Abstract
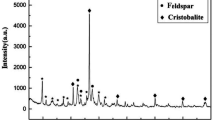
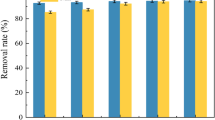
Although nano-sized Biogenic Manganese Oxide (BMO) provides excellent adsorption capacity, its use in water treatment has been limited because it is too small to be readily separated from treated water. Therefore, this work investigated the feasibility of immobilizing BMO on zeolite (BMO/Zeolite) and the use of this material for heavy metal adsorption. BMO/Zeolite was prepared by incubating Pseudomonas putida strain MnB1 in the presence of Mn2+ and natural zeolite pretreated with NaCl (NaCl-Zeolite). BMO immobilization was confirmed by transmission electron microscopy and energy dispersive X-ray analysis. The maximum BMO loading (BMO/Zeolite) was 17.09 mg/g, and the specific surface area increased as the BMO loading was increased. Isotherms and kinetics studies were performed to evaluate the heavy metal adsorption characteristics. The maximum adsorption capacities of Pb2+, Cd2+, and Zn2+ with the BMO/Zeolite were 36.4-70.5% higher than with the NaCl-Zeolite. The amount of heavy metal adsorption increased with higher pH and temperature and with lower ionic strength. The results from this study demonstrate that immobilized BMO not only promotes heavy metal adsorption.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Calvo, B., Canoira, L., Morante, F., Martínez-Bedia, J. M., Vinagre, C., García-González, J. E., Elsen, J., and Alcantara, R. (2009). “Continuous elimination of Pb2+, Cu2+, Zn2+, H+ and NH4 + from acidic waters by ionic exchange on natural zeolites.” J. Hazard. Mater., Vol. 166, pp. 619–627, DOI: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2008.11.087.
Camacho, L. M., Parra, R. R., and Deng, S. (2011). “Arsenic removal from groundwater by MnO2-modified natural clinoptilolite zeolite: Effects of pH and initial feed concentration.” J. Hazard. Mater., Vol. 189, pp. 286–293, DOI: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2011.02.035.
Caspi, R., Tebo, B. M., and Haygood, M. C. (1998). “c-Type cytochromes and manganese oxidation in Pseudomonas putida MnB1.” Appl. Environ. Microb., Vol. 64, No. 10, pp. 3549–3555.
Castaldi, P., Santona, L., Enzo, S., and Melis, P. (2008). “Sorption processes and XRD analysis of a natural zeolite exchanged with Pb2+, Cd2+ and Zn2+ cations.” J. Hazard. Mater., Vol. 156, Nos. 1-3, pp. 428–434, DOI: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2007.12.040.
Cozmuta, L. M., Cozmuta, A. M., Peter, A., Nicula, C., Nsimba, E. B., and Tutu, H. (2012). “The influence of pH on the adsorption of lead by Naclinoptilolite: kinetic and equilibrium studies.” Water SA, Vol. 38, No. 2, pp. 269–278, DOI: 10.4314/wsa.v38i2.13.
Cozmuta, L. M., Cozmuta, A. M., Peter, A., Nicula, C., Tutu, H., Silipas, D., and Indrea, E. (2014). “Adsorption of heavy metal cations by Na-clinoptilolite: Equilibrium and selectivity studies.” J. Environ. Manage., Vol. 137, pp. 69–80, DOI: 10.1016/j.jenvman. 2014.02.007.
David, R. L. (2005). “CRC Handbook of chemistry and physics.” CRC Press, Boca Raton, FL, Internet Version. http://www.hbcpnetbase.com.
Fachini, A. and Vasconcelos, M. T. (2006). “Effects of zeolites on cultures of marine micro-algae: A brief review.” Environ. Sci. Pollut. R., Vol. 13, No. 6, pp. 414–417, DOI: 10.1065/espr2006.01.293.
