Abstract
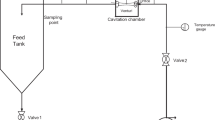
Chlorpyrifos (O,O-diethyl O-3,5,6-trichloropyridin-2-yl phosphorothioate) is a broad spectrum organophosphate pesticide which is widely used in agriculture and residential pest control throughout the world. It is moderately toxic to humans, which persists in nature for relatively long period due to its physicochemical and structural properties, low volatilization, affecting environmental matrices. Thus has been selected as model pollutant for degradation using hybrid treatment method of Hydrodynamic Cavitation (HC). It was found that Chlorpyrifos in real effluent sample can be degraded with orifice induced cavitating conditions. Effect of various process parameters such as operating inlet pressure (over range of 3-8 bars), operating temperatures (with sets of intense cooling, moderate cooling and uncontrolled operation) and pH (natural pH = 10, neutral = 7 and acidic = 3) is investigated for extent of degradation of Chlorpyrifos. Results reflect that an optimum value of inlet pressure (5 bars) gave maximum removal/degradation of 72.7%, high temperature and acidic pH of 3 are suitable. To study the effect of intensification, ozone was used as an intensifying agent. Ozone alone gave 12.2% degradation, but when combined with hydrodynamic cavitation, it resulted into 100% efficiency in 45 minutes of treatment time. Work presented in this paper can be said to be concluding to the effective use of hydrodynamic cavitation in combination with ozone for the degradation of Chlorpyrifos in real wastewaters.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abraham, J. and Silambarasan, S. (2013). “Biodegradation of chlorpyrifos and its hydrolyzing metabolite.” Process Biochemistry, vol. 48, no. 10, pp. 1559–1564, DOI: 10.1016/j.procbio.2013.06.034.
Affam, A. C., Chaudhuri, M., Kutty, S. R. M., and Muda, K. (2014). “UV fenton and sequencing batch reactor treatment of chlorpyrifos, cypermethrin and chlorothalonil pesticide wastewater.” International Biodeterioration and Biodegradation, vol. 93, pp. 195–201, DOI: 10.1016/j.ibiod.2014.06.002.
Agudelo, R. M., Peñuela, G., Aguirre, N. J., Morató, J., and Jaramillo, M. L. (2010). “Simultaneous removal of chlorpyrifos and dissolved organic carbon using horizontal sub-surface flow pilot wetlands.” Ecological Engineering, vol. 36, no. 10, pp. 1401–1408, DOI: 10.1016/j.ecoleng.2010.06.019.
Alina, C., Sanda, B., Monica, T., and Ioana, B. (2011). “The study for determination chlorpyrifos residual from fruit samples.” Analele Universităţii din Oradea, vol. 17, Nos. 3–5, pp. 635–640.
Amin, L. P., Gogate, P. R., Burgess, A. E., and Bremner, D. H. (2010). “Optimization of a hydrodynamic cavitation reactor using salicylic acid dosimetry.” Chemical Engineering Journal, vol. 156, no. 1, pp. 165–169, DOI: 10.1016/j.cej.2009.09.043.
Anwar, S., Liaquat, F., Khan, Q. M., Khalid, Z. M., and Iqbal, S. (2009). “Biodegradation of chlorpyrifos and its hydrolysis product 3, 5, 6-Trichloro-2-Pyridinol by Bacillus Pumilus Strain C2A1.” Journal of Hazardous Materials, vol. 168, no. 1, pp. 400–405, DOI: 10.1016/j.jhazmat. 2009.02.059.
Authority, N. R. and Chemicals, V. (n.d.). “The NRA Review of Chlorpyrifos: Section 6 Environmental Assessment.” 2000.
Badve, M., Gogate, P., Pandit, A., and Csoka, L. (2013). “Hydrodynamic cavitation as a novel approach for wastewater treatment in wood finishing industry.” Separation and Purification Technology, vol. 106, pp. 15–21, DOI: 10.1016/j.seppur.2012.12.029.
Bagal, M. V. and Gogate, P. R. (2013). “Degradation of 2,4-Dinitrophenol Using a combination of hydrodynamic cavitation, chemical and advanced oxidation processes.” Ultrasonics Sonochemistry, vol. 20, no. 5, pp. 1226–1235, DOI: 10.1016/j.ultsonch.2013.02.004.
Bagal, M. V. and Gogate, P. R. (2014a). “Wastewater treatment using hybrid treatment schemes based on cavitation and fenton Chemistry: A review.” Ultrasonics Sonochemistry, vol. 21, no. 1, pp. 1–14, DOI: 10.1016/j.ultsonch.2013.07.009.
Bagal, M. V. and Gogate, P. R. (2014b). “Degradation of diclofenac sodium using combined processes based on hydrodynamic cavitation and heterogeneous photocatalysis.” Ultrasonics Sonochemistry, vol. 21, no. 3, pp. 1035–1043, DOI: 10.1016/j.ultsonch.2013.10.020.
