity blind region (almost not influenced by the shear-thinning effect) appears behind it when one bubble rises in the shear-thinning fluid (J. Non-Newton Fluid. Mech. 165, 555-567 (2010); Phys. Fluids. 29, 033103 (2017), J. Non-Newton. Fluid. Mech. 239, 53 -61 (2017); etc.). As a matter of fact, the occurrence of the viscosity blind region has the important effect on heat and mass transfer between bubble and liquid phases. Therefore, volume of fluid method is implemented to study the formation and evolution mechanisms of the viscosity blind region in the shear-thinning fluid. The results show that the viscosity blind region can be split into two regions, namely the first and the second viscosity blind region. The stronger the gravity level and the shear-thinning effect are, or the smaller the surface tension is, the more easily the viscosity blind region appears in the bubble wake. The viscosity blind region appears much easily in the wake of a skirt bubble under the same conditions. And in the rising process of the bubble, there is a stagnant flow region in the bubble wake, where the shear rate is very small, so the viscosity blind region appears in that region. In addition, the appearance of double wake vortices can split the stagnant flow region into two parts, which leads to the formation of the second viscosity blind region.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amirnia, S., de Bruyn, J.R., Bergougnou, M., Margaritis, A.: Continuous rise velocity of air bubbles in non-Newtonian biopolymer solutions. Chem. Eng. Sci. 94, 60–68 (2013)
Araújo J.D.P., Miranda J.M., Campos J.B.L.M.: Taylor bubbles rising through flowing non-Newtonian inelastic fluids. J. Non-Newton Fluid. Mech. 245, 49–66 (2017)
Bhaga, D., Weber, M.E.: Bubbles in viscous liquids: shapes, wakes and velocities. J. Fluid Mech. 105, 61–85 (1981)
Brackbill, J.U., Kothe, D.B., Zemach, C.A.: A continuum method for modeling surface tension. J. Comput. Phys. 100, 335–354 (1992)
Chhabra, R.: Bubbles, drops, and particles in non-Newtonian fluids. CRC Press, Boca Raton, USA (2007)
DeKee, D., Carreau, P.J.: Friction factors and bubble dynamics in polymer solutions. Can. J. Chem. Eng. 71(2), 183–188 (1993)
Dimakopoulos, Y., Makrigiorgos, G., Gc, G., Tsamopoulos, J.: The pal (penalized augmented Lagrangian) method for computing viscoplastic flows: a new fast converging scheme. J. Non-Newton. Fluid Mech. 256, 23–41 (2018)
Dilleswara, R.K., Vasukiran, M., Gollakota, A.R.K., Kishore, N.: Buoyancy driven bubble rise and deformation in milli/micro channels filled with shear-thinning nanofluids. Colloid. Surface. A. 467, 66–77 (2015)
Gummalam, S., Narayan, K.A., Chhabra, R.P.: Rise velocity of a swarm of spherical bubbles through a non-Newtonian fluid: effect of zero shear viscosity. Int. J. Multiphase Flow. 14, 361–373 (1988)
Imai, R., Imamura, T., Sugioka, M., Higashino, K.: Research on liquid management technology in water tank and reactor for propulsion system with hydrogen production system utilizing aluminum and water reaction. Microgravity Sci. Technol. 29, 475–484 (2017)
Kawase, Y., Moo-Young, M.: Approximate solutions for drag coefficient of bubbles moving in shear-thinning elastic fluids. Rheol. Acta. 24, 202–206 (1985)
Li, S.B., Ma, Y.G., Fu, T.T., Zhu, C.Y., Li, H.Z.: The viscosity distribution around a rising bubble in shear-thinning non-newtonian fluids. Braz. J. Chem. Eng. 29, 265–274 (2012)
Liu, L., Yan, H.J., Zhao, G.J., Zhuang, J.C.: Experimental studies on the terminal velocity of air bubbles in water and glycerol aqueous solution. Exp. Thermal Fluid Sci. 78, 254–265 (2016)
Liu, J.R., Zhu, C.Y., Fu, T.T., Ma, Y.G.: Numerical simulation of the interactions between three equal-interval parallel bubbles rising in non-Newtonian fluids. Chem. Eng. Sci. 93, 55–66 (2013)
Ohta, M., Kimura, S., Furukawa, T., Yoshida, Y., Sussman, M.: Numerical simulations of a bubble rising through a shear-thickening fluid. J. Chem. Eng. Jpn. 45(9), 713–720 (2012)
Ohta, M., Yoshida, Y., Sussman, M.: A computational study of the dynamic motion of a bubble rising in Carreau model fluids. Fluid Dyn. Res. 42, 025501 (2010)
