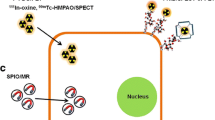
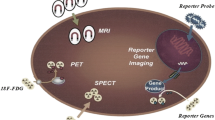
Abstract
The interest in the use of stem cells as a source for therapy has increased dramatically over the last decades. Different stem cell types have been tested in both in vitro and in vivo models, because of their properties such as differentiation potential, trophic effects and immune modulatory properties. To further optimize the use of different stem cell types for the treatment of disease in a clinical setting, it is necessary to know more about the in vivo behavior of these cells following engraftment. Until now, the golden standard to preclinically evaluate cell therapy was histology, which is an invasive method as the animals need to be sacrificed. This hampers the generation of dynamic information and results in only one single point in time available for analysis per animal. For more information regarding cell migration, in situ persistence, viability, proliferation and differentiation, molecular imaging can be used for imaging cells after transplantation dynamically and longitudinally, in a noninvasive way. With this technology, it becomes possible to track cells within the same subjects over a long period of time.















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Le Blanc, K., Frassoni, F., Ball, L., Locatelli, F., Roelofs, H., Lewis, I., et al. (2008). Mesenchymal stem cells for treatment of steroid-resistant, severe, acute graft-versus-host disease: a phase II study. Lancet, 371(9624), 1579–86.
Sohni, A., & Verfaillie, C. M. (2011). Multipotent adult progenitor cells. Best Practice & Research Clinical Haematology, 24(1), 3–11.
Cao, Y. A., Wagers, A. J., Beilhack, A., Dusich, J., Bachmann, M. H., Negrin, R. S., et al. (2004). Shifting foci of hematopoiesis during reconstitution from single stem cells. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 101(1), 221–6.
Reumers, V., Deroose, C. M., Krylyshkina, O., Nuyts, J., Geraerts, M., Mortelmans, L., et al. (2008). Noninvasive and quantitative monitoring of adult neuronal stem cell migration in mouse brain using bioluminescence imaging. Stem Cells, 26(9), 2382–90.
Jacobs, R. E., & Cherry, S. R. (2001). Complementary emerging techniques: high-resolution PET and MRI. Current Opinion in Neurobiology, 11(5), 621–9.
Phelps, M. E., Hoffman, E. J., Mullani, N. A., & Ter-Pogossian, M. M. (1975). Application of annihilation coincidence detection to transaxial reconstruction tomography. Journal of Nuclear Medicine, 16(3), 210–24.
Vastenhouw, B., & Beekman, F. (2007). Submillimeter total-body murine imaging with U-SPECT-I. Journal of Nuclear Medicine, 48(3), 487–93.
Jones, T., & Rabiner, E. A. (2012). The development, past achievements, and future directions of brain PET. Journal of Cerebral Blood Flow and Metabolism, 32(7), 1426–54.
Krause, B. J., Schwarzenbock, S., & Souvatzoglou, M. (2013). FDG PET and PET/CT. Recent Results in Cancer Research, 187, 351–69.
Paterson, D. I., OMeara, E., Chow, B. J., Ukkonen, H., & Beanlands, R. S. (2011). Recent advances in cardiac imaging for patients with heart failure. Current Opinion in Cardiology, 26(2), 132–43.
Bhargava, K. K., Gupta, R. K., Nichols, K. J., & Palestro, C. J. (2009). In vitro human leukocyte labeling with (64) Cu: an intraindividual comparison with (111) in-oxine and (18) F-FDG. Nuclear Medicine and Biology, 36(5), 545–9.
Doyle, B., Kemp, B. J., Chareonthaitawee, P., Reed, C., Schmeckpeper, J., Sorajja, P., et al. (2007). Dynamic tracking during intracoronary injection of 18F-FDG-labeled progenitor cell therapy for acute myocardial infarction. Journal of Nuclear Medicine, 48(10), 1708–14.
Elhami, E., Goertzen, A. L., Xiang, B., Deng, J., Stillwell, C., Mzengeza, S., et al. (2011). Viability and proliferation potential of adipose-derived stem cells following labeling with a positron-emitting radiotracer. European Journal of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging, 38(7), 1323–34.