Feng, X. H., Zhan, L. M., Tan, W. F., Lin, F., and He, J. Z. (2007). “Adsorption and redox reactions of heavy metals on synthesized Mn oxide minerals.” Environ. Pollut., Vol. 147, No. 2, pp. 366–373, DOI: 10.1016/j.envpol.2006.05.028.
Foo, K. Y. and Hameed, B. H. (2010). “Insights into the modeling of adsorption isotherm systems.” Chem. Eng. J., Vol. 156, No. 1, pp. 2–10, DOI: 10.1016/j.cej.2009.09.013.
Gerlach, I., Kawase, M., and Miura, K. (2009). “In-situ preparation of supported precious metal and metal oxide nanoparticles by Nano reactor flash pyrolysis.” Micropor. Mesopor. Mat., Vol. 122, Nos. 1-3, pp. 79–86, DOI: 10.1016/j.micromeso.2009.02.019.
Günay, A., Arslankaya, E., and Tosun, I. (2007). “Lead removal from aqueous solution by natural and pretreated clinoptilolite: Adsorption equilibrium and kinetics.” J. Hazard. Mater., Vol. 146, Nos. 1-2, pp. 362–371, DOI: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2006.12.034.
Ho, Y. S. (2006). “Review of second-order models for adsorption systems.” J. Hazard. Mater., Vol. 136, No. 3, pp. 681–689, DOI: 10.1002/chin.200648222.
Hsu, J. N., Tsai, C. J., Chiang, C., and Li, S. N. (2007). “Silane removal at ambient temperature by using alumina-supported metal oxide adsorbents.” JAPCA J. Air Waste Ma., Vol. 57, No. 2, pp. 204–210, DOI: 10.1080/10473289.2007.10465309.
Joseph, L., Flora, J. R. V., Park, Y. G., Badawy, M., Saleh, H., and Yoon, Y. (2012). “Removal of natural organic matter from potential drinking water sources by combined coagulation and adsorption using carbon nanomaterials.” Sep. Purif. Technol., Vol. 95, No. 19, pp. 64–72, DOI: 10.1016/j.seppur.2012.04.033.
Kiran, I., Akar, T., Ozcan, A. S., Ozcan, A., and Tunali, S. (2006). “Biosorption kinetics and isotherm studies of Acid Red 57 by dried Cephalosporium aphidicola cells from aqueous solutions.” Biochem. Eng. J., Vol. 31, No. 3, pp. 197–203, DOI: 10.1016/j.bej.2006.07.008.
Kragovic, M., Dakovic, A., Sekulic, Z., Trgo, M., Ugrina, M., Peric, J., and Gattac, G. D. (2012). “Removal of lead from aqueous solutions by using the natural and Fe(III)-modified zeolite.” Appl. Surf. Sci., Vol. 258, No. 8, pp. 3667–3673, DOI: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2011.12.002.
Liu, Y. (2008). “New insights into pseudo-second-order kinetic equation for adsorption: Short communication.” Colloid Surface A, Vol. 320, Nos. 1-3, pp. 275–278, DOI: 10.1016/j.colsurfa.2008.01.032.
Mandernack, K. W., Fogel, M. L., Tebo, B. M., and Usui, A. (1995). “Oxygen isotope analyses of chemically and microbially produced manganese oxides and manganates.” Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta, Vol. 59, No. 21, pp. 4409–4425, DOI: 10.1016/0016-7037(95)00299-f.
Meng, Y. T., Zheng, Y. M., Zhang, L. M., and He, J. Z. (2009). “Biogenic Mn oxides for effective adsorption of Cd from aquatic environment.” Environ. Pollut., Vol. 157, Nos. 8-9, pp. 2577–2583, DOI: 10.1016/j.envpol.2009.02.035.
Nelson, Y. M., Lion, L. W., Ghiorse, W. C., and Shuler, M. L. (1999). “Production of biogenic Mn oxides by Leptothrix discophora SS-1 in a chemically defined growth medium and evaluation of their Pb adsorption characteristics.” Appl. Bioche. Biotechnol., Vol. 65, No. 1, pp. 75–180, DOI: 10.1016/0016-7037(88)90186-x.