Pang, M.J., Wei, J.J., Yu, B.: Investigation on effect of gravity level on bubble distribution and liquid turbulence modification for Horizontal Channel bubbly flow. Microgravity Sci. Technol. 29, 313–324 (2017)
Poryles, R., Vidal, V.: Rising bubble instabilities and fragmentation in a confined polymer solution. J. Non-Newtonian Fluid Mech. 241, 26–33 (2017)
Premlata, A.R., Tripathi, M.K., Karri, B., Sahu, K.C.: Numerical and experimental investigations of an air bubble rising in a CarreauYasuda shear-thinning liquid. Phys. Fluids. 29, 033103 (2017a)
Premlata, A.R., Tripathi, M.K., Karri, B., Sahu, K.C.: Dynamics of an air bubble rising in a non-Newtonian liquid in the axisymmetric regime. J. Non-Newton. Fluid. Mech. 239, 53–61 (2017b)
Salim, A., Colin, C., Dreyer, M.: Experimental investigation of a bubbly two-phase flow in an open Capillary Channel under microgravity conditions. Microgravity Sci. Technol. 22, 87–96 (2010)
Sikorski, D., Tabuteau, H., de Bruyn, J.R.: Motion and shape of bubbles rising through a yield-stress fluid. J. Non-Newtonian Fluid Mech. 159, 10–16 (2009)
Sun, D.K., Zhu, M.F., Wang, J., Sun, B.D.: Lattice Boltzmann modeling of bubble formation and dendritic growth in solidification of binary alloys. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 94, 474–487 (2016)
Tripathi, M.K., Sahu, C., Govindarajan, R.: Dynamics of an initially spherical bubble rising in quiescent liquid. Nat. comom. 6268, 6 (2015a)
Tripathi, M.K., Sahu, K.C., Karapetsas, G., Matar, O.K.: Bubble rise dynamics in a viscoplastic material. J. Non-Newtonian Fluid Mech. 222, 217–226 (2015b)
Tsamopoulos, J., Dimakopoulos, Y., Chatzidai, N., Karapetsas, G., Pavlidis, M.: Steady bubble rise and deformation in Newtonian and viscoplastic fluids and conditions for bubble entrapment. J. Fluid Mech. 601, 123–164 (2008)
Wang, T., Li, H.Z., Zhao, J.F.: Three-dimensional numerical simulation of bubble dynamics in microgravity under the influence of nonuniform electric fields. Microgravity Sci. Technol. 28, 133–142 (2016)
Wu, K., Li, Z.D., Zhao, J.F., Li, H.X., Li, K.: Partial nucleate Pool boiling at low heat flux: preliminary ground test for SOBER-SJ10. Microgravity Sci. Technol. 28, 165–178 (2016)
Worner, M.: Numerical modeling of multiphase flows in microfluidics and micro process engineering: a review of methods and applications. Microfluid. Nanofluid. 12, 841–886 (2012)
Zacharioudaki, M., Kouris, M., Dimakopoulos, Y., Tsamopoulos, J.: A direct comparison between volume and surface tracking methods with a boundary-fitted coordinate transformation and third-order upwinding. J. Math. Phys. 227(2), 1428–1469 (2008)
Zenit, R., Feng, J.J.: Hydrodynamic interactions among bubbles, drops, and particles in non-Newtonian liquids. Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 50, 505–534 (2018)
Zhang, L., Yang, C., Mao, Z.S.: Numerical simulation of a bubble rising in shear-thinning fluids. J. Non-Newton Fluid. Mech. 165, 555–567 (2010)
Zhao, J.F., Zhang, L., Li, Z.D., Qin, W.T.: Topological structure evolvement of flow and temperature fields in deformable drop Marangoni migration in microgravity. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 54, 4655–4663 (2011)
Zhao, J.F., Zhang, L., Yan, N., Wang, S.F.: Bubble behavior and heat transfer in quasi-steady pool boiling in microgravity. Microgravity Sci. Technol. 21, 175–183 (2009)
Zhang, Y.H., Liu, B., Zhao, J.F., Deng, Y.P., Wei, J.J.: Experimental study of subcooled flow boiling heat transfer on a smooth surface in short-term microgravity. Microgravity Sci. Technol. 97, 417–430 (2018)
Acknowledgements
We gratefully acknowledge the financial support from the NSFC Fund (No. 51376026) and Qinglan Project of Jiangsu province.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors report no conflict of interest and have received no payment in preparation of this manuscript.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lu, M., Pang, M. & Chao, J. Distribution Regularity of Dynamic Viscosity Blind Region behind the Bubble in Shear-Thinning Fluids under Different Gravity Levels. Microgravity Sci. Technol. 31, 139–150 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12217-019-9673-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12217-019-9673-6