Abstract
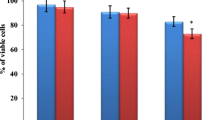
The zinc oxide (ZnO) nanoparticle has been widely used in biomedical applications and cancer therapy and has been reported to induce a selective cytotoxic effect on cancer cell proliferation. The present study investigated the cytotoxicity of ZnO nanoparticles against co-cultured C2C12 myoblastoma cancer cells and 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Our results showed that the ZnO nanoparticles could be cytotoxic to C2C12 myoblastoma cancer cells than 3T3-L1 cells. The messenger RNA (mRNA) expressions of p53 and bax were significantly increased 114.3 and 118.2 % in the C2C12 cells, whereas 42.5 and 40 % were increased in 3T3-L1 cells, respectively. The mRNA expression of bcl-2 was reduced 38.2 and 28.5 % in the C2C12 and 3T3-L1 cells, respectively, whereas the mRNA expression of caspase-3 was increased 80.7 and 51.6 % in the C2C12 and 3T3-L1 cells, respectively. The protein expressions of p53, bax, and caspase-3 were significantly increased 40, 81.8, and 80 % in C2C12 cells, whereas 20.3, 28.2, and 37.9 % were increased in 3T3-L1 cells, respectively. The mRNA expression of bcl-2 was significantly reduced 32.2 and 22.7 % in C2C12 and 3T3-L1 cells, respectively. Caspase-3 enzyme activity and reactive oxygen species (ROS) were increased in co-cultured C2C12 cells compared to 3T3-L1 cells. Taking all these data together, it may suggest that ZnO nanoparticles severely induce apoptosis in C2C12 myoblastoma cancer cells than 3T3-L1 cells.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Muthuraman P, Kim DH (2015) In vitro toxicity of zinc oxide nanoparticles: a review. J Nanoparticle Res 17:158
Jae-Hyun L, Yong-Min H, Young-wook J, Jung-wook S, Jung-tak J, Ho-Taek S, Sungjun K, Eun-Jin C, Ho-Geun Y, Jin-Suck S, Jinwoo C (2007) Artificially engineered magnetic nanoparticles for ultra-sensitive molecular imaging. Nat Med 13:95–99
Wang ZL (2008) Splendid one-dimensional nanostructures of zinc oxide: a new nanomaterial family for nanotechnology. ACS Nano 2:1987–1992
Becheri A, Dürr M, Nostro PL, Baglioni P (2008) Synthesis and characterization of zinc oxide nanoparticles: application to textiles as UV-absorbers. J Nanoparticle Res 10: 679–689.
Padmavathy N, Vijayaraghavan R (2008) Enhanced bioactivity of ZnO nanoparticles-an antimicrobial study Sci. Technol Adv Mater 9:035004
Snyder-Talkingtona BN, Qiana Y, Castranovaa V, Guob NL (2012) New perspectives for in vitro risk assessment of multiwalled carbon nanotubes: application of Co-culture and bioinformatics. J Toxicol Environ Health B 15:468–492
Hanley C, Layne J, Punnoose A, Reddy KM, Coombs I, Coombs A, Feris K, Wingett D (2008) Preferential killing of cancer cells and activated human T cells using ZnO nanoparticles. Nanotechnology 19:295103
Premanathan M, Karthikeyan K, Jeyasubramanian K, Manivannan G (2011) Selective toxicity of ZnO nanoparticles toward Gram-positive bacteria and cancer cells by apoptosis through lipid peroxidation. Nanomedicine 7:184–192
Akhtar MJ, Ahamed M, Kumar S, Khan MM, Ahmad J, Alrokayan SA (2012) Zinc oxide nanoparticles selectively induce apoptosis in human cancer cells through reactive oxygen species. Int J Nanomedicine 7:845–857