Ragnarsdottir, K. V., Graham, C. M., and Allen, G. C. (1996). “Surface chemistry of reacted heulandite determined by SIMS and XPS.” Chem. Geol., Vol. 131, Nos. 1-4, pp. 167–181, DOI: 10.1016/0009-2541(96) 00065-4.
Sasaki, K., Kaseyama, T., and Hirajima, T. (2009). “Selective sorption of Ce3+ over La3+ Ions on biogenic manganese oxides.” Adv. Mat. Res., Vols. 71-73, pp. 633-636, DOI: 10.4028/www.scientific.net/amr.71-73.633.
Sasaki, K., Matsuda, M., Urata, T., Hirajima, T., and Konno, H. (2008). “Sorption of CO2+ ions on the biogenic Mn oxide produced by a Mnoxidizing fungus, Paraconiothyrium sp. WL-2.” Mater. Trans., Vol. 49, No. 03, pp. 605–611, DOI: 10.2320/matertrans.m-mra2007888.
Sasaki, K., Yu, Q., Momoki, T., and Kaseyama, T. (2014). “Adsorption characteristics of Cs+ on biogenic birnessite.” Appl. Clay Sci., Vol. 101, pp. 23–29, DOI: 10.1016/j.clay.2014.06.028.
Serrano, S., O’Day, P. A., Vlassopoulos, D., García-González, M. T., and Garrido, F. (2009). “A surface complexation and ion exchange model of Pb and Cd competitive sorption on natural soils.” Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta, Vol. 73, No. 3, pp. 543–558, DOI: 10.1016/j.gca. 2008.11.018.
Shin, W. S., Kang, K., and Kim, Y. K. (2014). “Adsorption characteristics of multi-metal ions by red mud, zeolite, limestone, and oyster shell.” Environ. Eng. Res., Vol. 19, No. 1, pp. 15–22, DOI: 10.4028/www.scientific.net/kem.368-372.1541.
Sprynskyy, M., Buszewski, B., Terzyk, A. P., and Namiesnik, J. (2006). “Study of the selection mechanism of heavy metal (Pb2+, Cu2+, Ni2+, and Cd2+) adsorption on clinoptilolite.” J. Colloid Interface Sci., Vol. 304, No. 1, pp. 21–28, DOI: 10.1016/j.jcis.2006.07.068.
Taffarel, S. R. and Rubio, J. (2009). “On the removal of Mn2+ ions by adsorption onto natural and activated Chilean zeolites.” Miner. Eng., Vol. 22, No. 4, pp. 336–343, DOI: 10.1016/j.mineng.2008.09.007.
Taguchi, A. and Schüth, F. (2005). “Ordered mesoporous materials in catalysis.” Micropor. Mesopor. Mater., Vol. 77, No. 1, pp. 1–45, DOI: 10.1016/j.micromeso.2004.06.030.
Tahir, S. S. and Rauf, N. (2003). “Thermodynamic studies of Ni (II) sorption onto bentonite from aqueous solution.” J. Chem. Thermodyn., Vol. 35, No. 12, pp. 2003–2009, DOI: 10.1016/s0021-9614(03) 00153-8.
Tani, Y., Ohashi, M., Miyata, N., Seyama, H., Iwahori, K., and Soma, M. (2004). “Sorption of Co(II), Ni(II), and Zn(II) on biogenic manganese oxides produced by a Mn-oxidizing fungus, strain KR21-2.” J. Environ. Sci. Heal. A, Vol. 39, No. 10, pp. 2641–2660, DOI: 10.1081/ese-200027021.
Tebo, B. M., Bargar, J. R., Clement, B. G., Dick, G. J., Murray, K. J., Parker, D., Verity, R., and Webb, S. M. (2004). “Biogenic manganese oxides: Properties and mechanisms of formation.” Annu. Rev. Earth. Pl. Sc., Vol. 32, pp. 287–328, DOI: 10.1146/annurev.earth.32.101802. 120213.