Zhang, Y., Thorn, S., DaSilva, J. N., Lamoureux, M., DeKemp, R. A., Beanlands, R. S., et al. (2008). Collagen-based matrices improve the delivery of transplanted circulating progenitor cells: development and demonstration by ex vivo radionuclide cell labeling and in vivo tracking with positron-emission tomography. Circulation. Cardiovascular Imaging, 1(3), 197–204.
Chen, M. F., Lin, C. T., Chen, W. C., Yang, C. T., Chen, C. C., Liao, S. K., et al. (2006). The sensitivity of human mesenchymal stem cells to ionizing radiation. International Journal of Radiation Oncology, Biology, and Physics, 66(1), 244–53.
Wolfs, E., Struys, T., Notelaers, T., Roberts, S. J., Sohni, A., Bormans, G., et al. (2013). 18F-FDG labeling of mesenchymal stem cells and multipotent adult progenitor cells for PET imaging: effects on ultrastructure and differentiation capacity. Journal of Nuclear Medicine, 54(3), 447–54.
Hofmann, M., Wollert, K. C., Meyer, G. P., Menke, A., Arseniev, L., Hertenstein, B., et al. (2005). Monitoring of bone marrow cell homing into the infarcted human myocardium. Circulation, 111(17), 2198–202.
Kang, W. J., Kang, H. J., Kim, H. S., Chung, J. K., Lee, M. C., & Lee, D. S. (2006). Tissue distribution of 18F-FDG-labeled peripheral hematopoietic stem cells after intracoronary administration in patients with myocardial infarction. Journal of Nuclear Medicine, 47(8), 1295–301.
Thakur, M. L., Segal, A. W., Louis, L., Welch, M. J., Hopkins, J., & Peters, T. J. (1977). Indium-111-labeled cellular blood components: mechanism of labeling and intracellular location in human neutrophils. Journal of Nuclear Medicine, 18(10), 1022–6.
Horcajada, J. P., Gutierrez-Cuadra, M., Martinez-Rodriguez, I., Salas, C., Parra, J. A., Benito, N., et al. (2012). High prevalence of upper urinary tract involvement detected by 111indium-oxine leukocyte scintigraphy in patients with candiduria. European Journal of Clinical Microbiology & Infectious Diseases, 31(3), 237–42.
Chin, B. B., Nakamoto, Y., Bulte, J. W., Pittenger, M. F., Wahl, R., & Kraitchman, D. L. (2003). 111In oxine labelled mesenchymal stem cell SPECT after intravenous administration in myocardial infarction. Nuclear Medicine Communications, 24(11), 1149–54.
Brenner, W., Aicher, A., Eckey, T., Massoudi, S., Zuhayra, M., Koehl, U., et al. (2004). 111In-labeled CD34+ hematopoietic progenitor cells in a rat myocardial infarction model. Journal of Nuclear Medicine, 45(3), 512–8.
Nowak, B., Weber, C., Schober, A., Zeiffer, U., Liehn, E. A., von Hundelshausen, P., et al. (2007). Indium-111 oxine labelling affects the cellular integrity of haematopoietic progenitor cells. European Journal of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging, 34(5), 715–21.
Mitkari, B., Kerkela, E., Nystedt, J., Korhonen, M., Mikkonen, V., Huhtala, T., et al. (2013). Intra-arterial infusion of human bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells results in transient localization in the brain after cerebral ischemia in rats. Experimental Neurology, 239, 158–62.
Kraitchman, D. L., Tatsumi, M., Gilson, W. D., Ishimori, T., Kedziorek, D., Walczak, P., et al. (2005). Dynamic imaging of allogeneic mesenchymal stem cells trafficking to myocardial infarction. Circulation, 112(10), 1451–61.
Gholamrezanezhad, A., Mirpour, S., Bagheri, M., Mohamadnejad, M., Alimoghaddam, K., Abdolahzadeh, L., et al. (2011). In vivo tracking of 111In-oxine labeled mesenchymal stem cells following infusion in patients with advanced cirrhosis. Nuclear Medicine and Biology, 38(7), 961–7.
Schots, R., De Keulenaer, G., Schoors, D., Caveliers, V., Dujardin, M., Verheye, S., et al. (2007). Evidence that intracoronary-injected CD133+ peripheral blood progenitor cells home to the myocardium in chronic postinfarction heart failure. Experimental Hematology, 35(12), 1884–90.