Rasmussen JW, Martinez E, Louka P, Wingett DG (2010) Zinc oxide nanoparticles for selective destruction of tumor cells and potential for drug delivery applications. Expert Opin Drug Deliv 7:1063–1077
Sherr CJ (2004) Principles of tumor suppression. Cell 116:235–246
Ahamed M, Karns M, Goodson M, Rowe J, Hussain SM, Schlager JJ, Hong Y (2008) DNA damage response to the different surface chemistry of silver nanoparticles in mammalian cells. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 233:404–410
Farnebo M, Bykov VJ, Wiman KG (2010) The p53 tumor suppressor: a master regulator of diverse cellular processes and therapeutic target in cancer. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 396:85–89
Chougule M, Patel AR, Sachdeva P, Jackson T, Singh M (2011) Anticancer activity of noscapine, an opioid alkaloid in combination with cisplatin in human non-small cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer 71:271–282
Tang X, Guo Y, Nakamura K, Huang H, Hamblin M, Chang L, Villacorta L, Yin K, Ouyang H, Zhang J (2010) Nitroalkenes induce rat aortic smooth muscle cell apoptosis via activation of caspase-dependent pathways. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 397:239–244
Ahamed M, Akhtar MJ, Siddiqui J, Musarrat J, Al-Khedhairy AA, AlSalhi MS, Alrokayan SA (2011) Oxidative stress-mediated apoptosis induced by nickel ferrite nanoparticles in cultured A549 cells. Toxicology 283:101–108
Nel A, Xia T, Mädler L, Li N (2006) Toxic potential of materials at the nanolevel. Science 311:622–627
Yip NC, Fombon IS, Liu P, Brown S, Kannappan V, Armesilla AL, Xu B, Cassidy J, Darling JL, Wang W (2011) Disulfiram modulated ROS-MAPK and NFkappaB pathways and targeted breast cancer cells with cancer stem cell-like properties. Br J Cancer 104:1564–1574
Muthuraman P, Inho H (2014) Application of cell co-culture system to study fat and muscle cells. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 98:7359–7364
Ravikumar S, Muthuraman P (2014) Cortisol effect on heat shock proteins in the C2C12 and 3T3-L1 cells. In Vitro Cell Dev Bio Anim 50:581–586
Muthuraman P, Jeong Eun P, Eunjung K (2014) Aspartame downregulates 3T3-L1 differentiation. In Vitro Cell Dev Bio Anim 50:851–857
Muthuraman P, Ramkumar K, Kim DH (2014) Analysis of the dose-dependent effect f zinc oxide nanoparticles on the oxidative stress and antioxidant enzyme activity in adipocytes. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 174:2851–2863
Muthuraman P, Kim DH, Muthuviveganandavel V, Vikramathithan J, Ravikumar S (2015) Differential bio-potential of ZnS nanoparticles to normal MDCK cells and cervical carcinoma hela cells. J Nanosci Nanotechnol 15:1–8
Muthuraman P, Muthuviveganandavel V, Kim DH (2015) Cytotoxicity of zinc oxide nanoparticles on antioxidant enzyme activities and mRNA expression in the cocultured C2C12 and 3T3-L1 cells. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 175:1270–1280
Muthuraman P, Enkhtaivan G, Bhupendra M, Chandrasekaran M, Rafi N, Kim DH (2015) Investigation of the role of aspartame in apoptosis process in Hela cells. Saudi Journal of Biological Sciences. DOI: org/10.1016/j.sjbs.2015.06.01.
