Abstract
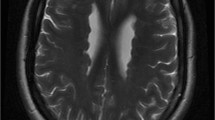
We describe the clinical and molecular evaluation of two patients, mother and daughter (proband), with bilateral periventricular nodular heterotopia (BPNH). The clinical evaluation revealed a more severe phenotype in the proband, with mental retardation and seizures. Imaging studies showed bilateral periventricular nodules in both patients. We identified a novel mutation, c.987G→C mutation in exon 6 of the Filamin A (FLNA) gene in the genomic DNA of both patients. Complementary DNA (cDNA) sequencing revealed the maintenance of intron 6 in the mutated allele. Bioinformatics analysis indicates that the mutation identified in both patients probably destroyed the intron 6 donor-splicing site, which is likely to introduce a premature stop codon resulting in a truncated FLNA protein. In addition, X-chromosome inactivation studies in DNA of blood cells revealed a skewed pattern in the proband, and real time quantitative polymerase chain reaction (PCR) showed a higher expression of the mutated allele in the proband compared to that of the mother. This variation in expression of the mutated allele may be responsible for the differences in the clinical manifestations observed in both patients.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allen, R. C., Zoghbi, H. Y., Moseley, A. B., et al. (1992). Methylation of HpaII and HhaI sites near the polymorphic CAG repeat in the human androgen-receptor gene correlates with X chromosome inactivation. American Journal of Human Genetics, 51(6), 1229–1239.
Carmel, I., Tal, S., Vig, I., & Ast, G. (2004). Comparative analysis detects dependencies among the 5′ splice-site positions. RNA, 10(5), 828–840 May.
Corpet, F. (1988). Multiple sequence alignment with hierarchical clustering. Nucleic Acids Research, 16(22), 10881–10890.
Cunningham, C., Gorlin, J., Kwiatkwoski, D., et al. (1992). Actin-binding protein requirement for cortical stability and efficient locomotion. Science, 255, 325–327.
Eksioglu, Y. Z., Scheffer, I. E., Cardenas, P., et al. (1996). Periventricular heterotopia: an X-linked dominant epilepsy locus causing aberrant cerebral cortical development. Neuron, 16(1), 77–87.
Fox, J., Lamperti, E., Eksioglu, Y., et al. (1998). Mutations in filamin 1 arrest migration of cerebral cortical neurons in human periventricular heterotopia. Neuron, 21, 1315–1325.
Gasteiger, E., Gattiker, A., Hoogland, C., Ivanyi, I., Appel, R. D., & Bairoch, A. (2003). ExPASy: the proteomics server for in-depth protein knowledge and analysis. Nucleic Acids Research, 31, 3784–3788.
Glogauer, M., Arora, P., Chou, D., et al. (1998). The role of actin-binding protein 280 in integrin-dependent mechanoprotection. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 275, 1689–1698.
Guerrini, R., Mei, D., Sisodiya, S., et al. (2004). Germline and mosaic mutations of FLN1 in men with periventricular heterotopia. Neurology, 63(1), 51–56.
Montenegro, M. A., Guerreiro, M. M., Lopes-Cendes, I., et al. (2002). Interrelationship of Genetics and Prenatal Injury in the Genesis of Malformations of Cortical Development. Archives of Neurology, 59, 1147–1153.
Moro, F., Carrozo, R., Veggiotti, P., et al. (2002). Familial periventricular heterotopia: missense and distal truncating mutations of the FLN1 gene. Neurology, 58, 916–921.
Newman, A. J. (1997). The role of U5 snRNP in pre-mRNA splicing. The EMBO Journal, 16(19), 5797–5800.
Ott, I., Fischer, E., Miyagi, Y., et al. (1998). A role for tissue factor in cell adhesion and migration mediated by interaction with actin-binding protein 280. Journal of Cell Biology, 140, 1241–1253.
Parrini, E., Mei, D., Wright, M., et al. (2004). Mosaic mutations of the FLN1 gene cause a mild phenotype in patients with periventricular heterotopia. Neurogenetics, 5(3), 191–196.
Parrini, E., Ramazzotti, A., Dobyns, W. B., et al. (2006). Periventricular heterotopia: phenotypic heterogeneity and correlation with Filamin A mutations. Brain, 129(Pt 7), 1892–1906.
Robertson, S. P. (2005). Filamin A: phenotypic diversity. Current Opinion in Genetics & Development, 15(3), 301–307.
Robertson, S. P., Twigg, S. R. F., Sutherland-Smith, A. J., et al. (2003). Localized mutations in the gene encoding the cytoskeletal protein filamin A cause diverse malformations in humans. Nature Genetics, 33, 487–491.
Sheen, V. L., Dixon, P. H., Fox, J. W., et al. (2001). Mutations in the X-linked filamin 1 gene cause periventricular nodular heterotopia in males as well as in females. Human Molecular Genetics, 10, 1775–1783.
Stendahl, O., Hartwig, J., Brotschi, E., et al. (1980). Distribution of actin-biding protein and myosin in macrophages during spreading and phagocytosis. Journal of cell biology, 84, 215–224.
Thanaraj, T. A., & Clark, F. (2001). Human GC-AG alternative intron isoforms with weak donor sites show enhanced consensus at acceptor exon positions. Nucleic Acids Research, 29(12), 2581–2593.
Web resources
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank the patients for their cooperation. This study was supported by Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado de São Paulo (FAPESP), Brazil. SST and FRT also received scholarships from FAPESP, Brazil.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tsuneda, S.S., Torres, F.R., Montenegro, M.A. et al. A New Missense Mutation Found in the FLNA Gene in a Family with Bilateral Periventricular Nodular Heterotopia (BPNH) Alters the Splicing Process. J Mol Neurosci 35, 195–200 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-008-9050-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-008-9050-1