Tebo, B. M., Clement, B. G., and Dick, G. J. (2007). “Biotransformations of Manganese.” In: Manual of Environmental Microbiology, 3rd Edition, Hurst, C. J., Crawford, R. L., Garland, J. L., Lipson, D. A., Mills A. L., and Stetzenbach, L.D. (Eds), ASM Press, Washington, D.C., pp. 1223–1238, DOI: 10.1128/9781555815882.ch100.
Thompson, I. A., Huber, D. M., and Schulze, D. G. (2006). “Evidence of a multicopper oxidase in Mn oxidation by Gaeumannomyces graminis var tritici.” Phytopathology, Vol. 62, No. 2, pp. 130–136, DOI: 10.1094/phyto-96-0130.
Toner, B., Manceau, A., Web, S. M., and Sposito, G. (2006). “Zinc sorption to biogenic hexagonal-birnessite particles within a hydrated bacterial biofilm.” Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta, Vol. 70, No. 1, pp. 27–43, DOI: 10.1016/j.gca.2005.08.029.
Trgo, M., Periæ, J., and Medvidovic, N. V. (2006a). “A comparative study of ion exchange kinetics in zinc/leaddmodified zeoliteclinoptilolite systems.” J. Hazard. Mater., Vol. 136, No. 3, pp. 938–945, DOI: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2006.01.032.
Trgo, M., Periæ, J., and Medvidovic, N. V. (2006b). “Investigation of different kinetic models for zinc ions uptake by natural zeolitic tuff.” J. Environ. Manage., Vol. 79, No. 3, pp. 298–304, DOI: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2005.07.009.
Turan, M., Mart, U., Yüksel, B., and Çelik, M. S. (2005). “Lead removal in fixed-bed columns by zeolite and sepiolite.” Chemosphere, Vol. 60, No. 10, pp. 1487–1492, DOI: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2005. 02.036.
Villalobos, M., Bargar, J., and Sposito, G. (2005). “Mechanisms of Pb (II) Sorption on a biogenic manganese oxide.” Environ. Sci. Technol., Vol. 39, No. 2, pp. 569–576, DOI: 10.1021/es049434a.
Villalobos, M., Toner, B., Bargar, J., and Sposito, G. (2003). “Characterization of the Mn oxide produced by Pseudomonas putida strain MnB1.” Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta, Vol. 67, No. 14, pp. 2649–2662, DOI: 10.1002/chin.200551272.
Wang, W., Shao, Z., Liu, Y., and Wang, G. (2009). “Removal of multiheavy metals using biogenic manganese oxides generated by a deep-sea sedimentary bacterium -Brachybacterium sp. strain Mn32.” Microbiology+, Vol. 155, pp. 1989–1996, DOI: 10.1099/mic.0.024141-0.
Xu, Y., Boonfueng, T., Axe, L., Maeng, S., and Tyson, T. (2006). “Surface complexation of Pb(II) on amorphous iron oxide and manganese oxide: Spectroscopic and time studies.” J. Colloid Interf. Sci., Vol. 299, No. 1, pp. 28–40, DOI: 10.1016/j.jcis.2006.01.041.
Yang, X., Yang, S. B., Yang, S. T., Hu, J., Tan, X. L., and Wang, X. K. (2011). “Effect of pH, ionic strength and temperature on sorption of Pb(II) on NKF-6 zeolite studied by batch technique.” Chem. Eng. J., Vol. 168, No. 1, pp. 86–93, DOI: 10.1016/j.cej.2010.12.039.
Zhou, D., Kim, D. G., and Ko, S. O. (2014). “Heavy metal adsorption with biogenic manganese oxides generated by Pseudomonas putida strain MnB1.” J. Ind. Eng. Chem., In Press, DOI: 10.1016/j.jiec. 2014.09.020.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, DG., Nhung, T.T. & Ko, SO. Enhanced adsorption of heavy metals with biogenic manganese oxide immobilized on zeolite. KSCE J Civ Eng 20, 2189–2196 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12205-016-0356-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12205-016-0356-1