Bhagobaty, R. K., Joshi, S. R., and Malik, A. M. (2006). “Microbial degradation of organophosphorous pesticide: Chlorpyrifos (Mini-Review).” The Internet Journal of Microbiology, vol. 4, no. 1, pp. 1–6, DOI: 10.5580/1282.
Bokhari, A., Chuah, L. F., Yusup, S., Klemeš, J. J., Akbar, M. M., and Kamil, R. N. M. (2016). “Cleaner production of rubber seed oil methyl ester using a hydrodynamic cavitation: Optimisation and parametric study.” Journal of Cleaner Production, Vol. 136, DOI: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2016.04.091.
Capocelli, M., Musmarra, D., Prisciandaro, M., and Lancia, A. (2014). “Chemical effect of hydrodynamic cavitation: Simulation and experimental comparison.” AIChE Journal, vol. 60, no. 7, pp. 2566–2572, DOI: 10.1002/aic.14472.
Capocelli, M., Prisciandaro, M., Lancia, A., and Musmarra, D. (2014). “Hydrodynamic cavitation of P-Nitrophenol: A theoretical and experimental insight.” Chemical Engineering Journal, vol. 254, pp. 1–8, DOI: 10.1016/j.cej.2014.05.102.
Capocelli, M., Prisciandaro, M., Musmarra, D., and Lancia, A. (2013). “Understanding the physics of advanced oxidation in a venturi reactor.” Chemical Engineering Transactions, vol. 32, pp. 691–696, DOI: 10.3303/CET1332116.
Chand, R., Bremner, D. H., Namkung, K. C., Collier, P. J., and Gogate, P. R. (2007). “Water disinfection using the novel approach of ozone and a liquid whistle reactor.” Biochemical Engineering Journal, vol. 35, no. 3, pp. 357–364, DOI: 10.1016/j.bej.2007.01.032.
Deng, S., Chen, Y., Wang, D., Shi, T., Wu, X., Ma, X., Li, X., Hua, R., Tang, X., and Li, Q. X. (2015). “Rapid biodegradation of organophosphorus pesticides by Stenotrophomonas Sp. G1.” Journal of Hazardous Materials, vol. 297, pp. 17–24, DOI: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2015.04.052.
Farhan, M., Khan, U., Wahid, A., Ahmad, M., and Ahmad, F. (2012). “Biodegradation of chlorpyrifos using indigenous pseudomonas Sp. isolated from industrial drain.” Pakistan Journal of Nutrition, vol. 11, no. 12, pp. 1183–1189, DOI: 10.3923/pjn.2012.1183.1189.
George W. Ware (2012). Review of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 131st edn, (Springer Science and Business Media).
George, N., Chauhan, P. S., Sondhi, S., Saini, S., and Puri, N. (2014). ‘Biodegradation and analytical methods for detection of organophosphorous pesticide: Chlorpyrifos.” Int. J. Pure Appl. Sci. Technol., vol. 20, no. 2, pp. 79–94.
Gogate, P. R. (2011). “Hydrodynamic cavitation for food and water processing.” Food and Bioprocess Technology, vol. 4, no. 6, pp. 996–1011, DOI: 10.1007/s11947-010-0418-1.
Gogate, P. R. and Patil, P. N. (2015). “Combined treatment technology based on synergism between hydrodynamic cavitation and advanced oxidation processes.” Ultrasonics Sonochemistry, vol. 25, no. 1, pp. 60–69, DOI: 10.1016/j.ultsonch.2014.08.016.
Gogate, P. R., Mededovic-Thagard, S., McGuire, D., Chapas, G., Blackmon, J., and Cathey, R. (2014). “Hybrid reactor based on combined cavitation and ozonation: From concept to practical reality.” Ultrasonics Sonochemistry, vol. 21, no. 2, pp. 590–598, DOI: 10.1016/j.ultsonch. 2013.08.016.
Hossain, M. S., Fakhruddin, A. N. M., Zaman, M. A., and Alam, M. K. (2013). “Degradation of chlorpyrifos, an organophosphorus insecticide in aqueous solution with gamma irradiation and natural sunlight.” Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering Vol. 1, no. 3, pp. 270–274, DOI: 10.1016/j.jece.2013.05.006.
Ismail, M., Khan, H. M., Sayed, M., and Cooper, W. J. (2013). “Advanced oxidation for the treatment of chlorpyrifos in aqueous solution.” Chemosphere, vol. 93, no. 4, pp. 645–651, DOI: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2013.06.051.
Jawale, R. H., Gogate, P. R., and Pandit, A. B. (2014). “Treatment of cyanide containing wastewater using cavitation based approach.” Ultrasonics Sonochemistry, vol. 21, no. 4, pp. 1392–1329, DOI: DOI: 10.1016/j.ultsonch.2014.01.025.
John, E. M. and Shaike, J. M. (2015). “Chlorpyrifos: Pollution and remediation.” Environmental Chemistry Letters, vol. 13, no. 3, pp. 269–291.