Caveliers, V., De Keulenaer, G., Everaert, H., Van Riet, I., Van Camp, G., Verheye, S., et al. (2007). In vivo visualization of 111In labeled CD133+ peripheral blood stem cells after intracoronary administration in patients with chronic ischemic heart disease. The Quarterly Journal of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging, 51(1), 61–6.
Jorgensen, C., Couret, I., Bologna, C., Rossi, M., & Sany, J. (1995). Radiolabelled lymphocyte migration in rheumatoid synovitis. Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 54(1), 39–44.
Detante, O., Moisan, A., Dimastromatteo, J., Richard, M. J., Riou, L., Grillon, E., et al. (2009). Intravenous administration of 99mTc-HMPAO-labeled human mesenchymal stem cells after stroke: in vivo imaging and biodistribution. Cell Transplantation, 18(12), 1369–79.
Park, B. N., Shim, W., Lee, G., Bang, O. Y., An, Y. S., Yoon, J. K., et al. (2011). Early distribution of intravenously injected mesenchymal stem cells in rats with acute brain trauma evaluated by (99 m) Tc-HMPAO labeling. Nuclear Medicine and Biology, 38(8), 1175–82.
Goussetis, E., Manginas, A., Koutelou, M., Peristeri, I., Theodosaki, M., Kollaros, N., et al. (2006). Intracoronary infusion of CD133+ and CD133-CD34+ selected autologous bone marrow progenitor cells in patients with chronic ischemic cardiomyopathy: cell isolation, adherence to the infarcted area, and body distribution. Stem Cells, 24(10), 2279–83.
Kollaros, N., Theodorakos, A., Manginas, A., Kitziri, E., Katsikis, A., Cokkinos, D., et al. (2012). Bone marrow stem cell adherence into old anterior myocardial infarction: a scintigraphic study using Tl-201 and Tc-99 m-HMPAO. Annals of Nuclear Medicine, 26(3), 228–33.
Tarantal, A. F., Lee, C. C., Batchelder, C. A., Christensen, J. E., Prater, D., & Cherry, S. R. (2012). Radiolabeling and in vivo imaging of transplanted renal lineages differentiated from human embryonic stem cells in fetal rhesus monkeys. Molecular Imaging and Biology, 14(2), 197–204.
Ma, B., Hankenson, K. D., Dennis, J. E., Caplan, A. I., Goldstein, S. A., & Kilbourn, M. R. (2005). A simple method for stem cell labeling with fluorine 18. Nuclear Medicine and Biology, 32(7), 701–5.
Zhang, Y., Dasilva, J. N., Hadizad, T., Thorn, S., Kuraitis, D., Renaud, J. M., et al. (2012). (18) F-FDG cell labeling may underestimate transplanted cell homing: more accurate, efficient and stable cell labeling with hexadecyl-4-[(18) F] fluorobenzoate for in vivo tracking of transplanted human progenitor cells by positron emission tomography. Cell Transplantation, 21, 1821–35.
Gambhir, S. S., Herschman, H. R., Cherry, S. R., Barrio, J. R., Satyamurthy, N., Toyokuni, T., et al. (2000). Imaging transgene expression with radionuclide imaging technologies. Neoplasia, 2(1–2), 118–38.
De, A., Lewis, X. Z., & Gambhir, S. S. (2003). Noninvasive imaging of lentiviral-mediated reporter gene expression in living mice. Molecular Therapy, 7(5 Pt 1), 681–91.
Schipper, M. L., & Gambhir, S. S. (2000). Imaging Gene Expression: Concepts and Future Outlook. In C. Schiepers (Ed.), Diagnostic nuclear medicine (pp. p. 253–72). Berlin: Springer.
Li, Z., Dullmann, J., Schiedlmeier, B., Schmidt, M., von Kalle, C., Meyer, J., et al. (2002). Murine leukemia induced by retroviral gene marking. Science, 296(5567), 497.
Bushman, F., Lewinski, M., Ciuffi, A., Barr, S., Leipzig, J., Hannenhalli, S., et al. (2005). Genome-wide analysis of retroviral DNA integration. Nature Reviews Microbiology, 3(11), 848–58.
Schroder, A. R., Shinn, P., Chen, H., Berry, C., Ecker, J. R., & Bushman, F. (2002). HIV-1 integration in the human genome favors active genes and local hotspots. Cell, 110(4), 521–9.
