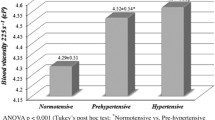
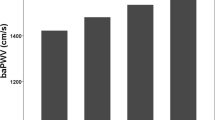
Abstract
Type 2 diabetes mellitus (DM) carries an increased risk for cardiovascular complications. The brachial-ankle pulse wave velocity (baPWV) is an index for early atherosclerotic changes. Recently, the effect of altered blood rheology on atherosclerosis has received attention. Therefore, this study aimed to examine the association of hemorheological parameters with baPWV in patients with DM. In this cross-sectional study, we investigated the relationship between rheological parameters and baPWV in 323 control subjects (160 men and 163 women) and 382 patients with DM (170 men and 212 women). The participants with DM had higher whole blood viscosity (WBV) levels both at low shear rate (3 s−1) and at high shear rate (200 s−1) than those without DM. Different metabolic parameters were compared across WBV (3 s−1) quartiles. The mean values of baPWV gradually increased with WBV (3 s−1) quartiles. In addition, there was a positive correlation between baPWV and WBV 3 s−1 in patients with DM after adjusting confounding factors (r = 0.285, p = 0.039). Stepwise multiple linear regression analysis further revealed that WBV (3 s−1) is a significant determinant for increased baPWV in DM (β = 0.184; p < 0.001). However, there were no association between WBV (3 s−1) and baPWV in control subjects. The findings showed that baPWV increased as WBV (3 s−1) elevated in DM. Moreover, WBV (3 s−1) is independently associated with baPWV even after adjusting other cardiovascular risk factors. Early detection of abnormal WBV levels at low shear rate should warrant for early search of undetected arterial stiffness in patients with DM.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
N. Sarwar, P. Gao, S.R. Seshasai, R. Gobin, S. Kaptoge, A.E. Di, E. Ingelsson, D.A. Lawlor, E. Selvin, M. Stampfer, C.D. Stehouwer, S. Lewington, L. Pennells, A. Thompson, N. Sattar, I.R. White, K.K. Ray, J. Danesh, Diabetes mellitus, fasting blood glucose concentration, and risk of vascular disease: a collaborative meta-analysis of 102 prospective studies. Lancet 375, 2215–2222 (2010)
S.R. Seshasai, S. Kaptoge, A. Thompson, A.E. Di, P. Gao, N. Sarwar, P.H. Whincup, K.J. Mukamal, R.F. Gillum, I. Holme, I. Njolstad, A. Fletcher, P. Nilsson, S. Lewington, R. Collins, V. Gudnason, S.G. Thompson, N. Sattar, E. Selvin, F.B. Hu, J. Danesh, Diabetes mellitus, fasting glucose, and risk of cause-specific death. N. Engl. J. Med. 364, 829–841 (2011)
A.J. Garber, Attenuating CV risk factors in patients with diabetes: clinical evidence to clinical practice. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 4(Suppl 1), S5–S12 (2002)
G.W. Davison, T. Ashton, L. George, I.S. Young, J. McEneny, B. Davies, S.K. Jackson, J.R. Peters, D.M. Bailey, Molecular detection of exercise-induced free radicals following ascorbate prophylaxis in type 1 diabetes mellitus: a randomised controlled trial. Diabetologia 51, 2049–2059 (2008)
E.U. Nwose, E. Butkowski, N. Cann, Whole blood viscosity determination in diabetes management: perspective in practice. N. Am. J. Med. Sci. 1, 110–113 (2009)
R.B. Paisey, J. Harkness, M. Hartog, T. Chadwick, The effect of improvement in diabetic control on plasma and whole blood viscosity. Diabetologia 19, 345–349 (1980)
A. Redheuil, W.C. Yu, C.O. Wu, E. Mousseaux, A. de Cesare, R. Yan, N. Kachenoura, D. Bluemke, J.A. Lima, Reduced ascending aortic strain and distensibility: earliest manifestations of vascular aging in humans. Hypertension 55, 319–326 (2010)