Joshi, R. K. and Gogate, P. R. (2012). “Degradation of dichlorvos using hydrodynamic cavitation based treatment strategies.” Ultrasonics Sonochemistry, vol. 19, no. 3, pp. 532–539, DOI: 10.1016/j.ultsonch. 2011.11.005.
Manjunatha, B., Tirado, J. O., and Philip, G. H. (2015). “Determination of chlorpyrifos residues in water and liver tissue of zebrafish (Danio Rerio) by High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) with UV Detection.” Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research, vol. 7, no. 6, pp. 721–726.
Patil, P. N. and Gogate, P. R. (2012). “Degradation of methyl parathion using hydrodynamic cavitation: Effect of operating parameters and intensification using additives.” Separation and Purification Technology, vol. 95, pp. 172–179, DOI: 10.1016/j.seppur.2012.04.019.
Pengphol, S., Uthaibutra, J., Arquero, O., Nomura, N., and Whangchai, K. (2012). “Oxidative degradation and detoxification of chlorpyrifos by ultrasonic and ozone treatments.” Journal of Agricultural Science, vol. 4, no. 8, pp. 164–172, DOI: 10.5539/jas.v4n8p164.
Phung, D. T., Connell, D., Miller, G., Hodge, M., Patel, R., Cheng, R., Abeyewardene, M., and Chu, C. (2012). “Biological monitoring of chlorpyrifos exposure to rice farmers in vietnam.” Chemosphere, vol. 87, no. 4, pp. 294–300, DOI: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2011. 11.075.
Pradhan, A. and Gogate, P. R. (2010). “Removal of P-Nitrophenol using hydrodynamic cavitation and fenton chemistry at pilot scale operation.” Chemical Engineering Journal, vol. 156, no. 1, pp. 77–82, DOI: 10.1016/j.cej.2009.09.042.
Racke, K. D. (1993). “Environmental fate of chlorpyrifos.” Reviews of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, vol. 131, pp. 1–150, DOI: 10.1007/978-1-4612-4362-5_1.
Raut-jadhav, S., Badve, M. P., Pinjari, D. V, Saini, D. R., Sonawane, S. H., and Pandit, A. B. (2016). “Treatment of the pesticide industry effluent using hydrodynamic cavitation and its combination with process intensifying additives (H2O2 and Ozone).” Chemical Engineering Journal, vol. 295, pp. 326–335, DOI: 10.1016/j.cej.2016.03.019.
Saharan, V. K., Badve, M. P., and Pandit, A. B. (2011). “Degradation of reactive red 120 Dye using hydrodynamic cavitation.” Chemical Engineering Journal, vol. 178, pp. 100–107, DOI: 10.1016/j.cej. 2011.10.018.
Saharan, V. K., Pandit, A. B., Satish Kumar, P. S., and Anandan, S. (2012). “Hydrodynamic cavitation as an advanced oxidation technique for the degradation of acid red 88 Dye.” Industrial and Engineering Chemistry Research, vol. 51, no. 4, pp. 1981–1989, DOI: 10.1021/ie200249k.
Senthil Kumar, P., Siva Kumar, M., and Pandit, A. B. (2000). “Experimental quantification of chemical effects of hydrodynamic cavitation.” Chemical Engineering Science, vol. 55, no. 9, pp. 1633–1639, DOI: 10.1016/S0009-2509(99)00435-2.
Taylor, P., Ghoshdastidar, A. J., Saunders, J. E., Brown, K. H., and Tong, A. Z. (2012). “Membrane bioreactor treatment of commonly used organophosphate pesticides.” Journal of Environmental Science and Health, Part, vol. 47, pp. 742–750, DOI: 10.1080/03601234.2012. 669334.
Theerthagiri, J., Senthil, R. A., Thirumalai, D., and Madhavan, J. (2015). “Handbook of ultrasonics and sonochemistry.” pp. 1–29, DOI: 10.1007/978-981-287-470-2.
Vichare, N. P., Gogate, P. R., and Pandit, a B. (2000). “Optimization of hydrodynamic cavitation using a model reaction.” Chemical Engineering & Technology, vol. 23, pp. 683–690, DOI: 10.1002/1521-4125 (200008)23:8%3C683::AID-C.
W. Ware, G. (2012). Reviews of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 160th edn, (Springer Science and Business Media).
Wang, X. and Zhang, Y. (2009). “Degradation of alachlor in aqueous solution by using hydrodynamic cavitation.” Journal of Hazardous Materials, vol. 161, no. 1, pp. 202–207, DOI: 10.1016/j.jhazmat. 2008.03.073.
Yue, W., Yao, P., Wei, Y., and Mo, H. (2008). “Synergetic effect of ozone and ultrasonic radiation on degradation of chitosan.” Polymer Degradation and Stability, vol. 93, no. 10, pp. 1814–1821, DOI: 10.1016/j.polymdegradstab.2008.07.010.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Randhavane, S.B., Khambete, A.K. Hydrodynamic Cavitation: An approach to Degrade Chlorpyrifos Pesticide from Real Effluent. KSCE J Civ Eng 22, 2219–2225 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12205-017-2045-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12205-017-2045-0