Ellis, J. (2005). Silencing and variegation of gammaretrovirus and lentivirus vectors. Human Gene Therapy, 16(11), 1241–6.
Hockemeyer, D., Soldner, F., Beard, C., Gao, Q., Mitalipova, M., DeKelver, R. C., et al. (2009). Efficient targeting of expressed and silent genes in human ESCs and iPSCs using zinc-finger nucleases. Nature Biotechnology, 27(9), 851–7.
Kotin, R. M., Linden, R. M., & Berns, K. I. (1992). Characterization of a preferred site on human chromosome 19q for integration of adeno-associated virus DNA by non-homologous recombination. EMBO Journal, 11(13), 5071–8.
Tan, I., Ng, C. H., Lim, L., & Leung, T. (2001). Phosphorylation of a novel myosin binding subunit of protein phosphatase 1 reveals a conserved mechanism in the regulation of actin cytoskeleton. The Journal of Biological Chemistry, 276(24), 21209–16.
Smith, J. R., Maguire, S., Davis, L. A., Alexander, M., Yang, F., Chandran, S., et al. (2008). Robust, persistent transgene expression in human embryonic stem cells is achieved with AAVS1-targeted integration. Stem Cells, 26(2), 496–504.
DeKelver, R. C., Choi, V. M., Moehle, E. A., Paschon, D. E., Hockemeyer, D., Meijsing, S. H., et al. (2010). Functional genomics, proteomics, and regulatory DNA analysis in isogenic settings using zinc finger nuclease-driven transgenesis into a safe harbor locus in the human genome. Genome Research, 20(8), 1133–42.
Wang, Y., Zhang, W. Y., Hu, S., Lan, F., Lee, A. S., Huber, B., et al. (2012). Genome editing of human embryonic stem cells and induced pluripotent stem cells with zinc finger nucleases for cellular imaging. Circulation Research, 111(12), 1494–503.
Filbin, M. E., & Kieft, J. S. (2009). Toward a structural understanding of IRES RNA function. Current Opinion in Structural Biology, 19(3), 267–76.
Ibrahimi, A., Vande Velde, G., Reumers, V., Toelen, J., Thiry, I., Vandeputte, C., et al. (2009). Highly efficient multicistronic lentiviral vectors with peptide 2A sequences. Human Gene Therapy, 20(8), 845–60.
Ahn, B. C. (2012). Sodium iodide symporter for nuclear molecular imaging and gene therapy: from bedside to bench and back. Theranostics, 2(4), 392–402.
Rath, P., Shi, H., Maruniak, J. A., Litofsky, N. S., Maria, B. L., & Kirk, M. D. (2009). Stem cells as vectors to deliver HSV/tk gene therapy for malignant gliomas. Current Stem Cell Research & Therapy, 4(1), 44–9.
Deroose, C. M., Reumers, V., Debyser, Z., & Baekelandt, V. (2009). Seeing genes at work in the living brain with non-invasive molecular imaging. Current Gene Therapy, 9(3), 212–38.
Serganova, I., Ponomarev, V., & Blasberg, R. (2007). Human reporter genes: potential use in clinical studies. Nuclear Medicine and Biology, 34(7), 791–807.
Yaghoubi, S. S., Campbell, D. O., Radu, C. G., & Czernin, J. (2012). Positron emission tomography reporter genes and reporter probes: gene and cell therapy applications. Theranostics, 2(4), 374–91.
Immonen, A., Vapalahti, M., Tyynela, K., Hurskainen, H., Sandmair, A., Vanninen, R., et al. (2004). AdvHSV-tk gene therapy with intravenous ganciclovir improves survival in human malignant glioma: a randomised, controlled study. Molecular Therapy, 10(5), 967–72.
Valery, C. A., Seilhean, D., Boyer, O., Marro, B., Hauw, J. J., Kemeny, J. L., et al. (2002). Long-term survival after gene therapy for a recurrent glioblastoma. Neurology, 58(7), 1109–12.
Tjuvajev, J. G., Avril, N., Oku, T., Sasajima, T., Miyagawa, T., Joshi, R., et al. (1998). Imaging herpes virus thymidine kinase gene transfer and expression by positron emission tomography. Cancer Research, 58(19), 4333–41.