M.F. O’Rourke, S.S. Franklin, Arterial stiffness: reflections on the arterial pulse. Eur. Heart J. 27, 2497–2498 (2006)
J. Blacher, A.D. Protogerou, O. Henry, S. Czernichow, P. Iaria, Y. Zhang, D. Agnoletti, M.E. Safar, Aortic stiffness, inflammation, denutrition and type 2 diabetes in the elderly. Diabetes. Metab. 38, 68–75 (2012)
A.S. Mansour, A. Yannoutsos, N. Majahalme, D. Agnoletti, M.E. Safar, S. Ouerdane, J. Blacher, Aortic stiffness and cardiovascular risk in type 2 diabetes. J. Hypertens. 31, 1584–1592 (2013)
C. Carallo, C. Irace, M.S. De Franceschi, F. Coppoletta, R. Tiriolo, C. Scicchitano, F. Scavelli, A. Gnasso, The effect of aging on blood and plasma viscosity. An 11.6 years follow-up study. Clin. Hemorheol. Microcirc. 47, 67–74 (2011)
I. Velcheva, N. Antonova, E. Titianova, P. Damianov, N. Dimitrov, I. Ivanov, Hemorheological parameters in correlation with the risk factors for carotid atherosclerosis. Clin. Hemorheol. Microcirc. 35, 195–198 (2006)
M. Wiewiora, K. Sosada, L. Slowinska, J. Piecuch, M. Gluck, W. Zurawinski, B. Turczynski, Sex-dependent differences in rheological properties and the relation of blood viscosity to erythrocyte aggregation indices among morbidly obese patients. Clin. Hemorheol. Microcirc. 44, 259–267 (2010)
J. Danesh, R. Collins, R. Peto, G.D. Lowe, Haematocrit, viscosity, erythrocyte sedimentation rate: meta-analyses of prospective studies of coronary heart disease. Eur. Heart J. 21, 515–520 (2000)
G.D. Lowe, F.G. Fowkes, J. Dawes, P.T. Donnan, S.E. Lennie, E. Housley, Blood viscosity, fibrinogen, and activation of coagulation and leukocytes in peripheral arterial disease and the normal population in the Edinburgh Artery Study. Circulation 87, 1915–1920 (1993)
G.D. Lowe, A.J. Lee, A. Rumley, J.F. Price, F.G. Fowkes, Blood viscosity and risk of cardiovascular events: the Edinburgh Artery Study. Br. J. Haematol. 96, 168–173 (1997)
A. Hoieggen, E. Fossum, A. Moan, E. Enger, S.E. Kjeldsen, Whole-blood viscosity and the insulin-resistance syndrome. J. Hypertens. 16, 203–210 (1998)
D.C. Le, T. Khodabandehlou, M. Vimeux, Impaired hemorheological properties in diabetic patients with lower limb arterial ischaemia. Clin. Hemorheol. Microcirc. 25, 43–48 (2001)
D.C. Le, M. Vimeux, T. Khodabandehlou, Blood rheology in patients with diabetes mellitus. Clin. Hemorheol. Microcirc. 30, 297–300 (2004)
F. Jung, From hemorheology to microcirculation and regenerative medicine: Fahraeus Lecture 2009. Clin. Hemorheol. Microcirc. 45, 79–99 (2010)
K.U. Eckardt, J.S. Berns, M.V. Rocco, B.L. Kasiske, Definition and classification of CKD: the debate should be about patient prognosis—a position statement from KDOQI and KDIGO. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 53, 915–920 (2009)
R.T. Wang, Y. Li, X.Y. Zhu, Y.N. Zhang, Increased mean platelet volume is associated with arterial stiffness. Platelets 22, 447–451 (2011)
R.Y. Li, Z.G. Cao, J.R. Zhang, Y. Li, R.T. Wang, Decreased serum bilirubin is associated with silent cerebral infarction. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 34, 946–951 (2014)
J.F. Brun, E. Varlet-Marie, R. de Mauverger, J. Mercier, Minimal model-derived insulin sensitivity, insulin secretion and glucose tolerance: relationships with blood rheology. Clin. Hemorheol. Microcirc. 51, 21–27 (2012)