Muthuraman P (2014) Effect of cortisol on caspases in the co-cultured C2C12 and 3T3-L1 cells. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 173:980–988
Tassel KAV, Goldman RH (2011) The growing consumer exposure to nanotechnology in the everyday product: regulating innovative technologies in light of lessons from the past. Conn Law Rev 44:481
Wang M, Thanou M (2010) Targeting nanoparticles to cancer. Pharmacol Res 62:90–99
Li J, Guo D, Wang X, Wang H, Jiang H, Chen B (2010) The photodynamic effect of different size ZnO nanoparticles on cancer cell proliferation in vitro. Nanoscale Res Lett 5:1063–1071
Hackenberg S, Scherzed A, Kessler M, Froelich K, Ginzkey C, Koehler C, Burghartz M, Hagen R, Kleinsasser N (2010) Zinc oxide nanoparticles induce photocatalytic cell death in human head and neck squamous cell carcinoma cell lines in vitro. Int J Oncol 37:1583–1590
Wu YN, Yang LX, Shi XY, Li IC, Biazik JM, Ratinac KR, Chen DH, Thordarson P, Shieh DB, Braet F (2011) The selective growth inhibition of oral cancer by iron core-gold shell nanoparticles through mitochondria-mediated autophagy. Biomaterials 32:4565–4573
Ostrovsky S, Kazimirsky G, Gedanken A, Brodie C (2009) Selective cytotoxic effect of ZnO nanoparticles on glioma cells. Nano Res 2:882–890
Nair S, Sasidharan A, Divya Rani VV, Menon D, Manzoor K, Raina S (2009) Role of size scale of ZnO nanoparticles and microparticles on toxicity toward bacteria and osteoblast cancer cells. J Mater Sci Mater Med 20:S235–S241
Bai W, Zhang Z, Tian W, He X, Ma Y, Zhao Y, Chai Z (2009) Toxicity of zinc oxide nanoparticles to zebrafish embryo: a physicochemical study of toxicity mechanism. J Nanoparticle Res 12:1645–1654
Gojova A, Guo B, Kota RS, Rutledge JC, Kennedy IM, Barakat AI (2007) Induction of inflammation in vascular endothelial cells by metal oxide nanoparticles: effect of particle composition. Environ Health Perspect 115:403–409
Premanathan M, Karthikeyan K, Jeyasubramanian K, Manivannan G (2011) Selective toxicity of ZnO nanoparticles toward Gram-positive bacteria and cancer cells by apoptosis through lipid peroxidation. Nanomedicine 7:184–192
Hanley C, Layne J, Punnoose A, Reddy KM, Coombs I, Coombs A, Feris K, Wingett D (2008) Preferential killing of cancer cells and activated human T cells using ZnO nanoparticles. Nanotechnology 19:295103
Gopinath P, Gogoi SK, Sanpui P, Paul A, Chattopadhyay A, Ghosh SS (2010) Signaling gene cascade in silver nanoparticle-induced apoptosis. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces 77:240–245
Compton MM (1992) A biochemical hallmark of apoptosis: internucleosomal degradation of the genome. Cancer Metastasis Rev 11:105–119
Sanchez-Perez Y, Chirino YI, Osornio-Vargas AR, Morales-Barcenas R, Gutierrez-Ruiz C, Vazquez-Lopez I, Garcia-Cuellar CM (2009) DNA damage response of A549 cells treated with particulate matter (PM10) of urban air pollutants. Cancer Lett 278:192–200
Cohen G, Riahi Y, Sasson S (2011) Lipid peroxidation of polyunsaturated fatty acids in normal and obese adipose tissues. Arch Physiol Biochem 117:131–139
Ryter SW, Kim HP, Hoetzel A, Park JW, Nakahira K, Wang X, Choi AM (2007) Mechanisms of cell death in oxidative stress. Antioxid Redox Signal 9:49–89
Ott M, Gogvadze V, Orrenius S, Zhivotovsky B (2007) Mitochondria, oxidative stress and cell death. Apoptosis 12:913–922
Wang H, Joseph JA (1999) Structure-activity relationships of quercetin in antagonizing hydrogen peroxide-induced calcium dysregulation in PC12 cells. Free Radic Biol Med 27:683–694
Dawei A, Zhisheng W, Anguo Z (2010) Protective effects of nano-ZnO on the primary culture mice intestinal epithelial cells in vitro against oxidative injury. World J Agric Sci 6:149–153
Syamaa S, Reshmaa SC, Sreekanthb PJ, Varmab HK, Mohanana PV (2013) Effect of zinc oxide nanoparticles on cellular oxidative stress and antioxidant defense mechanisms in mouse liver. Toxicol Environ Chem 95:495–503
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by KU Research Professor Program, Konkuk University, Seoul, South Korea.
This research work was supported by the KU Brain Pool (2015-2016) of Konkuk University, Seoul, Republic of Korea
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chandrasekaran, M., Pandurangan, M. In Vitro Selective Anti-Proliferative Effect of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles Against Co-Cultured C2C12 Myoblastoma Cancer and 3T3-L1 Normal Cells. Biol Trace Elem Res 172, 148–154 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-015-0562-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-015-0562-6