Yaghoubi, S., Barrio, J. R., Dahlbom, M., Iyer, M., Namavari, M., Satyamurthy, N., et al. (2001). Human pharmacokinetic and dosimetry studies of [(18)F]FHBG: a reporter probe for imaging herpes simplex virus type-1 thymidine kinase reporter gene expression. Journal of Nuclear Medicine, 42(8), 1225–34.
Jacobs, A., Braunlich, I., Graf, R., Lercher, M., Sakaki, T., Voges, J., et al. (2001). Quantitative kinetics of [124I] FIAU in cat and man. Journal of Nuclear Medicine, 42(3), 467–75.
Culver, K. W., Ram, Z., Wallbridge, S., Ishii, H., Oldfield, E. H., & Blaese, R. M. (1992). In vivo gene transfer with retroviral vector-producer cells for treatment of experimental brain tumors. Science, 256(5063), 1550–2.
Li, S., Tokuyama, T., Yamamoto, J., Koide, M., Yokota, N., & Namba, H. (2005). Bystander effect-mediated gene therapy of gliomas using genetically engineered neural stem cells. Cancer Gene Therapy, 12(7), 600–7.
Matuskova, M., Hlubinova, K., Pastorakova, A., Hunakova, L., Altanerova, V., Altaner, C., et al. (2010). HSV-tk expressing mesenchymal stem cells exert bystander effect on human glioblastoma cells. Cancer Letters, 290(1), 58–67.
Love, Z., Wang, F., Dennis, J., Awadallah, A., Salem, N., Lin, Y., et al. (2007). Imaging of mesenchymal stem cell transplant by bioluminescence and PET. Journal of Nuclear Medicine, 48(12), 2011–20.
Miletic, H., Fischer, Y., Litwak, S., Giroglou, T., Waerzeggers, Y., Winkeler, A., et al. (2007). Bystander killing of malignant glioma by bone marrow-derived tumor-infiltrating progenitor cells expressing a suicide gene. Molecular Therapy, 15(7), 1373–81.
Cao, F., Drukker, M., Lin, S., Sheikh, A. Y., Xie, X., Li, Z., et al. (2007). Molecular imaging of embryonic stem cell misbehavior and suicide gene ablation. Cloning and Stem Cells, 9(1), 107–17.
Perin, E. C., Tian, M., Marini, F. C., 3rd, Silva, G. V., Zheng, Y., Baimbridge, F., et al. (2011). Imaging long-term fate of intramyocardially implanted mesenchymal stem cells in a porcine myocardial infarction model. PloS One, 6(9), e22949.
Ram, Z., Culver, K. W., Oshiro, E. M., Viola, J. J., DeVroom, H. L., Otto, E., et al. (1997). Therapy of malignant brain tumors by intratumoral implantation of retroviral vector-producing cells. Nature Medicine, 3(12), 1354–61.
Jacobs, A., Voges, J., Reszka, R., Lercher, M., Gossmann, A., Kracht, L., et al. (2001). Positron-emission tomography of vector-mediated gene expression in gene therapy for gliomas. Lancet, 358(9283), 727–9.
Penuelas, I., Mazzolini, G., Boan, J. F., Sangro, B., Marti-Climent, J., Ruiz, M., et al. (2005). Positron emission tomography imaging of adenoviral-mediated transgene expression in liver cancer patients. Gastroenterology, 128(7), 1787–95.
Yaghoubi, S. S., Jensen, M. C., Satyamurthy, N., Budhiraja, S., Paik, D., Czernin, J., et al. (2009). Noninvasive detection of therapeutic cytolytic T cells with 18F-FHBG PET in a patient with glioma. Nature Clinical Practice Oncology, 6(1), 53–8.
Riddell, S. R., Elliott, M., Lewinsohn, D. A., Gilbert, M. J., Wilson, L., Manley, S. A., et al. (1996). T-cell mediated rejection of gene-modified HIV-specific cytotoxic T lymphocytes in HIV-infected patients. Nature Medicine, 2(2), 216–23.
Verzeletti, S., Bonini, C., Marktel, S., Nobili, N., Ciceri, F., Traversari, C., et al. (1998). Herpes simplex virus thymidine kinase gene transfer for controlled graft-versus-host disease and graft-versus-leukemia: clinical follow-up and improved new vectors. Human Gene Therapy, 9(15), 2243–51.