A.G. Tsai, C. Acero, P.R. Nance, P. Cabrales, J.A. Frangos, D.G. Buerk, M. Intaglietta, Elevated plasma viscosity in extreme hemodilution increases perivascular nitric oxide concentration and microvascular perfusion. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 288, H1730–H1739 (2005)
H.A. Silber, D.A. Bluemke, P. Ouyang, Y.P. Du, W.S. Post, J.A. Lima, The relationship between vascular wall shear stress and flow-mediated dilation. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 38, 1859–1865 (2001)
S. Hamed, B. Brenner, A. Roguin, Nitric oxide: a key factor behind the dysfunctionality of endothelial progenitor cells in diabetes mellitus type-2. Cardiovasc. Res. 91, 9–15 (2011)
J. Bellien, J. Favre, M. Iacob, J. Gao, C. Thuillez, V. Richard, R. Joannides, Arterial stiffness is regulated by nitric oxide and endothelium-derived hyperpolarizing factor during changes in blood flow in humans. Hypertension 55, 674–680 (2010)
S. Hamed, B. Brenner, A. Aharon, D. Daoud, A. Roguin, Nitric oxide and superoxide dismutase modulate endothelial progenitor cell function in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 8, 56 (2009)
S. Forconi, T. Gori, Endothelium and hemorheology. Clin. Hemorheol. Microcirc. 53, 3–10 (2013)
M. Charakida, F. O’Neil, S. Masi, N. Papageorgiou, D. Tousoulis, Inflammatory disorders and atherosclerosis: new therapeutic approaches. Curr. Pharm. Des. 17, 4111–4120 (2011)
A. Vaya, A. Hernandez-Mijares, E. Bonet, R. Sendra, E. Sola, R. Perez, D. Corella, B. Laiz, Association between hemorheological alterations and metabolic syndrome. Clin. Hemorheol. Microcirc. 49, 493–503 (2011)
A. Damaske, S. Muxel, F. Fasola, M.C. Radmacher, S. Schaefer, A. Jabs, D. Orphal, P. Wild, J.D. Parker, M. Fineschi, T. Munzel, S. Forconi, T. Gori, Peripheral hemorheological and vascular correlates of coronary blood flow. Clin. Hemorheol. Microcirc. 49, 261–269 (2011)
E.A. Olausson, A. Kilander, Glycaemic index of modified cornstarch in solutions with different viscosity. A study in subjects with diabetes mellitus type 2. Clin. Nutr. 27, 254–257 (2008)
I.A. Tikhomirova, A.O. Oslyakova, S.G. Mikhailova, Microcirculation and blood rheology in patients with cerebrovascular disorders. Clin. Hemorheol. Microcirc. 49, 295–305 (2011)
J.F. Brun, E. Varlet-Marie, R.E. de Mauverger, Relationships between insulin sensitivity measured with the oral minimal model and blood rheology. Clin. Hemorheol. Microcirc. 51, 29–34 (2012)
G. de Simone, R.B. Devereux, S. Chien, M.H. Alderman, S.A. Atlas, J.H. Laragh, Relation of blood viscosity to demographic and physiologic variables and to cardiovascular risk factors in apparently normal adults. Circulation 81, 107–117 (1990)
G.D. Sloop, D.W. Garber, The effects of low-density lipoprotein and high-density lipoprotein on blood viscosity correlate with their association with risk of atherosclerosis in humans. Clin. Sci. 92, 473–479 (1997)
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (No. 2013M541409) and Technology Foundation for Selected Overseas Chinese Scholar, Ministry of Personnel of China (No. 2013578).
Conflict of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Y., Tian, Xx., Liu, T. et al. Association between whole blood viscosity and arterial stiffness in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Endocrine 49, 148–154 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12020-014-0451-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12020-014-0451-3