Eriksson, S., Munch-Petersen, B., Johansson, K., & Eklund, H. (2002). Structure and function of cellular deoxyribonucleoside kinases. Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences, 59(8), 1327–46.
Al-Madhoun, A. S., Tjarks, W., & Eriksson, S. (2004). The role of thymidine kinases in the activation of pyrimidine nucleoside analogues. Mini Reviews in Medicinal Chemistry, 4(4), 341–50.
Wang, J., & Eriksson, S. (1996). Phosphorylation of the anti-hepatitis B nucleoside analog 1-(2′-deoxy-2′-fluoro-1-beta-D-arabinofuranosyl)-5-iodouracil (FIAU) by human cytosolic and mitochondrial thymidine kinase and implications for cytotoxicity. Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy, 40(6), 1555–7.
Wang, J., Su, C., Neuhard, J., & Eriksson, S. (2000). Expression of human mitochondrial thymidine kinase in Escherichia coli: correlation between the enzymatic activity of pyrimidine nucleoside analogues and their inhibitory effect on bacterial growth. Biochemical Pharmacology, 59(12), 1583–8.
Deroose, C. M., Chitneni, S. K., Gijsbers, R., Vermaelen, P., Ibrahimi, A., Balzarini, J., et al. (2012). Preliminary validation of varicella zoster virus thymidine kinase as a novel reporter gene for PET. Nuclear Medicine and Biology, 39(8), 1266–74.
Chitneni, S. K., Deroose, C. M., Balzarini, J., Gijsbers, R., Celen, S., Debyser, Z., et al. (2007). A p-[18F] fluoroethoxyphenyl bicyclic nucleoside analogue as a potential positron emission tomography imaging agent for varicella-zoster virus thymidine kinase gene expression. Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, 50(26), 6627–37.
Eberling, J. L., Cunningham, J., Pivirotto, P., Bringas, J., Daadi, M. M., & Bankiewicz, K. S. (2003). In vivo PET imaging of gene expression in Parkinsonian monkeys. Molecular Therapy, 8(6), 873–5.
Qin, C., Cheng, K., Chen, K., Hu, X., Liu, Y., Lan, X., et al. (2013). Tyrosinase as a multifunctional reporter gene for Photoacoustic/MRI/PET triple modality molecular imaging. Scientific Reports, 3, 1490.
Bunzow, J. R., Van Tol, H. H., Grandy, D. K., Albert, P., Salon, J., Christie, M., et al. (1988). Cloning and expression of a rat D2 dopamine receptor cDNA. Nature, 336(6201), 783–7.
Strange, P. G. (1990). Aspects of the structure of the D2 dopamine receptor. Trends in Neurosciences, 13(9), 373–8.
Liang, Q., Satyamurthy, N., Barrio, J. R., Toyokuni, T., Phelps, M. P., Gambhir, S. S., et al. (2001). Noninvasive, quantitative imaging in living animals of a mutant dopamine D2 receptor reporter gene in which ligand binding is uncoupled from signal transduction. Gene Therapy, 8(19), 1490–8.
Chen, I. Y., Wu, J. C., Min, J. J., Sundaresan, G., Lewis, X., Liang, Q., et al. (2004). Micro-positron emission tomography imaging of cardiac gene expression in rats using bicistronic adenoviral vector-mediated gene delivery. Circulation, 109(11), 1415–20.
Hwang do, W., Kang, J. H., Chang, Y. S., Jeong, J. M., Chung, J. K., Lee, M. C., et al. (2007). Development of a dual membrane protein reporter system using sodium iodide symporter and mutant dopamine D2 receptor transgenes. Journal of Nuclear Medicine, 48(4), 588–95.
Bousquet, C., Puente, E., Buscail, L., Vaysse, N., & Susini, C. (2001). Antiproliferative effect of somatostatin and analogs. Chemotherapy, 47(Suppl 2), 30–9.
Reubi, J. C., Kvols, L., Krenning, E., & Lamberts, S. W. (1990). Distribution of somatostatin receptors in normal and tumor tissue. Metabolism, 39(9 Suppl 2), 78–81.
Forrer, F., Valkema, R., Kwekkeboom, D. J., de Jong, M., & Krenning, E. P. (2007). Neuroendocrine tumors. Peptide receptor radionuclide therapy. Best Practice & Research Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism, 21(1), 111–29.
Ginj, M., Zhang, H., Waser, B., Cescato, R., Wild, D., Wang, X., et al. (2006). Radiolabeled somatostatin receptor antagonists are preferable to agonists for in vivo peptide receptor targeting of tumors. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 103(44), 16436–41.
Parry, J. J., Chen, R., Andrews, R., Lears, K. A., & Rogers, B. E. (2012). Identification of critical residues involved in ligand binding and G protein signaling in human somatostatin receptor subtype 2. Endocrinology, 153(6), 2747–55.
Rogers, B. E., Chaudhuri, T. R., Reynolds, P. N., Della Manna, D., & Zinn, K. R. (2003). Non-invasive gamma camera imaging of gene transfer using an adenoviral vector encoding an epitope-tagged receptor as a reporter. Gene Therapy, 10(2), 105–14.
Rogers, B. E., McLean, S. F., Kirkman, R. L., Della Manna, D., Bright, S. J., Olsen, C. C., et al. (1999). In vivo localization of [(111)In]-DTPA-D-Phe1-octreotide to human ovarian tumor xenografts induced to express the somatostatin receptor subtype 2 using an adenoviral vector. Clinical Cancer Research, 5(2), 383–93.
Chaudhuri, T. R., Rogers, B. E., Buchsbaum, D. J., Mountz, J. M., & Zinn, K. R. (2001). A noninvasive reporter system to image adenoviral-mediated gene transfer to ovarian cancer xenografts. Gynecologic Oncology, 83(2), 432–8.
Zinn, K. R., Buchsbaum, D. J., Chaudhuri, T. R., Mountz, J. M., Grizzle, W. E., & Rogers, B. E. (2000). Noninvasive monitoring of gene transfer using a reporter receptor imaged with a high-affinity peptide radiolabeled with 99mTc or 188Re. Journal of Nuclear Medicine, 41(5), 887–95.
Singh, S. P., Yang, D., Ravoori, M., Han, L., & Kundra, V. (2009). In vivo functional and anatomic imaging for assessment of in vivo gene transfer. Radiology, 252(3), 763–71.
Cotugno, G., Aurilio, M., Annunziata, P., Capalbo, A., Faella, A., Rinaldi, V., et al. (2011). Noninvasive repetitive imaging of somatostatin receptor 2 gene transfer with positron emission tomography. Human Gene Therapy, 22(2), 189–96.
Furukawa, T., Lohith, T. G., Takamatsu, S., Mori, T., Tanaka, T., & Fujibayashi, Y. (2006). Potential of the FES-hERL PET reporter gene system – basic evaluation for gene therapy monitoring. Nuclear Medicine and Biology, 33(1), 145–51.
Vandeputte, C., Evens, N., Toelen, J., Deroose, C. M., Bosier, B., Ibrahimi, A., et al. (2011). A PET brain reporter gene system based on type 2 cannabinoid receptors. Journal of Nuclear Medicine, 52(7), 1102–9.
Dohan, O., De la Vieja, A., Paroder, V., Riedel, C., Artani, M., Reed, M., et al. (2003). The sodium/iodide Symporter (NIS): characterization, regulation, and medical significance. Endocrine Reviews, 24(1), 48–77.
Van Sande, J., Massart, C., Beauwens, R., Schoutens, A., Costagliola, S., Dumont, J. E., et al. (2003). Anion selectivity by the sodium iodide symporter. Endocrinology, 144(1), 247–52.
Chung, J. K. (2002). Sodium iodide symporter: its role in nuclear medicine. Journal of Nuclear Medicine, 43(9), 1188–200.
Mandell, R. B., Mandell, L. Z., & Link, C. J., Jr. (1999). Radioisotope concentrator gene therapy using the sodium/iodide symporter gene. Cancer Research, 59(3), 661–8.
Shimura, H., Haraguchi, K., Miyazaki, A., Endo, T., & Onaya, T. (1997). Iodide uptake and experimental 131I therapy in transplanted undifferentiated thyroid cancer cells expressing the Na+/I- symporter gene. Endocrinology, 138(10), 4493–6.
Spitzweg, C., O’Connor, M. K., Bergert, E. R., Tindall, D. J., Young, C. Y., & Morris, J. C. (2000). Treatment of prostate cancer by radioiodine therapy after tissue-specific expression of the sodium iodide symporter. Cancer Research, 60(22), 6526–30.
Schipper, M. L., Weber, A., Behe, M., Goke, R., Joba, W., Schmidt, H., et al. (2003). Radioiodide treatment after sodium iodide symporter gene transfer is a highly effective therapy in neuroendocrine tumor cells. Cancer Research, 63(6), 1333–8.
Faivre, J., Clerc, J., Gerolami, R., Herve, J., Longuet, M., Liu, B., et al. (2004). Long-term radioiodine retention and regression of liver cancer after sodium iodide symporter gene transfer in wistar rats. Cancer Research, 64(21), 8045–51.
Terrovitis, J., Kwok, K. F., Lautamaki, R., Engles, J. M., Barth, A. S., Kizana, E., et al. (2008). Ectopic expression of the sodium-iodide symporter enables imaging of transplanted cardiac stem cells in vivo by single-photon emission computed tomography or positron emission tomography. Journal of the American College of Cardiology, 52(20), 1652–60.
Quach, C. H., Jung, K. H., Paik, J. Y., Park, J. W., Lee, E. J., & Lee, K. H. (2012). Quantification of early adipose-derived stem cell survival: comparison between sodium iodide symporter and enhanced green fluorescence protein imaging. Nuclear Medicine and Biology, 39(8), 1251–60.
Wolfs, E., Holvoet, B., Gijsbers, R., Casteels, C., Roberts, S. J., Struys, T., et al. (2014). Optimization of multimodal imaging of mesenchymal stem cells using the human sodium iodide symporter for PET and Cerenkov luminescence imaging. PloS One, 9(4), e94833.
Higuchi, T., Anton, M., Dumler, K., Seidl, S., Pelisek, J., Saraste, A., et al. (2009). Combined reporter gene PET and iron oxide MRI for monitoring survival and localization of transplanted cells in the rat heart. Journal of Nuclear Medicine, 50(7), 1088–94.
Dwyer, R. M., Ryan, J., Havelin, R. J., Morris, J. C., Miller, B. W., Liu, Z., et al. (2011). Mesenchymal stem cell-mediated delivery of the sodium iodide symporter supports radionuclide imaging and treatment of breast cancer. Stem Cells, 29(7), 1149–57.
Knoop, K., Kolokythas, M., Klutz, K., Willhauck, M. J., Wunderlich, N., Draganovici, D., et al. (2011). Image-guided, tumor stroma-targeted 131I therapy of hepatocellular cancer after systemic mesenchymal stem cell-mediated NIS gene delivery. Molecular Therapy, 19(9), 1704–13.
Templin, C., Zweigerdt, R., Schwanke, K., Olmer, R., Ghadri, J. R., Emmert, M. Y., et al. (2012). Transplantation and tracking of human-induced pluripotent stem cells in a pig model of myocardial infarction: assessment of cell survival, engraftment, and distribution by hybrid single photon emission computed tomography/computed tomography of sodium iodide symporter transgene expression. Circulation, 126(4), 430–9.
Barton, K. N., Stricker, H., Brown, S. L., Elshaikh, M., Aref, I., Lu, M., et al. (2008). Phase I study of noninvasive imaging of adenovirus-mediated gene expression in the human prostate. Molecular Therapy, 16(10), 1761–9.
Moroz, M. A., Serganova, I., Zanzonico, P., Ageyeva, L., Beresten, T., Dyomina, E., et al. (2007). Imaging hNET reporter gene expression with 124I-MIBG. Journal of Nuclear Medicine, 48(5), 827–36.
Doubrovin, M. M., Doubrovina, E. S., Zanzonico, P., Sadelain, M., Larson, S. M., & O’Reilly, R. J. (2007). In vivo imaging and quantitation of adoptively transferred human antigen-specific T cells transduced to express a human norepinephrine transporter gene. Cancer Research, 67(24), 11959–69.
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare no potential conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wolfs, E., Verfaillie, C.M., Van Laere, K. et al. Radiolabeling Strategies for Radionuclide Imaging of Stem Cells. Stem Cell Rev and Rep 11, 254–274 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12015-014-9575-3
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12015-014-9575-3